لتنفيذ التحديثات عبر اتصال لاسلكي، يجب أن يكون برنامج الإقلاع قادرًا على الوصول إلى قرص RAM الخاص بالاسترداد أثناء عملية الإقلاع. إذا كان الجهاز يستخدم صورة استرداد AOSP غير معدَّلة، يقرأ برنامج الإقلاع أول 32 بايت على قسم misc. وإذا كانت البيانات المتوفّرة تطابق boot-recovery، يبدأ برنامج الإقلاع في تشغيل صورة recovery. تتيح هذه الطريقة مواصلة أي عملية استرداد معلّقة (مثل تطبيق تحديث عبر الأثير أو إزالة البيانات) إلى حين اكتمالها.
للحصول على تفاصيل حول محتوى وحدة التخزين المحظورة في ذاكرة الفلاش المستخدَمة في الاتصالات من خلال وضع الاسترداد وبرنامج التشغيل، يُرجى الرجوع إلى bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.h.
الأجهزة التي تتلقّى تحديثات من النوع أ/ب
لإتاحة تحديثات عبر الأثير على الأجهزة التي تستخدم تحديثات A/B، تأكَّد من أنّ برنامج تحميل التشغيل على الجهاز يستوفي المعايير التالية.
المعايير العامة
يجب أن تكون جميع الأقسام التي يتم تحديثها من خلال تحديث عبر شبكة غير سلكية قابلة للتحديث أثناء تشغيل النظام الرئيسي (وليس أثناء التحديث في وضع الاسترداد).
لبدء تشغيل القسم
system، يمرِّر برنامج التحميل القيمة التالية في سطر أوامر النواة:ro root=/dev/[node] rootwait init=/init.يتحمّل إطار عمل Android مسؤولية استدعاء
markBootSuccessfulمن طبقة HAL. يجب ألا يضع برنامج الإقلاع علامة على أي قسم للإشارة إلى أنّه تم تشغيله بنجاح.
دعم طبقة تجريد الأجهزة الخاصة بالتحكّم في التشغيل
يجب أن يتيح برنامج الإقلاع استخدام boot_control HAL كما هو محدّد في
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h. يستعلم برنامج التحديث عن
HAL الخاص بأداة التحكم في عملية التشغيل،
ويحدّث فتحة التشغيل غير المستخدَمة، ويغيّر فتحة التشغيل النشطة باستخدام
HAL، ثم يعيد التشغيل إلى نظام التشغيل المحدَّث. لمزيد من التفاصيل، يُرجى الاطّلاع على
تنفيذ طبقة HAL الخاصة بالتحكّم في عملية التشغيل.
التوافق مع الفترات الزمنية
يجب أن يتيح برنامج الإقلاع وظائف ذات صلة بالأقسام وفتحات التخزين، بما في ذلك:
يجب أن تتضمّن أسماء الأقسام لاحقة تحدّد الأقسام التي تنتمي إلى فتحة معيّنة في برنامج التشغيل. لكل قسم من هذه الأقسام، هناك متغيّر مطابق
has-slot:partition base nameبقيمةyes. يتم تسمية الخانات أبجديًا على النحو التالي: أ، ب، ج، وما إلى ذلك، بما يتوافق مع الأقسام التي تتضمّن اللاحقة_aو_bو_cوما إلى ذلك. على برنامج التشغيل الأوّلي إبلاغ نظام التشغيل بالخانة التي تم تشغيلها باستخدام السمةandroidboot.slot_suffixفي سطر الأوامر. يتم ضبط هذه السمة من خلال bootconfig للأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 12 من نظام التشغيل Android أو الإصدارات الأحدث.تتم إعادة ضبط القيمة
slot-retry-countإلى قيمة موجبة (عادةً3) إما من خلال HAL الخاص بعنصر التحكّم في التشغيل عبر معاودة الاتصالsetActiveBootSlotأو من خلال الأمرfastboot set_active. عند تعديل قسم يمثّل جزءًا من فتحة، يمحو برنامج الإقلاع عبارة "تم الإقلاع بنجاح" ويعيد ضبط عدد محاولات إعادة التشغيل للفتحة.
يجب أن يحدّد برنامج الإقلاع أيضًا المكان الذي سيتم تحميله منه. يوضّح الشكل مثالاً على عملية اتّخاذ القرار.
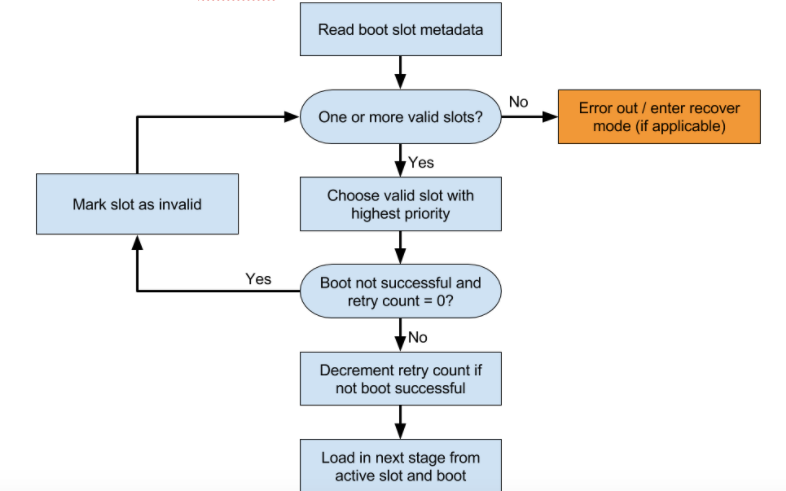
حدِّد الفتحة التي تريد محاولة ملئها. لا تحاول تحميل خانة تحمل العلامة
slot-unbootable. يجب أن تكون هذه الخانة متوافقة مع القيم التي تعرضها fastboot، ويُشار إليها باسم الخانة الحالية.إذا لم يتم وضع علامة
slot-successfulعلى الخانة الحالية وكانت تتضمّنslot-retry-count = 0، ضَع علامةslot-unbootableعلى الخانة الحالية. بعد ذلك، اختَر خانة مختلفة غير مميّزة بالعلامةunbootableومميّزة بالعلامةslot-successful، وستصبح هذه الخانة هي الخانة المحدّدة. إذا لم تتوفر أي فتحة حالية، يجب الانتقال إلى وضع الاسترداد أو عرض رسالة خطأ مفهومة للمستخدم.اختَر
boot.imgالمناسب وأدرِج المسار إلى قسم النظام الصحيح في سطر أوامر النواة.املأ المَعلمة
slot_suffixفي سطر أوامر النواة.التشغيل إذا لم يتم وضع علامة
slot-successful، يجب إنقاصslot-retry-count.
تحدّد الأداة المساعدة fastboot القسم الذي سيتم تحديثه عند تنفيذ أي أوامر تحديث. على سبيل المثال، يؤدي تنفيذ الأمر fastboot flash system system.img
أولاً إلى طلب البحث عن المتغيّر current-slot ثم ربط النتيجة بالنظام لإنشاء اسم القسم الذي يجب تثبيته (system_a وsystem_b وما إلى ذلك).
عند ضبط الفتحة الحالية باستخدام الأمر set_active fastboot أو الأمر setActiveBootSlot HAL الخاص بالتحكّم في عملية التشغيل، على برنامج التشغيل تحديث الفتحة الحالية ومحو slot-unbootable وslot-successful وإعادة ضبط عدد المحاولات (هذه هي الطريقة الوحيدة لمحو slot-unbootable).
الأجهزة التي لا تتضمّن تحديثات A/B
لإتاحة تحديثات عبر الأثير على الأجهزة التي لا تستخدم تحديثات A/B (راجِع الأجهزة التي يمكن تحديثها بدون استخدام نظام A/B)، تأكَّد من أنّ برنامج التشغيل الأوّلي للجهاز يستوفي المعايير التالية.
يجب أن يحتوي القسم
recoveryعلى صورة قادرة على قراءة صورة نظام من أحد الأقسام المتوافقة (cacheأوuserdata) وكتابتها في القسمsystem.يجب أن يتيح برنامج الإقلاع إمكانية التشغيل مباشرةً في وضع الاسترداد.
في حال توفّر تحديثات صور الراديو، يجب أن يكون القسم
recoveryقادرًا أيضًا على تحديث الراديو. يمكن إجراء ذلك بإحدى الطريقتَين التاليتَين:يومض برنامج الإقلاع الراديو. في هذه الحالة، من المفترض أن يكون من الممكن إعادة التشغيل من قسم الاسترداد إلى برنامج الإقلاع لإكمال التحديث.
تعرض صورة الاسترداد الراديو. يمكن توفير هذه الوظيفة كأداة أو مكتبة ثنائية.
