
Android มีสแต็กบลูทูธเริ่มต้นที่รองรับทั้งบลูทูธคลาสสิกและบลูทูธพลังงานต่ำ (BLE) อุปกรณ์ Android สามารถใช้บลูทูธเพื่อสร้างเครือข่ายส่วนบุคคลเพื่อส่งและรับข้อมูลกับอุปกรณ์บลูทูธที่อยู่ใกล้เคียง
ใน Android 4.3 ขึ้นไป สแต็กบลูทูธของ Android จะมีความสามารถ ในการใช้ BLE หากต้องการใช้ BLE API อย่างเต็มรูปแบบ ให้ทำตามข้อกำหนด HCI ของบลูทูธใน Android อุปกรณ์ Android ที่มีชิปเซ็ตที่ผ่านการรับรองจะใช้บลูทูธแบบคลาสสิก หรือทั้งบลูทูธแบบคลาสสิกและ BLE ก็ได้ BLE ไม่สามารถทำงานร่วมกับชิปเซ็ตบลูทูธรุ่นเก่าได้
ใน Android 8.0 สแต็กบลูทูธมีคุณสมบัติครบถ้วนสำหรับบลูทูธ 5 หากต้องการใช้ฟีเจอร์บลูทูธ 5 ที่พร้อมใช้งาน อุปกรณ์ต้องมีชิปเซ็ตที่ผ่านการรับรองบลูทูธ 5
สถาปัตยกรรม Android
แอปบลูทูธจะสื่อสารกับกระบวนการบลูทูธผ่าน Binder กระบวนการบลูทูธใช้ Java Native Interface (JNI) เพื่อสื่อสารกับ สแต็กบลูทูธ และให้สิทธิ์นักพัฒนาแอปเข้าถึงโปรไฟล์บลูทูธต่างๆ แผนภาพนี้แสดงโครงสร้างทั่วไปของสแต็กบลูทูธ
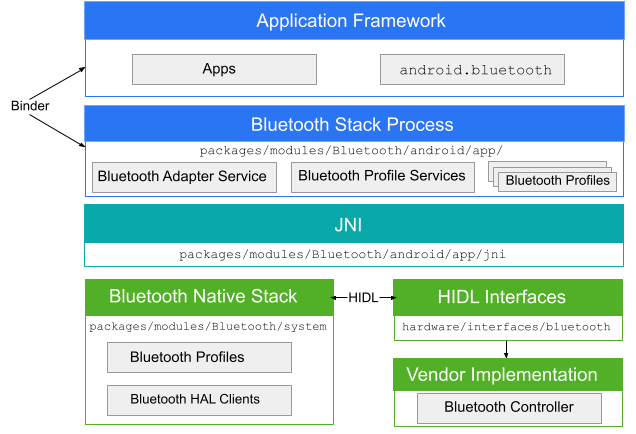
รูปที่ 1 สถาปัตยกรรมบลูทูธของ Android
- เฟรมเวิร์กแอป
- ที่ระดับเฟรมเวิร์กของแอปคือโค้ดของแอป ซึ่งใช้
android.bluetoothAPI เพื่อโต้ตอบกับฮาร์ดแวร์บลูทูธ ภายใน โค้ดนี้จะเรียกใช้ กระบวนการบลูทูธผ่านกลไก Binder IPC - แอปบลูทูธ
- แอปบลูทูธซึ่งอยู่ใน
packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/appได้รับการแพ็กเกจเป็นแอป Android และใช้โปรไฟล์บลูทูธที่ เลเยอร์เฟรมเวิร์ก Android แอปนี้เรียกใช้สแต็กบลูทูธผ่าน JNI - JNI
- โค้ด JNI ที่เชื่อมโยงกับ
android.bluetoothอยู่ในpackages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app/jniโค้ด JNI จะเรียกใช้สแต็กบลูทูธเมื่อมีการดำเนินการบลูทูธบางอย่าง เช่น เมื่อมีการค้นพบอุปกรณ์ - สแต็กบลูทูธ
- สแต็กบลูทูธเริ่มต้นมีอยู่ใน AOSP และอยู่ใน
packages/modules/Bluetooth/systemโดยสแต็กจะใช้ HAL บลูทูธทั่วไปและปรับแต่งด้วยส่วนขยายและการเปลี่ยนแปลงการกำหนดค่า - การติดตั้งใช้งานของผู้ให้บริการ
- อุปกรณ์ของผู้ให้บริการจะโต้ตอบกับสแต็กบลูทูธโดยใช้ภาษาคำจำกัดความของอินเทอร์เฟซ HAL (HIDL)
HIDL
HIDL กำหนดอินเทอร์เฟซระหว่าง
สแต็ก Bluetooth กับการติดตั้งของผู้ให้บริการ หากต้องการสร้างไฟล์ HIDL ของบลูทูธ
ให้ส่งไฟล์อินเทอร์เฟซบลูทูธไปยังเครื่องมือสร้าง HIDL
ไฟล์อินเทอร์เฟซจะอยู่ใน
hardware/interfaces/bluetooth
การพัฒนาสแต็กบลูทูธ
สแต็กบลูทูธของ Android เป็นสแต็กบลูทูธที่สมบูรณ์ในตัวเอง รายการการรับรองอยู่ในเว็บไซต์ของ Bluetooth SIG (ต้องลงชื่อเข้าใช้) ในส่วน QDID 169365
สแต็กบลูทูธหลักอยู่ใน
packages/modules/Bluetooth
การพัฒนาเกิดขึ้นใน AOSP และเรายินดีรับการมีส่วนร่วม
