Android 10 支援使用 Android 建構系統建構 odm 分區。
關於 ODM 分區
原始設計製造商 (ODM) 會將晶片系統 (SoC) 供應商的板級支援套件 (BSP) 自訂為特定裝置 (其板級)。這可讓他們為特定板子的元件、特定板子的守護程序,或在硬體抽象層 (HAL) 上實作自己的功能,實作核心模組。他們也可能會想要取代或自訂 SoC 元件。
在較舊的 Android 版本中,這類自訂設定會導致裝置無法使用單一供應商映像檔,即使裝置搭載相同的 SoC (或搭載不同 SoC,但屬於同一家族) 也是如此。在 Android 10 以上版本中,您可以使用單獨的 odm 分割區進行自訂,這樣就能將單一供應商映像檔用於多個硬體 SKU。
使用產品和 ODM 分區
Android 9 新增了建構 product 區隔的支援功能,可讓您使用單一系統映像檔,為不同 product.img 映像檔提供的多個軟體 SKU 提供服務。product 區隔區是用於軟體 SKU,odm 區隔區則是用於硬體 SKU。
透過專屬產品和 ODM 區隔,您可以使用 system 區隔來代管通用程式碼,以便在多個軟體 SKU 之間共用,並使用 vendor 區隔來代管 SoC 專屬 BSP 程式碼,以便在多個裝置之間共用特定 SoC。
使用個別分割區有其缺點,例如難以管理磁碟空間 (例如,您必須為日後的擴充預留有限的空間)。不過,Android 10 支援動態分割區,可解決磁碟問題,並在無線更新 (OTA) 期間重新分割裝置。
ODM 元件
odm 分區包含下列 ODM 專屬元件 (類似 vendor 分區),如下表所列。
| ODM 專屬元件 | 位置 |
|---|---|
| 可載入的核心模組 (LKM) | /odm/lib/modules/*.ko |
| 原生程式庫 | /odm/lib[64] |
| HAL | /odm/lib[64]/hw |
| SEPolicy | /odm/etc/selinux |
| VINTF 物件資料 | /odm/etc/vintf |
init.rc
檔案 |
/odm/etc/init |
| 系統屬性 | /odm/build.prop |
| 執行階段資源覆蓋 (RRO) | /odm/overlay/*.apk |
| 應用程式 | /odm/app/*.apk |
| Priv-apps | /odm/priv-app/*.apk |
| Java 程式庫 | /odm/framework/*.jar |
| Android 架構系統設定 | /odm/etc/sysconfig/*和/odm/etc/permissions/* |
沒有自訂圖片
請勿使用自訂圖片,因為這類圖片不支援以下功能:
- 將模組安裝到特定目標。自訂映像檔可將構件複製到映像檔,但無法將模組安裝到特定分區,因為您無法將目標分區指定為建構規則的一部分。
- Soong。
custom_images無法使用 Soong 建構系統進行建構。 - OTA 更新。自訂映像檔可用於無法透過 OTA 更新的出廠 ROM 映像檔。
維護分區之間的 ABI
odm 分區是 vendor 分區的擴充功能。考量應用程式二進位檔介面 (ABI) 穩定性時,請留意下列架構。
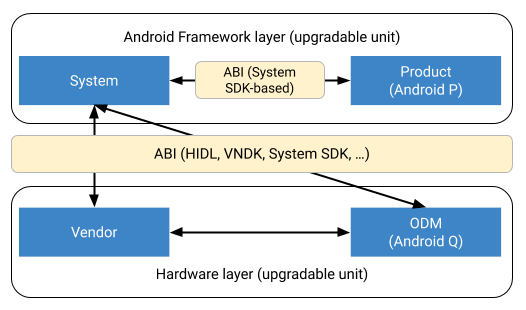
圖 1. 在分區之間維護 ABI。
odm和vendor區隔之間沒有 ABI 穩定性。兩個分割區必須同時升級。odm和vendor分區可以彼此依賴,但vendor分區「必須」在沒有odm分區的情況下運作。odm和system之間的 ABI 與vendor和system之間的 ABI 相同。
product 分區與 vendor 或 odm 分區之間不允許直接互動。(這是由 SEpolicy 強制執行。)
實作 ODM 分區
實作新分割區前,請先查看相關的 AOSP 變更。
設定 ODM 分區
如要設定 odm 分割區,請加入下列建構標記:
BOARD_ODMIMAGE_PARTITION_SIZE:固定分區大小PRODUCT_USE_DYNAMIC_PARTITIONS和BOARD_ODMIMAGE_PARTITION_RESERVED_SIZE可用於設定動態分區大小BOARD_ODMIMAGE_FILE_SYSTEM_TYPE用於 ODM 映像檔的檔案系統類型PRODUCT_ODM_PROPERTIES適用於/odm/build.prop,可用於$(call inherit-product path/to/device.mk)內,如PRODUCT_ODM_PROPERTIES += product.abc=ok
在 ODM 分區中安裝模組
使用這些建構標記,將模組安裝至 odm 分區:
Android.bp的device_specific: trueAndroid.mk的LOCAL_ODM_MODULE := true
啟用驗證開機程序
為避免惡意軟體竄改 odm 分區,請為這些分區啟用 Android 驗證啟動 (AVB) (就像為 vendor 和 system 分區啟用 AVB 一樣)。
如要啟用 AVB,請納入建構旗標 BOARD_AVB_ODM_ADD_HASHTREE_FOOTER_ARGS。如要進一步瞭解如何在動態分區中設定 AVB,請參閱「AVB 設定變更」。
將 /odm 視為另一個 /vendor 分割區
為確保系統將 odm 分區視為 vendor 分區,請將任何硬式編碼的 vendor 參照替換為一組以硬體為導向的分區 (目前為 odm 和 vendor)。平台中值得注意的 vendor 參照位置包括動態連結器、套件管理器和 shell/libc。
