
Android предоставляет стандартный стек Bluetooth, поддерживающий как классический Bluetooth, так и Bluetooth с низким энергопотреблением (BLE). Используя Bluetooth, устройства Android могут создавать персональные сети для обмена данными с находящимися поблизости Bluetooth-устройствами.
В Android 4.3 и более поздних версиях стек Bluetooth Android обеспечивает поддержку BLE. Для полноценного использования API BLE следуйте требованиям Android Bluetooth HCI . Устройства Android с соответствующим чипсетом могут поддерживать либо классический Bluetooth, либо оба варианта. BLE не имеет обратной совместимости со старыми чипсетами Bluetooth.
В Android 8.0 стек Bluetooth полностью квалифицирован для Bluetooth 5. Для использования доступных функций Bluetooth 5 устройство должно иметь чипсет, совместимый с Bluetooth 5.
Архитектура Android
Приложение Bluetooth взаимодействует с процессом Bluetooth через Binder. Процесс Bluetooth использует Java Native Interface (JNI) для взаимодействия со стеком Bluetooth и предоставляет разработчикам доступ к различным профилям Bluetooth. На этой диаграмме показана общая структура стека Bluetooth:
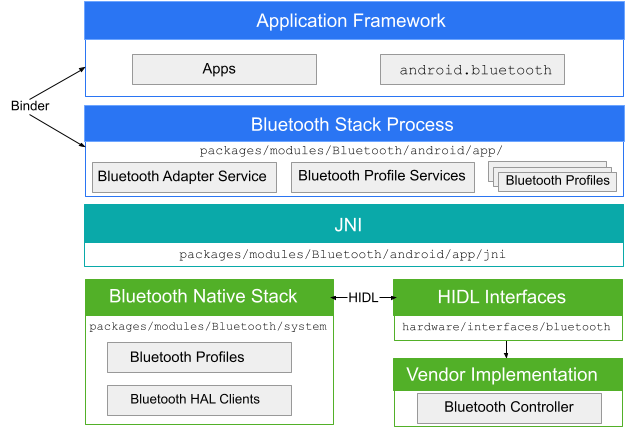
Рисунок 1. Архитектура Android Bluetooth.
- фреймворк приложения
- На уровне фреймворка приложения находится код приложения, который использует API
android.bluetoothдля взаимодействия с оборудованием Bluetooth. Внутри этот код вызывает процесс Bluetooth через механизм Binder IPC. - Bluetooth-приложение
- Приложение Bluetooth, расположенное в
packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app, упаковано как приложение Android и реализует профили Bluetooth на уровне фреймворка Android. Это приложение обращается к стеку Bluetooth через JNI. - JNI
- Код JNI, связанный с
android.bluetooth, находится вpackages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app/jni. Код JNI обращается к стеку Bluetooth при выполнении определённых операций Bluetooth, например, при обнаружении устройств. - Bluetooth-стек
- Стек Bluetooth по умолчанию предоставляется в AOSP и находится в
packages/modules/Bluetooth/system. Стек реализует универсальный Bluetooth HAL и настраивает его с помощью расширений и изменений конфигурации. - реализация поставщика
- Устройства-поставщики взаимодействуют со стеком Bluetooth, используя язык определения интерфейса HAL (HIDL).
ХИДЛ
HIDL определяет интерфейс между стеком Bluetooth и реализацией поставщика. Для генерации файлов Bluetooth HIDL передайте файлы интерфейса Bluetooth в инструмент генерации HIDL. Файлы интерфейса находятся в hardware/interfaces/bluetooth .
Разработка стека Bluetooth
Стек Bluetooth для Android — это полностью сертифицированный стек Bluetooth. Список сертификации доступен на сайте Bluetooth SIG (требуется регистрация) под QDID 169365 .
Основной стек Bluetooth находится в packages/modules/Bluetooth . Разработка ведётся в AOSP, и любые дополнения приветствуются.

