Android 9 ベンダー テストスイート(VTS)には、実行時にデバイス設定を使用して、そのデバイス ターゲットでスキップすべき VTS テストを特定する手段が用意されています。
VTS テストの柔軟性
Android 8.0 から、Android 8.0 以降を搭載して出荷されるデバイスには VTS テストが必要になりました。ただし、すべての VTS テストがすべてのデバイス ターゲットに適用されるわけではありません。例:
- テストする HAL(例: IR)を特定のデバイスがサポートしていない場合、VTS はその HAL テストのテストをそのデバイス ターゲットに対して実行する必要はありません。
- 複数のデバイスが同じ SoC とベンダー イメージを使用しているが、ハードウェアの機能は異なる場合、VTS は特定のデバイス ターゲットに対してテストを実行するかスキップするかを決定する必要があります。
VTS テストの種類
VTS には、次のテストタイプがあります。
- 準拠性テストでは、フレームワーク パーティションとベンダー パーティションとの間の互換性を確認します。Android 8.0 以降を搭載して出荷されるデバイスでは、これらのテストを実行し合格する必要があります。
- 準拠性以外のテストは、ベンダーが製品の品質を改善するのに役立ちます(パフォーマンス、ファジングなど)。ベンダーはこのテストを省略できます。
あるテストが準拠性テストであるかどうかは、どのプランで実行されるかによって決まります。VTS プランで実行されるテストは準拠性テストと見なされます。
サポートされる HAL の確認
VTS では、次のファイルを使用して、デバイス ターゲットが特定の HAL をサポートしているかどうかを判断できます。
/system/compatibility_matrix.xml: フレームワークで必要な HAL インスタンスを宣言します。例:<hal format="hidl" optional="true"> <name>android.hardware.vibrator</name> <version>1.0-1</version> <interface> <name>IVibrator</name> <instance>default</instance> </interface> </hal>optional属性は、HAL がフレームワークで厳密に必要かどうかを示します。- ファイルには、同じ HAL(同じ名前)にバージョンとインターフェースが異なる複数のエントリがあっても構いません。
- ファイルには、同じエントリに複数の
version設定があっても構いません。つまり、フレームワークで異なるバージョンを使用できるということです。 version1.0-1は、フレームワークが最初のバージョン 1.0 で動作し、1.1 より後のバージョンを必要としないことを意味します。
- デバイス
manifest.xml: ベンダーによって提供された HAL インスタンスを宣言します。例:<hal format="hidl"> <name>android.hardware.vibrator</name> <transport>hwbinder</transport> <version>1.2</version> <interface> <name>IVibrator</name> <instance>default</instance> </interface> </hal>- ファイルには、同じ HAL(同じ名前)にバージョンとインターフェースが異なる複数のエントリがあっても構いません。
- ファイルのエントリとして
versionに設定されたバージョンが 1 つだけの場合、たとえばversion1.2はベンダーが 1.0~1.2 のすべてのバージョンをサポートしていることを意味します。
- lshal:
hwservicemanagerを使用してデバイスに登録された HAL サービスに関するランタイム情報を表示するデバイス上のツールです。例:android.hardware.vibrator@1.0::IVibrator/default
lshalは、パススルー実装のある(つまり、デバイスに対応する-impl.soがある)HAL もすべて表示されます。例:android.hardware.nfc@1.0::I*/* (/vendor/lib/hw/) android.hardware.nfc@1.0::I*/* (/vendor/lib64/hw/)
準拠性テスト
準拠性テストでは、VTS は、ベンダー マニフェストに基づいて、デバイスから提供されるすべての HAL インスタンスを特定し、テストします。決定フロー:
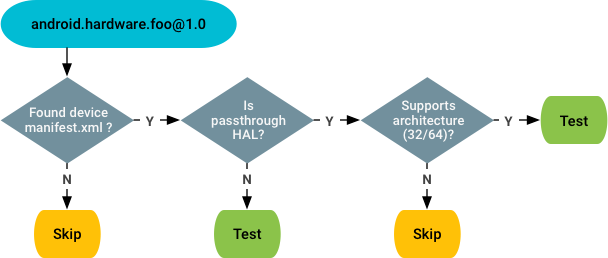
準拠性以外のテスト
準拠性以外のテストの場合、VTS はベンダー マニフェストと lshal の出力に基づいて、manifest.xml ファイルで宣言されていない実験対象の HAL を特定し、テストします。決定フロー:
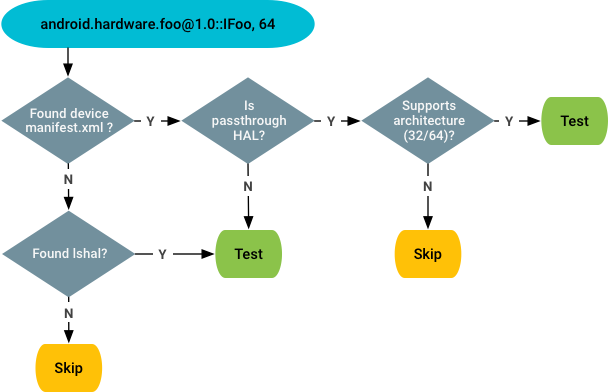
ベンダー マニフェストの場所
VTS は、ベンダー manifest.xml ファイルを次の場所から次の順序で見つけます。
/vendor/etc/vintf/manifest.xmlと ODM マニフェスト(両方の場所で同じ HAL が定義されている場合、ODM マニフェストが/vendor/etc/vintf/manifest.xmlのマニフェストに優先します)。/vendor/etc/vintf/manifest.xml- ODM の
manifest.xml: 次のファイルから次の順序で読み込まれます。/odm/etc/vintf/manifest_$(ro.boot.product.hardware.sku).xml/odm/etc/vintf/manifest.xml/odm/etc/manifest_$(ro.boot.product.hardware.sku).xml/odm/etc/manifest.xml/vendor/manifest.xml
VTS テスト可否チェッカー
vts_testibility_checker は、VTS にパッケージ化されたバイナリであり、VTS テスト フレームワークで、指定された HAL テストがテスト可能かどうかを判断するために使用されます。libvintf に基づいて、ベンダー マニフェスト ファイルを読み込んで解析し、前のセクションで説明した決定フローを実装します。
vts_testability_check は、次のように使用します。
- 準拠性テストの場合:
vts_testability_check -c -b <bitness> <hal@version>
- 準拠性以外のテストの場合:
vts_testability_check -b <bitness> <hal@version>
vts_testability_check の出力は、次の JSON 形式を使用します。
{testable: <True/False> Instances: <list of instance names of HAL service>}アクセスされる HAL の確認
VTS テストでアクセスされる HAL を確認するには、各 HAL テストで VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase テンプレートを使用してテストでアクセスされる HAL を登録します。その後、VTS テスト フレームワークで、テストの前処理の際に登録された HAL を抽出できます。
準拠性以外のテストの場合は、/system/etc/vintf/manifest.xml も確認できます。ここで定義されている HAL は、VTS がテストします。システムによって提供される HAL サービス(graphics.composer/vr など)の場合、HAL は /system/manifest.xml で宣言されています。
