Android 7.0 では、ネイティブ ライブラリの名前空間を導入して内部 API の公開を制限し、アプリが独自のライブラリではなく誤ってプラットフォーム ライブラリを使用することがないようにしています。アプリ固有の変更点については、Android デベロッパー ブログにて、Android 7.0 でのプライベート C/C++ シンボルの制限による安定性の向上に関する記事をご覧ください。
アーキテクチャ
Android 7.0 以降では、システム ライブラリはアプリ ライブラリから分離されています。
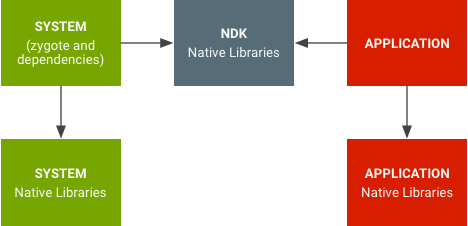
図 1. ネイティブ ライブラリの名前空間。
ネイティブ ライブラリの名前空間により、アプリはプライベート プラットフォームのネイティブ API を使用できなくなります(OpenSSL を使用した場合と同様)。また、アプリが独自のライブラリではなく誤ってプラットフォーム ライブラリを使用する(libpng で発生するような)事態も回避されます。アプリ ライブラリが誤って内部システム ライブラリを使用する(または内部システム ライブラリが誤ってアプリ ライブラリを使用する)可能性が低くなります。
その他のネイティブ ライブラリを追加する
標準の公開ネイティブ ライブラリに加えて、シリコン ベンダー(Android 7.0 以降)とデバイス メーカー(Android 9 以降)は、アプリがアクセスできるように、追加のネイティブ ライブラリを各ライブラリ フォルダに配置して、.txt ファイルで明示的に記述することもできます。
ライブラリ フォルダは次のとおりです。
- シリコン ベンダーのライブラリの
/vendor/lib(32 ビット用)と/vendor/lib64(64 ビット用) - デバイス メーカーのライブラリの
/system/lib(32 ビット用)と/system/lib64(64 ビット用)
.txt ファイルは次のとおりです。
- シリコン ベンダーのライブラリの
/vendor/etc/public.libraries.txt。 - デバイス メーカーのライブラリの
/system/etc/public.libraries-COMPANYNAME.txt(COMPANYNAMEはawesome.companyなどのメーカー名)。COMPANYNAMEは[A-Za-z0-9_.-]+、つまり英数字、「_」、「.」(ドット)、「-」と一致する必要があります。外部ソリューション プロバイダのライブラリを使用する場合は、デバイスで複数の .txt ファイルを使用できます。
デバイス メーカーによって公開される system パーティション内のネイティブ ライブラリの名前は、lib*COMPANYNAME.so の形式にする必要があります(例: libFoo.awesome.company.so)。つまり、会社名の接尾辞がない libFoo.so は公開できません。ライブラリ ファイル名の COMPANYNAME は、ライブラリ名がリストされている txt ファイル名の COMPANYNAME と一致している必要があります。
AOSP に含まれているネイティブ ライブラリは公開できません(デフォルトで公開される標準の公開ネイティブ ライブラリは除きます)。シリコン ベンダーまたはデバイス メーカーによって追加されたライブラリのみ、アプリからアクセス可能にできます。
Android 8.0 以降、ベンダーの公開ライブラリには以下の追加制限と必須設定が設けられています。
- アプリからアクセスできるように、ベンダーのネイティブ ライブラリには適切なラベルを付ける必要があります。あらゆるアプリ(サードパーティ アプリを含む)によるアクセスが必要な場合は、次のようにベンダー固有の
file_contextsファイルでライブラリにsame_process_hal_fileというラベルを付ける必要があります。/vendor/lib(64)?/libnative.so u:object_r:same_process_hal_file:s0
libnative.soはネイティブ ライブラリの名前です。 - ライブラリは、直接的であっても依存関係を介して推移的であっても、VNDK-SP ライブラリと LLNDK ライブラリ以外のシステム ライブラリに依存してはなりません。VNDK-SP ライブラリと LLNDK ライブラリのリストは、
development/vndk/tools/definition/tool/datasets/eligible-list-<version>-release.csvにあります。
Android 15 以降では、ベンダーの公開ライブラリをベンダー APEX に含めることができます。ベンダー APEX にパッケージ化する場合は、APEX マニフェストの provideNativeLibs プロパティ内にライブラリをリストします。
非公開のネイティブ ライブラリを使用しないようにアプリを更新する
この機能は SDK バージョン 24 以降をターゲットとするアプリに対してのみ有効です。下位互換性については、表 1. アプリが非公開ネイティブ ライブラリにリンクしている場合に予期される動作をご覧ください。アプリがアクセスできる Android ネイティブ ライブラリ(公開ネイティブ ライブラリとも呼ばれる)のリストは、CDD の 3.1.1 項に記載されています。バージョン 24 以降をターゲットとし、非公開ライブラリを使用しているアプリは更新する必要があります。詳しくは、プラットフォーム ライブラリにリンクしている NDK アプリをご覧ください。
アプリを更新してネイティブ ライブラリの依存関係を指定する
SDK バージョン 31(Android 12)以降をターゲットとするアプリは、アプリ マニフェストで <uses-native-library> タグを使用して、ネイティブ共有ライブラリの依存関係を明示的に指定する必要があります。リクエストされたライブラリの一部がデバイスに存在しない場合、アプリはインストールされません。アプリのインストール時には、アプリがリクエストしたネイティブ共有ライブラリのみが提供されます。つまり、アプリはアプリ マニフェストにないネイティブ共有ライブラリにアクセスすることはできません。
