하드웨어 평가는 햅틱을 호출하는 데 사용되는 일반적인 방법으로 샘플링된 세 가지 타겟 햅틱 효과의 정량적 특성을 제공합니다. 평가 끝에 각 타겟 햅틱 효과에 대한 각 기기의 성능을 성능 지도에 적용하여 결론을 도출할 수 있습니다.
성능 지도에는 현재 여러 Android 기기의 하드웨어 평가 결과가 표시됩니다. 목표는 합격 또는 불합격 판단이 아닌 맥락상 상대적인 비교를 사용하여 타겟 기기를 평가하는 것입니다. 이 개념을 중심으로 구성된 구체적인 질문은 다음과 같습니다. 내 휴대전화의 가격 등급과 액추에이터 유형을 고려할 때 성능이 경쟁업체와 비교해 어떤가요? 결과가 기대에 부합하나요? 그렇지 않다면 어떤 점을 개선해야 할까요?

그림 1. 햅틱 하드웨어 평가 프로세스 개요
평가에서는 Android 햅틱 프레임워크의 세 가지 메서드 결과를 관찰합니다.
효과 1: 사전 정의된 짧은 햅틱 상수
이 상수는 HAL과 API 간의 상수 매핑에 제공된 HAL-API 매핑의 기준 효과 또는 공통분모입니다.
가장 일반적으로 사용되는 효과인 HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_PRESS로 매핑됩니다.
이 효과를 평가하면 명확한 햅틱을 위한 대상 기기의 준비 상태를 판단하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
효과 2: 짧은 맞춤 햅틱 효과
VibrationEffect.createOneShot(20,255)
짧은 단일 맞춤 임펄스의 경우 지속 시간을 정의하는 데 권장되는 최대 기준점은 20ms입니다. 20ms보다 긴 단일 임펄스는 윙윙거리는 진동으로 감지되기 때문에 권장되지 않습니다.
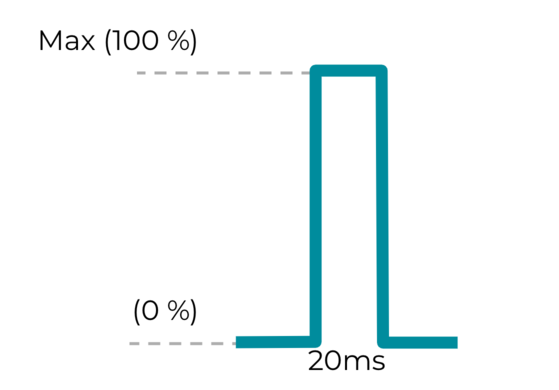
그림 2. 짧은 맞춤 햅틱 효과
효과 3: 진폭 변화가 있는 긴 맞춤 햅틱 효과
VibrationEffect.createWaveform(timings[], amplitudes[], int repeat)
맞춤 햅틱 효과를 위해 다양한 진폭을 생성하는 기능은 기기의 풍부한 햅틱 기능을 평가하는 지표 중 하나입니다.
권장되는 timings [ ] 및 amplitudes [ ]은 각각 {500, 500} 및 {128, 255}입니다. 진폭이 500ms 샘플링 레이트로 50% 에서 100% 로 증가하는 추세를 나타냅니다.
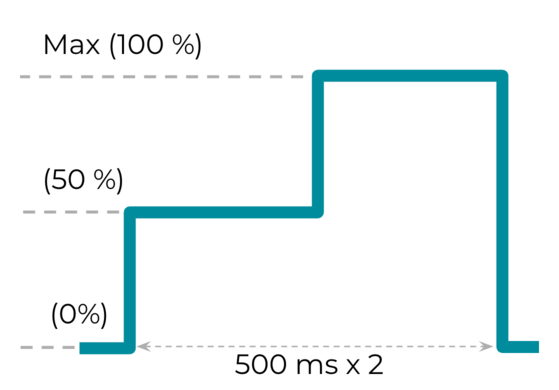
그림 3. 진폭 변화가 있는 긴 맞춤 햅틱 효과
효과 3의 진폭 제어에 관한 하드웨어 기능을 빠르게 확인하려면 Vibrator.hasAmplitudeControl()를 사용해 보세요.
의도대로 다양한 진폭을 사용하여 VibrationEffect.createWaveform을 실행하려면 결과가 true여야 합니다.
