硬體評估會定義三種觸覺效果,並標示為「效果 1」、「效果 2」和「效果 3」,以供這項特定評估使用。
效果 1:預先定義的短觸覺常數
VibrationEffect.EFFECT_CLICK 常數是 HAL-API 對應中的基準效果或公分母,請參閱「HAL 與 API 之間的對應常數」。並對應到最常使用的效果 HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_PRESS
。評估這項效果有助於判斷目標裝置是否已準備好清晰的觸覺回饋。
效果 2:短促的自訂觸覺效果
VibrationEffect.createOneShot(20,255) 常數適用於自訂觸覺效果。如果是短暫的單一自訂脈衝,建議將時間長度上限設為 20 毫秒。不建議使用超過 20 毫秒的單一脈衝,因為這會被視為嗡嗡作響的震動。
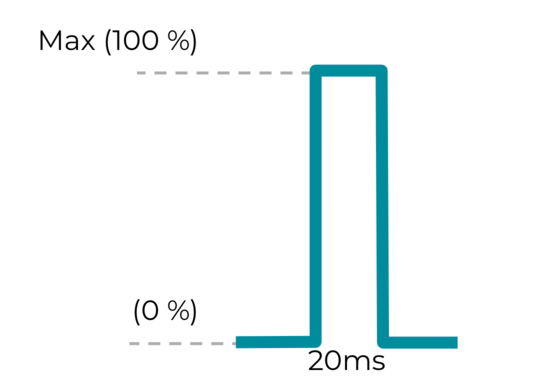
圖 19. 短促的自訂觸覺效果
效果 3:具有振幅變化的長自訂觸覺效果
VibrationEffect.createWaveform(timings[], amplitudes[], int
repeat) 常數適用於幅度變化較大的長時間自訂效果。能否為自訂觸覺效果產生不同振幅,是評估裝置豐富觸覺功能的一項指標。建議的 timings [] 和 分別為 {500, 500} 和 {128, 255},這代表振幅從 50% 增加到 100%,取樣率為 500 毫秒。amplitudes []
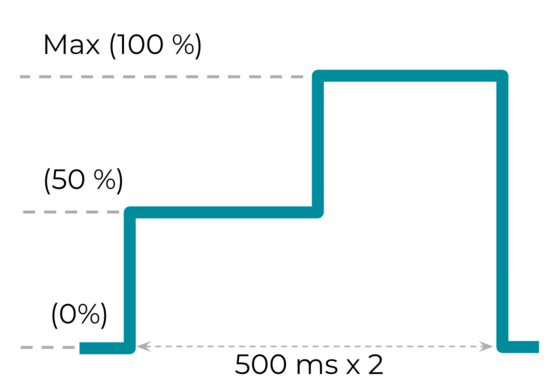
圖 20. 具有振幅變化的長自訂觸覺效果
如要檢查 Effect 3 的音量控制硬體功能,請使用 Vibrator.hasAmplitudeControl() 方法。結果必須是 true,才能執行 VibrationEffect.createWaveform,並按照預期改變振幅。
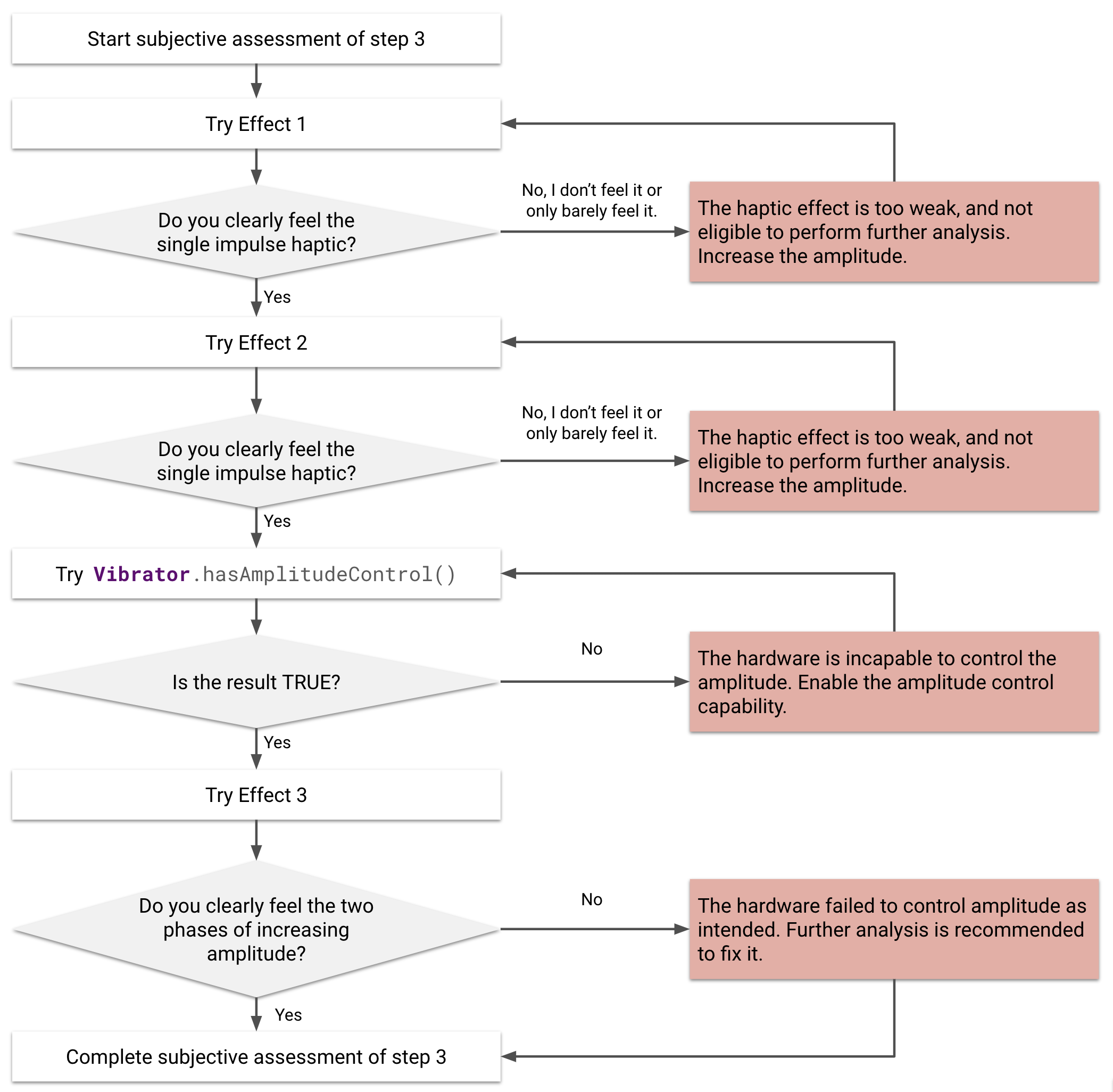
圖 21. 主觀評估觸覺效果 1、2 和 3
進行主觀評估
如要快速檢查連貫性,請先進行主觀評估。主觀評估的目的是觀察觸覺效果的振幅,判斷裝置是否能產生人體可感知的振幅。
圍繞這個概念的具體問題如下:裝置是否能如預期產生可感知觸覺效果?回答這個問題有助於避免觸覺回饋失敗,包括使用者無法感受到的觸覺回饋,或是波形未產生預期模式的非預期觸覺回饋。
執行進階評估
強烈建議執行進階品質評估。進階品質評估會描述觸覺效果的可量化屬性,以實作高品質觸覺效果。完成後,裝置製造商應能診斷目前的觸覺回饋狀態,也就是說,他們可以設定目標來提升整體品質。請參閱硬體評估。
