Android 仮想化フレームワーク(AVF)は、コード実行のための安全かつプライベートな実行環境を提供します。AVF は、Android のアプリ サンドボックスよりも強固で形式検証がなされた隔離保証を必要とするセキュリティ指向のユースケースに最適です。Android には、AVF の実装に必要なコンポーネントすべてのリファレンス実装が用意されています。現在、AVF は ARM64 デバイスでのみサポートされています。図 1 は、AVF のアーキテクチャを示しています。
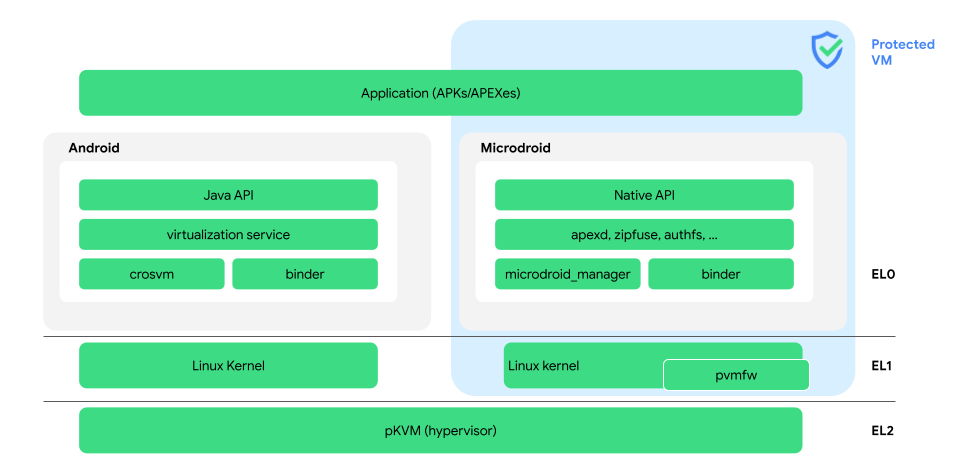
図 1 の重要な用語の定義は次のとおりです。
- apexd、zipfuse
- ホストからインポートされた APEX と APK を安全にマウントします。
- authfs
- Android と pVM(ホストとゲスト)の間で複数のファイルを安全に共有するための fuse ファイル システム。
- binder
- VM 間通信の主な手段。
- crosvm
- Rust で書かれた仮想マシンモニタ。crosvm は VM メモリを割り当て、仮想 CPU スレッドを作成して、仮想デバイスのバックエンドを実装します。
- 汎用カーネル イメージ(GKI)
- Android 共通カーネル(ACK)ソースツリーからビルドされた GKI カーネルを含み、Android デバイスの boot パーティションにフラッシュするのに適した、Google が認定したブートイメージ。詳細については、カーネルの概要をご覧ください。
- hypervisor
- AVF で使用される仮想化テクノロジー(pKVM とも呼ばれます)。このハイパーバイザは、ホストの Android や他の pVM が侵害された場合でも、実行されるコードの完全性と pVM アセットの機密性を維持します。
- Java API
- AVF をサポートするデバイスにのみ存在する VirtualizationService の Java API。これらの API はオプションであり、
thebootclasspathの一部ではありません。 - Microdroid
- pVM で動作する Google 提供のミニ Android OS。
- Microdroid Manager
- pVM のライフサイクル、pVM 内、インスタンス ディスクを管理します。
- Native API
- Android ネイティブ デベロッパー キット(NDK)のサブセット。
- 保護されたカーネルベースの仮想マシン(pKVM)
- ハイパーバイザをご覧ください。
- pVM ファームウェア(
pvmfw) - pVM で実行される最初のコード
pvmfwがペイロードを検証し、VM ごとのシークレットを導出します。 - 保護された仮想マシン(pVM)
メインの Android オペレーティング システム(「ホスト」)の隣で実行される、相互に信頼されていない隔離された実行環境(「ゲスト」)。pVM の重要なセキュリティ機能の 1 つに、ホストが侵害された場合にホストから pVM のメモリにアクセスできない点が挙げられます。pKVM は、pVM を実行する際の標準のハイパーバイザです。
既存の高信頼実行環境(TEE)と比較すると、pVM は Microdroid と呼ばれるミニ Android ディストリビューションを含むリッチな環境を提供します(ただし、Microdroid は保護されていない仮想マシン上でも実行可能です)。pVM は動的に使用でき、そこではサポート対象のすべてのデバイスで利用可能な高信頼環境内で標準の API セットが提供されます。
- VirtualizationService
pVM のライフサイクルを管理する Android サービス。
次のステップ
- AVF の必要性について詳しくは、AVF を使用する理由をご覧ください。
- AVF を隔離コンパイルに使用する方法については、ユースケースをご覧ください。
- AVF のリファレンス実装のアーキテクチャについて詳しくは、AVF のアーキテクチャをご覧ください。
- Microdroid について詳しくは、Microdroid をご覧ください。
- AVF におけるセキュリティの扱いにご関心をお持ちの場合は、セキュリティをご覧ください。
- 仮想化サービスの役割については、VirtualizationService をご覧ください。
- AVF のソースコード、または個々のコンポーネントに関する詳しい説明については、AOSP リポジトリをご覧ください。
