
Android מספקת מחסנית Bluetooth שמוגדרת כברירת מחדל ותומכת ב-Bluetooth קלאסי וב-Bluetooth עם צריכת אנרגיה נמוכה (BLE). באמצעות Bluetooth, מכשירי Android יכולים ליצור רשתות אזור אישיות כדי לשלוח ולקבל נתונים עם מכשירי Bluetooth בקרבת מקום.
ב-Android מגרסה 4.3 ואילך, מחסנית ה-Bluetooth של Android מאפשרת להטמיע BLE. כדי להשתמש במלוא הפוטנציאל של ממשקי ה-API של BLE, צריך לפעול לפי הדרישות של Android Bluetooth HCI. במכשירי Android עם ערכת שבבים מתאימה אפשר להטמיע Bluetooth קלאסי או גם Bluetooth קלאסי וגם BLE. BLE לא תואם לאחור לערכות שבבים ישנות יותר של Bluetooth.
ב-Android 8.0, מחסנית ה-Bluetooth עומדת בדרישות של Bluetooth 5. כדי להשתמש בתכונות הזמינות של Bluetooth 5, במכשיר צריך להיות ערכת שבבים שעומדת בדרישות של Bluetooth 5.
ארכיטקטורה ל-Android
אפליקציית Bluetooth מתקשרת עם תהליך ה-Bluetooth באמצעות Binder. תהליך ה-Bluetooth משתמש ב-Java Native Interface (JNI) כדי לתקשר עם מחסנית ה-Bluetooth, ומספק למפתחים גישה לפרופילים שונים של Bluetooth. הדיאגרמה הזו מציגה את המבנה הכללי של מחסנית Bluetooth:
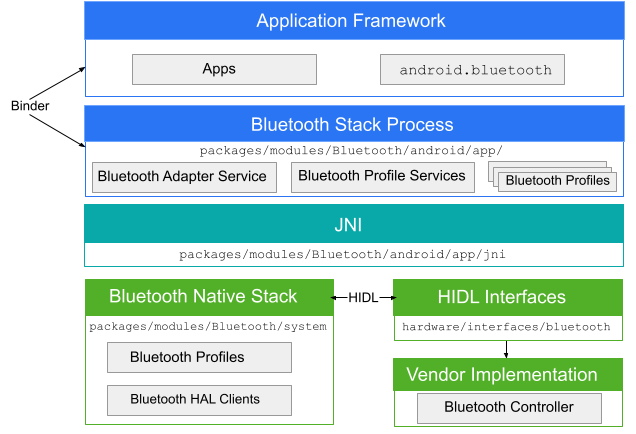
איור 1. ארכיטקטורת Bluetooth ב-Android.
- app framework
- ברמת מסגרת האפליקציה נמצא קוד האפליקציה, שמשתמש בממשקי
android.bluetoothAPI כדי ליצור אינטראקציה עם חומרת ה-Bluetooth. באופן פנימי, הקוד הזה מפעיל את תהליך ה-Bluetooth באמצעות מנגנון ה-IPC של Binder. - אפליקציית Bluetooth
- אפליקציית ה-Bluetooth, שנמצאת ב-
packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app, ארוזה כאפליקציית Android ומיישמת את פרופילי ה-Bluetooth בשכבת מסגרת Android. האפליקציה הזו קוראת ל-Bluetooth stack דרך JNI. - JNI הקוד של JNI שמשויך ל-
- קוד ה-JNI קורא למערך ה-Bluetooth כשמתרחשות פעולות מסוימות של Bluetooth, כמו כשמגלים מכשירים.
- Bluetooth stack
- מקבץ הפיצ'רים של Bluetooth שמוגדר כברירת מחדל מסופק ב-AOSP והוא נמצא ב-
packages/modules/Bluetooth/system. המקבץ מיישם את ה-HAL הגנרי של Bluetooth ומבצע בו התאמה אישית באמצעות תוספים ושינויים בהגדרות. - הטמעה של ספק
- מכשירי ספקים מקיימים אינטראקציה עם מחסנית Bluetooth באמצעות שפת ההגדרה של ממשק HAL (HIDL).
android.bluetooth נמצא ב-packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app/jni.HIDL
HIDL מגדיר את הממשק בין מחסנית Bluetooth לבין ההטמעה של הספק. כדי ליצור את קובצי ה-Bluetooth HIDL, מעבירים את קובצי ממשק ה-Bluetooth לכלי ליצירת HIDL. קבצי הממשק נמצאים בתיקייה
hardware/interfaces/bluetooth.
פיתוח של Bluetooth stack
מקבץ הפיצ'רים של Bluetooth ב-Android הוא מקבץ פיצ'רים מלא של Bluetooth. רשימת ההסמכות מופיעה באתר Bluetooth SIG (נדרשת כניסה) בקטע QDID 169365.
מקבץ הפיצ'רים של Bluetooth נמצא בתיקייה
packages/modules/Bluetooth.
הפיתוח מתבצע ב-AOSP, ואנחנו מקבלים בברכה הצעות לשיפורים.
