Android の権限を活用すると、ユーザーの意識を高めるコントロールを提供し、またアプリによるセンシティブ データへアクセスを制限できます。Android 8.0 以前での権限の設定には、許可リスト登録が含まれています。許可リスト登録を行わないと、特権アプリは priv-app パスに含まれていても無効になります。Android 9 以降では、正しく許可リストに登録されていないアプリの使用を試みるデバイスは起動しません。
Android 10 では、ロールという概念が導入されました。ロールは、特定の要件と権限に関連付けられたシステム内の一意の名前です。アプリにロールを割り当て、特定の目的に合わせて権限を付与したり、プラットフォーム構成リソースを使用してデフォルト ロールを設定したりできます。
有害な可能性があるアプリ(PHA)に対する保護の強化により、以下が改善されました。
- 有害な可能性があるアプリの動作に対する透明性。
- ユーザーによるアプリ動作の制御。
- 権限で保護されているプライベート データを使用する場合のアプリ デベロッパーの裁量。
パッケージ インストールと権限
Android 9 以前は、パッケージ インストールと権限コントロールの機能が PackageInstaller パッケージ(//packages/apps/PackageInstaller)に含まれていました。Android 10 以降では、権限コントロール機能が別のパッケージ PermissionController(//packages/apps/PermissionController)に含まれています。図 1 に Android 10 における 2 つのパッケージの格納場所を示します。
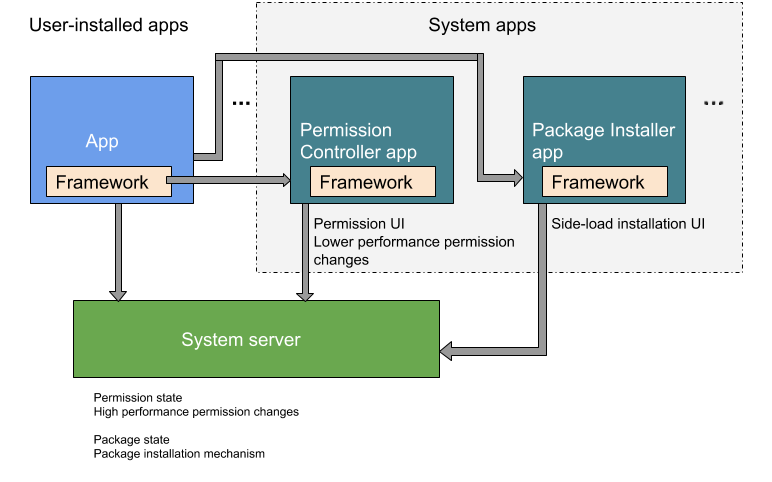
図 1. Android 10 のパッケージ インストールおよび権限コントロール機能
許可リストとアクセス
Android 6.0 以降では、アプリが実行時に危険な権限へのアクセスをリクエストします。Android 10 では、危険な権限の変更または許可をユーザーに求める、操作の認識(AR)ランタイム権限が追加されています。
Android 8.0 では、/etc/permissions ディレクトリのシステム構成 XML ファイルで特権アプリを明示的に許可リスト登録する必要がありました。Android 9 以降では、特権を許可リスト登録しないとデバイスを起動できません。
内部 API の公開を制限し、アプリが誤ってプラットフォーム ライブラリにアクセスするのを防ぐために、Android 7.0 でネイティブ ライブラリの名前空間が導入されました。これにより、システム ライブラリがアプリ ライブラリから分離され、デバイス メーカーが独自のネイティブ ライブラリを追加できるようになりました。
Android 10 以降、アプリがデバイスの画面コンテンツにアクセスするには、署名権限とユーザーの同意の両方が必要です。スクリーンショットの撮影などでサイレント キャプチャ機能を使用する特権アプリは、代わりに MediaProjection クラスを使用する必要があります。
Android 15 では、/etc/permissions ディレクトリ内のシステム構成 XML ファイルで、システム以外のアプリによってリクエストされた、またはシステムアプリのアップデートによって新たにリクエストされたプラットフォーム署名権限を明示的に許可リストに登録する必要があります。
透明性とプライバシー
Android 6.0 以降では、Wi-Fi サービス プロバイダとパケット アナライザがアクセスできないように、デバイスの出荷時 MAC アドレスが保護されています。Android 10 で追加された制限により、アプリは特権の許可リストに登録されていない限り、不変のデバイス ID にアクセスできません。携帯通信会社にも影響するため、デバイス ID に関連する情報については、接続セクションで説明します。
Android 9 以前では、ユーザーはアプリに位置情報へのアクセス権を付与する際に永続的な選択を行います。Android 10 以降では、位置情報の 3 段階の利用許可機能により、アプリにデバイスの位置情報へのアクセスを許可する方法が 3 つ用意されています。これらの権限要件は、ターゲット SDK に関係なく Android 10 のアプリに適用されます。
Android 10 以降での他の透明性およびプライバシー機能に対する権限の構成
- アプリがバックグラウンドで
ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION権限を使用してデバイスの位置情報にアクセスすると、バックグラウンドでの位置情報へのアクセスに関するリマインダーが表示されます。 - 連絡先プロバイダのコンポーネントで管理される連絡先アフィニティ関連のデータには、異なる方法でアクセスします。アプリがデータベースの連絡先アフィニティ データへの書き込み、または読み取りを行うことはできません。これは、呼び出し元関連の API に影響します。
簡素化された構成
Android 6.0 以降では、権限の構成が簡素化されています。
initによって起動されるサービスのアンビエント機能は、サービス構成のすべての要素を 1 つの.rcファイルに保持します。initによって起動されないサービスの機能を設定する場合は、代わりにfs_config.cを使用してファイル システム機能を構成します。- Android 7.x 以前では、デバイス固有の
android_filesystem_config.hファイルを使用してファイルシステム機能およびカスタムのデバイスメーカー AID(またはいずれか一方)を指定し、Android ID(AID)メカニズムを拡張します。Android 8.0 以降では、ファイルシステム機能を拡張する新しいメソッドがサポートされています。 - Android 8.0 では、USB コマンドの処理がデバイス固有の
initスクリプト(HAL レイヤの代用)からネイティブ USB デーモンに移行されました。Android 8.0 以降を搭載するすべてのデバイスに、USB HAL インターフェースを実装する必要があります。
