Android 權限提供控管機制,可提高使用者意識,並限制應用程式存取私密資料。在 Android 8.0 以下版本中設定權限時,必須將應用程式加入許可清單,否則即使應用程式位於 priv-app 路徑中,也會遭到停用。在 Android 9 以上版本中,如果裝置嘗試使用未正確加入允許清單的應用程式,將無法啟動。
Android 10 導入了「角色」的概念,這是系統中與特定需求和權限相關聯的專屬名稱。將角色指派給應用程式,授予特定用途的權限,並使用平台設定資源設定預設角色。
加強防範可能有害的應用程式 (PHA) 後,可提升以下方面的效能:
- 瞭解可能有害的應用程式行為。
- 使用者可控管應用程式行為。
- 應用程式開發人員可自行決定是否使用受權限保護的私人資料。
套件安裝和權限
在 Android 9 以下版本中,套件安裝和權限控制功能都包含在 PackageInstaller 套件 (//packages/apps/PackageInstaller) 中。在 Android 10 以上版本中,權限控制功能位於獨立的套件 PermissionController (//packages/apps/PermissionController) 中。圖 1 說明這兩個套件在 Android 10 中的位置。
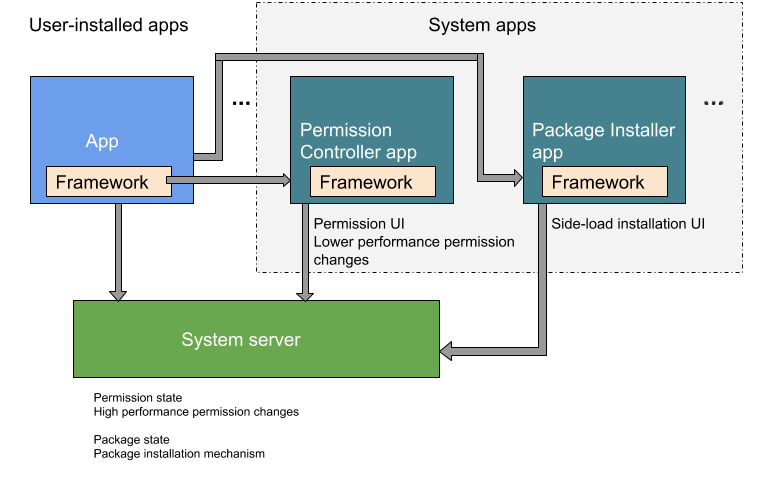
圖 1. Android 10 中的套件安裝和權限控管功能
允許清單和存取權
在 Android 6.0 以上版本中,應用程式會在執行階段要求危險權限。Android 10 新增了活動辨識 (AR) 執行階段權限,會提示使用者修改或允許危險權限。
Android 8.0 要求您在 /etc/permissions 目錄的系統設定 XML 檔案中,明確允許特權應用程式加入允許清單。在 Android 9 以上版本中,必須將具備特殊權限的權限加入許可清單,否則裝置無法啟動。
為限制內部 API 可見度,並防止應用程式意外存取平台程式庫,Android 7.0 導入了原生程式庫的命名空間。這樣一來,系統程式庫就會與應用程式程式庫分開,裝置製造商也能新增自己的原生程式庫。
從 Android 10 開始,應用程式必須同時具備簽章權限和使用者同意聲明,才能 存取裝置的螢幕內容。如果特權應用程式依賴無聲擷取功能 (例如擷取螢幕截圖),則應改用 MediaProjection 類別。
在 Android 15 中,您必須在 /etc/permissions 目錄的系統設定 XML 檔案中,明確允許非系統應用程式要求或系統應用程式更新後要求的新平台簽章權限。
資訊公開與隱私權
在 Android 6.0 以上版本中,裝置出廠 MAC 位址會受到保護,避免 Wi-Fi 服務供應商和封包分析器存取。Android 10 以上版本設有額外限制,除非應用程式 已列入特許權限的許可清單,否則無法存取不可變更的裝置 ID。(「 連線」一節會討論裝置 ID,因為這會影響電信業者。)
在 Android 9 以下版本中,使用者授予應用程式位置存取權時,會做出永久選擇。自 Android 10 起,三種狀態的位置資訊權限功能提供三種選項,讓使用者決定是否允許應用程式存取裝置位置資訊。無論目標 SDK 為何,Android 10 中的應用程式都必須符合這些權限規定。
從 Android 10 開始,設定其他資訊公開和隱私權功能的權限
- 當應用程式在背景使用
ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION權限存取裝置位置資訊時,系統會向使用者顯示 背景存取位置資訊提醒。 - 聯絡人親和度相關資料是由「聯絡人供應器」元件管理,存取方式不同:應用程式無法在資料庫中寫入或讀取聯絡人親和度資料。這會影響 與呼叫端相關的 API。
簡化設定
Android 6.0 以上版本已簡化權限設定。
init啟動的服務環境功能會將服務設定的所有層面保留在單一.rc檔案中。如要為非由init啟動的服務設定功能,請改用fs_config.c設定檔案系統功能。- Android 7.x 以下版本會擴充 Android ID (AID) 機制,使用裝置專屬的
android_filesystem_config.h檔案指定檔案系統功能和/或自訂裝置製造商 AID。Android 8.0 以上版本支援擴充檔案系統功能的新方法。 - 在 Android 8.0 中,USB 指令的處理作業已從裝置專屬的
init指令碼 (取代 HAL 層) 移至原生 USB 精靈。凡是搭載 Android 8.0 以上版本的裝置,都必須實作 USB HAL 介面。
