
Android fornisce uno stack Bluetooth predefinito che supporta sia Bluetooth classico che Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). Utilizzando il Bluetooth, i dispositivi Android possono creare reti personali per inviare e ricevere dati con i dispositivi Bluetooth nelle vicinanze.
In Android 4.3 e versioni successive, lo stack Bluetooth Android offre la possibilità di implementare BLE. Per utilizzare completamente le API BLE, segui i requisiti HCI Bluetooth di Android. I dispositivi Android con un chipset qualificato possono implementare Bluetooth Classic o sia Bluetooth Classic che BLE. BLE non è compatibile con le versioni precedenti dei chipset Bluetooth.
In Android 8.0, lo stack Bluetooth è completamente qualificato per Bluetooth 5. Per utilizzare le funzionalità Bluetooth 5 disponibili, il dispositivo deve disporre di un chipset qualificato Bluetooth 5.
Architettura Android
Un'app Bluetooth comunica con il processo Bluetooth tramite Binder. Il processo Bluetooth utilizza Java Native Interface (JNI) per comunicare con lo stack Bluetooth e fornisce agli sviluppatori l'accesso a vari profili Bluetooth. Questo diagramma mostra la struttura generale dello stack Bluetooth:
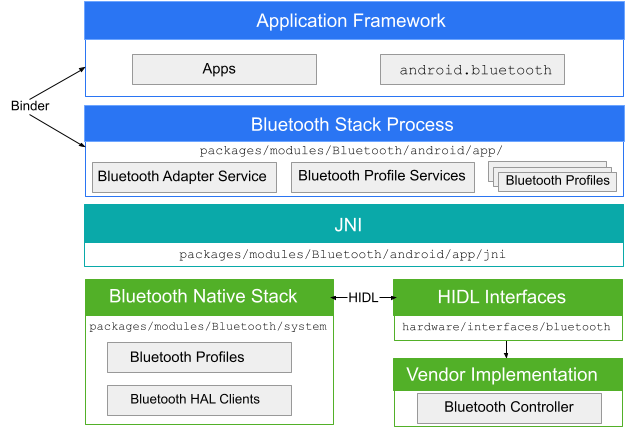
Figura 1. Architettura Bluetooth di Android.
- framework dell'app
- A livello di framework dell'app si trova il codice dell'app, che utilizza le
android.bluetoothAPI per interagire con l'hardware Bluetooth. Internamente, questo codice chiama il processo Bluetooth tramite il meccanismo Binder IPC. - App Bluetooth
- L'app Bluetooth, che si trova in
packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app, è inclusa come app per Android e implementa i profili Bluetooth a livello di framework Android. Questa app chiama lo stack Bluetooth tramite JNI. - JNI
- Il codice JNI associato a
android.bluetoothsi trova inpackages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app/jni. Il codice JNI chiama lo stack Bluetooth quando si verificano determinate operazioni Bluetooth, ad esempio quando vengono rilevati dispositivi. - Stack Bluetooth
- Lo stack Bluetooth predefinito è fornito in AOSP e si trova in
packages/modules/Bluetooth/system. Lo stack implementa l'HAL Bluetooth generico e lo personalizza con estensioni e modifiche alla configurazione. - implementazione del fornitore
- I dispositivi del fornitore interagiscono con lo stack Bluetooth utilizzando il linguaggio di definizione dell'interfaccia HAL (HIDL).
HIDL
HIDL definisce l'interfaccia tra lo
stack Bluetooth e l'implementazione del fornitore. Per generare i file HIDL Bluetooth, passa i file di interfaccia Bluetooth allo strumento di generazione HIDL. I file dell'interfaccia si trovano in
hardware/interfaces/bluetooth.
Sviluppo dello stack Bluetooth
Lo stack Bluetooth Android è uno stack Bluetooth completamente qualificato. L'elenco delle qualifiche è disponibile sul sito web di Bluetooth SIG (è necessario accedere) in QDID 169365.
Lo stack Bluetooth principale si trova in
packages/modules/Bluetooth.
Lo sviluppo avviene in AOSP e i contributi sono ben accetti.
