Android는 다음을 비롯하여 다양한 Wi-Fi 프로토콜 및 모드를 지원하는 기본 Android 프레임워크 구현을 제공합니다.
- Wi-Fi 인프라(STA)
- 테더링 모드 또는 로컬 전용 모드의 Wi-Fi 핫스팟(소프트 AP)
- Wi-Fi Direct(p2p)
- Wi-Fi Aware(NAN)
- Wi-Fi RTT(IEEE 802.11mc FTM)
Wi-Fi 서비스를 사용하는 애플리케이션은 바인더를 통해 다양한 Wi-Fi 서비스와 직접 통신합니다. Wi-Fi 서비스는 시스템 서비스에서 실행되고, 제공된 HIDL 및 AIDL 인터페이스를 통해 HAL과 통신합니다. 아래의 다이어그램은 Android Wi-Fi 스택의 일반적인 구조를 보여줍니다.
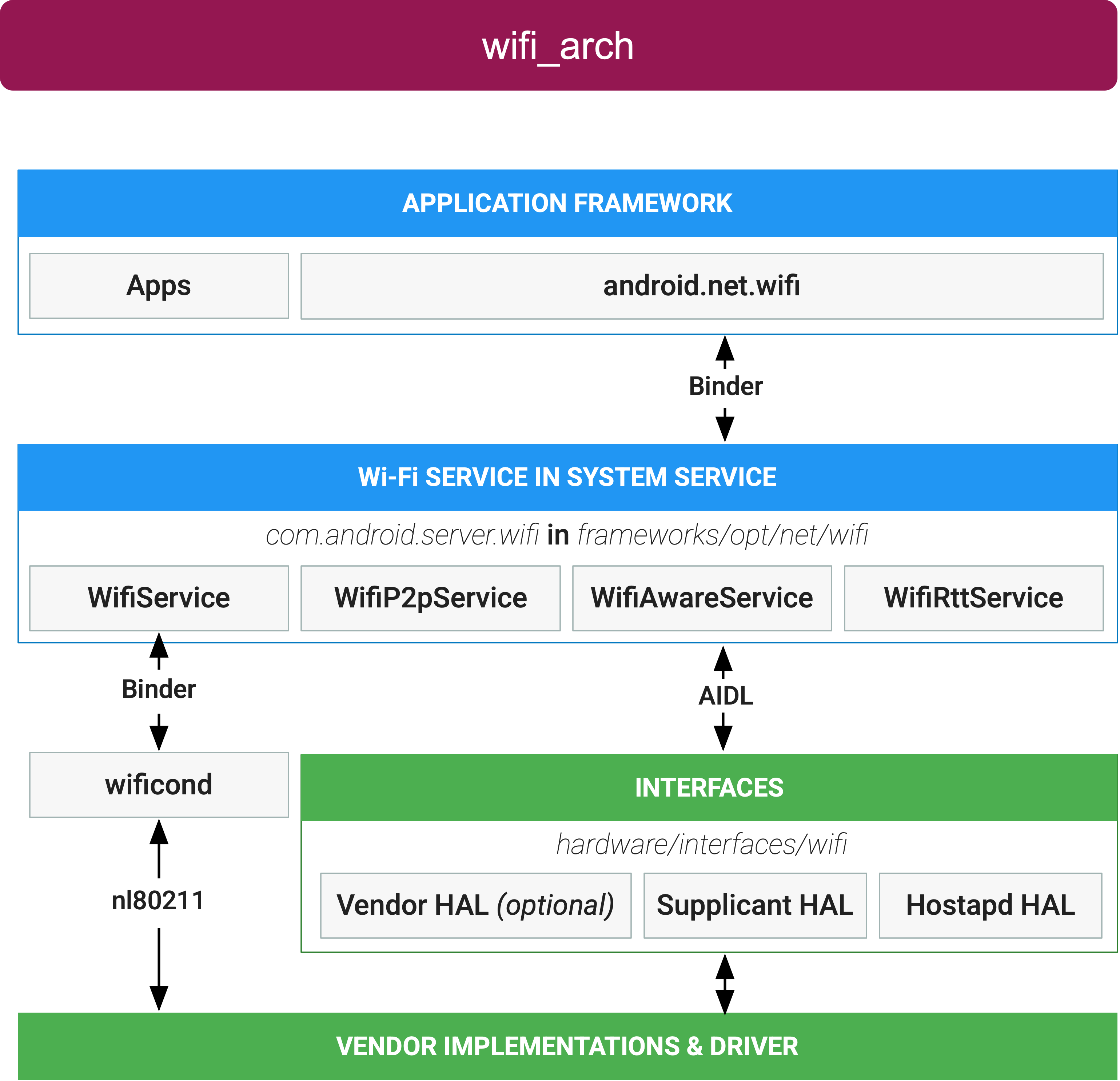
그림 1. Android Wi-Fi 아키텍처
애플리케이션 프레임워크
애플리케이션 프레임워크 수준에는 여러 android.net.wifi API를 사용하여 Wi-Fi 프레임워크 및 하드웨어와 상호작용하는 애플리케이션 코드가 있습니다. 내부적으로 이 코드는 바인더 IPC 메커니즘을 통해 Wi-Fi 프로세스를 호출합니다.
Wi-Fi 서비스
Wi-Fi 서비스는 시스템 서비스에서 실행되며 packages/modules/Wifi/service/에 있습니다. Wi-Fi 서비스는 AIDL을 통해 Wi-Fi HAL과 통신합니다.
다음과 같은 다양한 Wi-Fi 서비스가 있습니다.
- Wi-Fi 서비스: Wi-Fi 인프라 모드를 제어하는 기본 메커니즘입니다(STA 및 AP 모두).
- Wi-Fi P2P 서비스: Wi-Fi Direct 모드를 관리합니다.
- Wi-Fi Aware 서비스: Wi-Fi Aware 모드를 관리합니다.
- Wi-Fi RTT 서비스: IEEE 802.11mc FTM 기능을 관리합니다.
Wi-Fi 프레임워크에는 독립형 프로세스인 wificond(system/connectivity/wificond에 있음)도 포함되어 있습니다. wificond 프로세스는 표준 nl80211 명령어를 통해 Wi-Fi 드라이버와 통신합니다.
Wi-Fi HAL
Wi-Fi 프레임워크에는 Vendor HAL, Supplicant HAL, Hostapd HAL이라는 세 가지 인터페이스로 표현되는 세 개의 Wi-Fi HAL 노출 영역이 있습니다.
다양한 HAL의 구현에 관한 자세한 내용은 Wi-Fi HAL을 참고하세요.
