自 2026 年起,为了与我们的主干稳定开发模型保持一致,并确保生态系统的平台稳定性,我们将在第 2 季度和第 4 季度将源代码发布到 AOSP。对于构建 AOSP 和向 AOSP 贡献代码,我们建议使用 android-latest-release 而不是 aosp-main。android-latest-release 清单分支将始终引用推送到 AOSP 的最新版本。如需了解详情,请参阅 AOSP 变更。
实现触感反馈
使用集合让一切井井有条
根据您的偏好保存内容并对其进行分类。
设备制造商通常被认为是为每个设备创建的私有资产的所有者。因此,他们的工程工作往往围绕每台设备集中展开;为确保与生态系统中其他设备的一致性而开展的工作很少,甚至完全没有。
与之形成鲜明对比的是,开发者在努力构建可在生态系统中的所有 Android 手机上运行的应用(无论每类设备的技术规范如何)。这种方法上的差异可能会导致碎片化问题,例如,某些手机的硬件功能不符合应用开发者设定的预期。因此,如果触感反馈 API 适用于某些 Android 手机,但不适用于其他 Android 手机,就会导致生态系统不一致。正因如此,硬件配置在确保制造商能够在每台设备上实现 Android 触感反馈 API 方面发挥着关键作用。
本页面提供了一个分步核对清单,用于确保硬件合规,从而使得 Android 触感反馈 API 能充分发挥作用。
下图说明了如何在设备制造商和开发者之间建立共识,这是打造具有凝聚力的生态系统的关键一环。
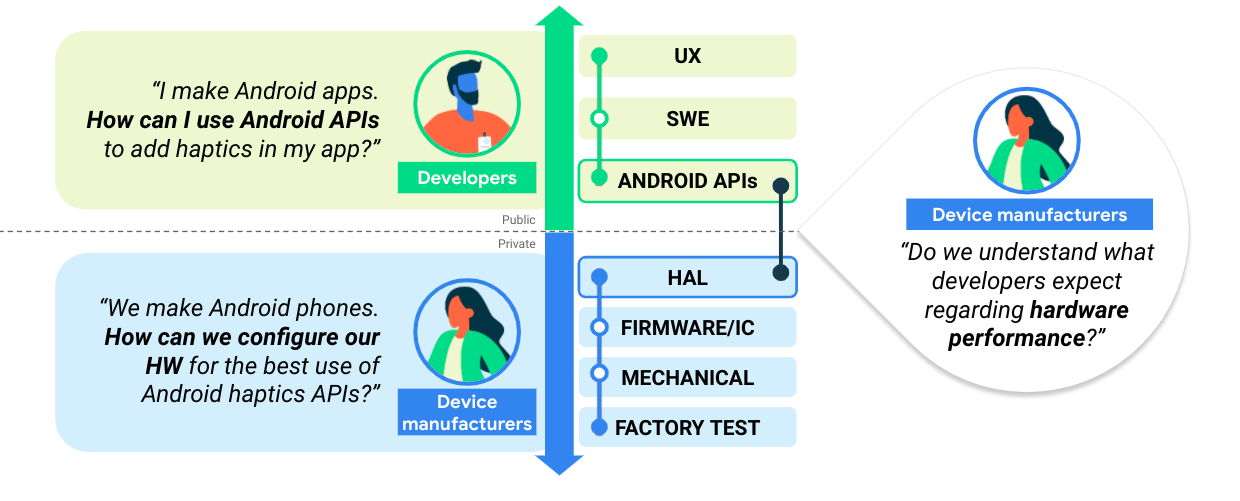
图 1. 在设备制造商和开发者之间建立共识
触感反馈实现核对清单
实现常量
实现基元
在 HAL 和 API 之间映射常量
- 公共 API 常量(在框架中名为占位符)和 HAL 常量(用于实现占位符)之间的映射建议。
- 如需详细了解此流程,请参阅指导推荐映射的设计原则。
评估硬件
- 有关目标触感反馈效果的说明。请按照相关说明对硬件执行快速检查。
本页面上的内容和代码示例受内容许可部分所述许可的限制。Java 和 OpenJDK 是 Oracle 和/或其关联公司的注册商标。
最后更新时间 (UTC):2025-03-11。
[[["易于理解","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["解决了我的问题","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["其他","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["没有我需要的信息","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["太复杂/步骤太多","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["内容需要更新","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["翻译问题","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["示例/代码问题","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["其他","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["最后更新时间 (UTC):2025-03-11。"],[],[]]

