Android 런타임(ART)에는 Android 애플리케이션 실행 시 성능을 지속적으로 개선하는 코드 프로파일링 기능이 있는 JIT 컴파일러가 포함되어 있습니다. JIT 컴파일러는 ART의 현재 AOT(ahead-of-time) 컴파일러를 보완하고 런타임 성능을 개선하며 저장공간을 절약하고 애플리케이션 및 시스템 업데이트를 가속화합니다. 또한 무선 업데이트(OTA)가 진행되는 동안 자동 애플리케이션 업데이트나 애플리케이션 재컴파일로 인한 시스템 속도 저하를 방지하여 AOT 컴파일러를 개선합니다.
JIT와 AOT는 유사하게 최적화된 동일한 컴파일러를 사용하지만 생성된 코드는 동일하지 않을 수 있습니다. JIT는 런타임 유형 정보를 활용하며 인라이닝을 개선할 수 있고 스택상 교체(OSR) 컴파일을 가능하게 합니다. 이러한 모든 작업에 따라 조금씩 다른 코드가 생성됩니다.
JIT 아키텍처
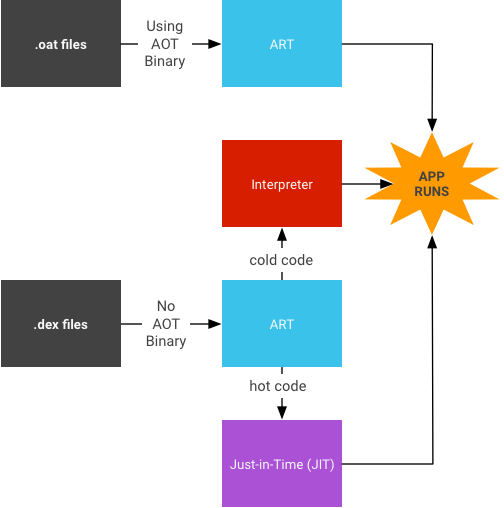
JIT 컴파일
JIT 컴파일에는 다음과 같은 작업이 포함됩니다.
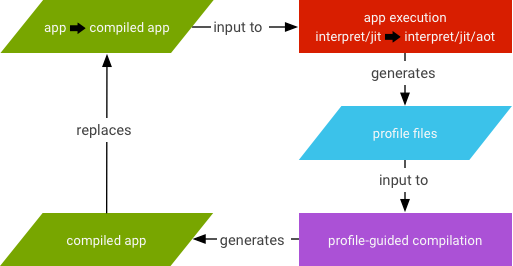
- 사용자가 앱을 실행하면 ART가 트리거되어
.dex파일을 로드합니다..oat파일(.dex파일의 AOT 바이너리)을 사용할 수 있는 경우 ART는 이를 직접 사용합니다..oat파일이 정기적으로 생성되더라도 컴파일된 코드(AOT 바이너리)가 항상 포함되지는 않습니다..oat파일에 컴파일된 코드가 없으면 ART가 JIT와 인터프리터를 통해 실행되어.dex파일을 실행합니다.
- JIT는
speed컴파일 필터에 따라 컴파일되지 않은 모든 애플리케이션에 사용 설정됩니다. 즉 '앱에서 가능한 만큼 컴파일'할 수 있습니다. - JIT 프로필 데이터는 애플리케이션만 액세스할 수 있는 시스템 디렉터리의 파일로 덤프됩니다.
- AOT 컴파일(
dex2oat) 데몬은 컴파일을 위해 파일을 파싱합니다.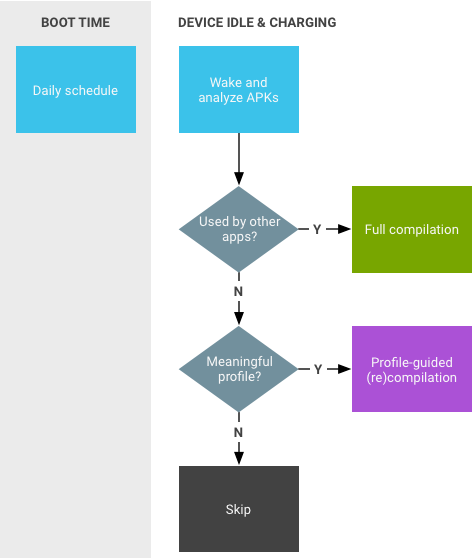
그림 3. JIT 데몬 작업입니다.
Google Play 서비스는 공유 라이브러리와 유사한 방식으로 동작하는 다른 애플리케이션에서 사용되는 예입니다.
JIT 워크플로
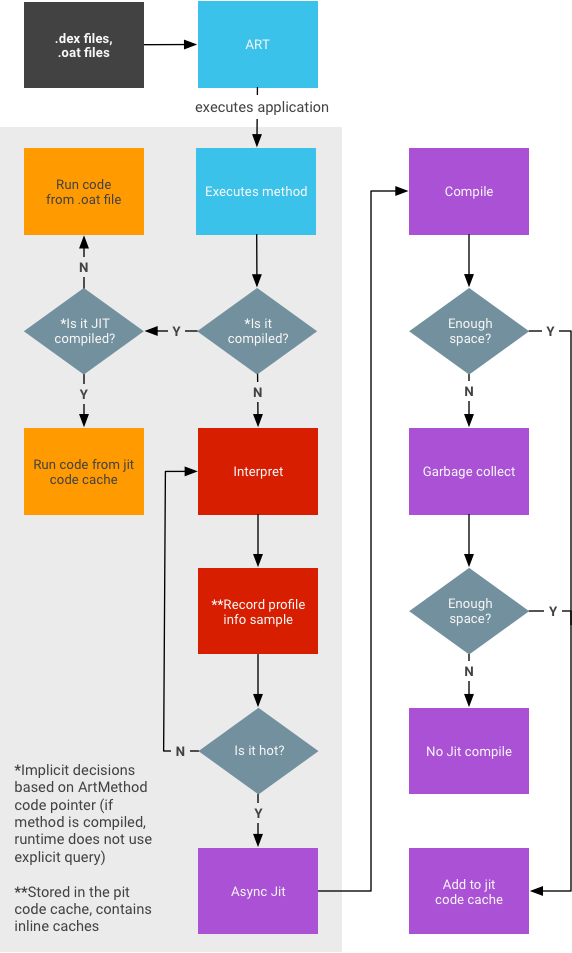
- 프로파일링 정보는 코드 캐시에 저장되며 메모리 부족 시 가비지 컬렉션이 실행됩니다.
- 애플리케이션이 백그라운드에 있었을 때 생성된 스냅샷에 완전한 데이터(JIT로 컴파일된 모든 데이터)가 포함된다는 보장은 없습니다.
- 런타임 성능에 영향을 줄 수 있으므로 모든 항목이 기록될 수 있도록 시도하지 않습니다.
- 메서드의 상태는 다음 3가지일 수 있습니다.
- 해석된 dex 코드
- JIT로 컴파일됨
- AOT로 컴파일됨
- 포그라운드 앱 성능에 영향을 주지 않고 JIT를 실행하기 위한 메모리 요구사항은 앱에 따라 다릅니다. 대용량 앱은 소용량 앱보다 많은 메모리가 필요합니다. 일반적으로 대용량 앱은 약 4MB에서 안정화됩니다.
JIT 로깅 사용 설정
JIT 로깅을 사용하려면 다음 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb rootadb shell stopadb shell setprop dalvik.vm.extra-opts -verbose:jitadb shell start
JIT 사용 중지
JIT를 사용하지 않으려면 다음 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb rootadb shell stopadb shell setprop dalvik.vm.usejit falseadb shell start
컴파일 강제 실행
강제로 컴파일하려면 다음을 실행합니다.
adb shell cmd package compile
특정 패키지를 강제 컴파일하는 일반적인 사용 사례:
- 프로필 기반:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed-profile -f my-package
- 잘림 처리되지 않음:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed -f my-package
모든 패키지를 강제 컴파일하는 일반적인 사용 사례:
- 프로필 기반:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed-profile -f -a
- 잘림 처리되지 않음:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed -f -a
프로필 데이터 삭제
프로필 데이터를 삭제하고 컴파일된 코드를 제거하려면 다음을 실행합니다.
- 패키지 1개:
adb shell cmd package compile --reset my-package
- 모든 패키지:
adb shell cmd package compile --reset -a
