הדרך הכי מהירה וקלה לבדוק מסכים משניים היא להשתמש במסך מדומה שנמצא בבעלות המערכת. היא נחשבת לאמינה ומורשית לארח את כל חלונות העיצוב והפעילויות כי היא חולקת את ה-UID system_server.
אם יש לכם מכשיר שתומך בחיבור חומרה (לדוגמה, HDMI או DisplayPort דרך USB-C), אתם יכולים להשתמש במסכים חיצוניים כדי לבדוק.
כברירת מחדל, מסכים וירטואליים שלא נמצאים בבעלות של מזהה המשתמש במערכת נחשבים לא מהימנים, ומוחלות עליהם מספר הגבלות כדי למנוע דליפה של נתוני משתמשים.
אפשר להשתמש במצב מחשב כדי לבדוק תכונות חדשות של חלונות ויכולות שנוספו לפלטפורמה ב-Android 10. זוהי אפשרות למפתחים שמיועדת למפתחי אפליקציות, והיא מאפשרת להם לבדוק אפליקציות בסביבות של ריבוי מסכים וחלונות צפים.
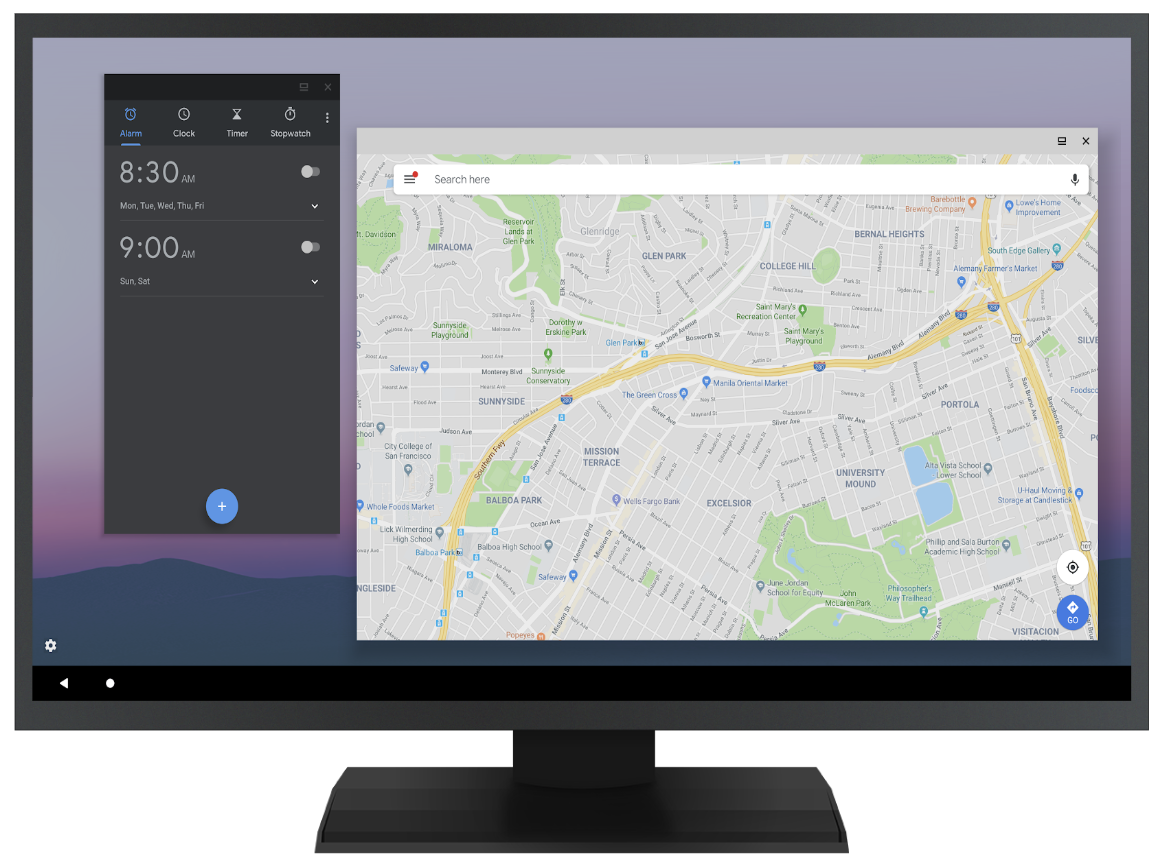
איור 1. מצב שולחן עבודה בשני מסכים, מדומה (למעלה) וחיצוני (למטה)
יצרני מכשירים שרוצים לספק חוויה שדומה לשימוש במחשב יכולים להשתמש בתכונה הזו כדי להציג את הדרך המומלצת להטמעה של חלק מהתכונות של חלונות.
- מפעילים את האפשרות למפתחים הפעלת מצב מחשב.
- מפעילים מחדש את הטלפון.
- מחברים את העכבר (באמצעות USB או Bluetooth).
- יוצרים תצוגה מדומה באפשרויות למפתחים או משתמשים בתצוגת חומרה.
- אפשר להפעיל פעילויות ממרכז האפליקציות בצג הזה ולהשתמש בעכבר כדי לבצע פעולות.
מרכז האפליקציות לתצוגה מרובת מסכים (platform/development/samples/MultiDisplay) שימושי לבדיקת הפעלה של פעילות ממוקדת ולבקשת מופע חדש.
