اجرای همپوشانی درخت دستگاه (DTOs) شامل تقسیم درخت دستگاه (DT)، ساخت، پارتیشن بندی و اجرا می شود. پس از اجرای کار، باید سازگاری بین دو DT را نیز حفظ کنید و یک استراتژی برای تضمین امنیت هر پارتیشن DT تعیین کنید.
DT را تقسیم کنید
با تقسیم DT به دو قسمت شروع کنید:
- DT اصلی بخش فقط SoC و تنظیمات پیش فرض ارائه شده توسط فروشنده SoC.
- روکش DT . پیکربندی های خاص دستگاه، ارائه شده توسط ODM/OEM.
پس از تقسیم DTها، باید از سازگاری بین DT اصلی و DT روکش اطمینان حاصل کنید تا ادغام DT اصلی و DT روکش منجر به یک DT کامل برای دستگاه شود. برای جزئیات بیشتر در مورد قالب و قوانین DTO، به نحو DTO مراجعه کنید. برای جزئیات بیشتر در مورد چند DT، به استفاده از چندین DT مراجعه کنید.
ساخت DT های اصلی و روکش
برای ساخت DT اصلی:
- DT
.dtsاصلی را در یک فایل.dtbکامپایل کنید. - فایل
.dtbرا در یک پارتیشن قابل دسترسی در زمان اجرا بوت لودر فلش کنید (جزئیات در [Partition DTs] (#partition)).
برای ساخت همپوشانی DT:
- همپوشانی DT
.dtsرا در یک فایل.dtboکامپایل کنید. در حالی که این فرمت فایل مشابه فایل.dtbاست که به صورت یک DT مسطح فرمت شده است، پسوند فایل متفاوت آن را از DT اصلی متمایز می کند. - فایل
.dtboرا در یک پارتیشن قابل دسترسی در زمان اجرا بوت لودر فلش کنید (جزئیات در [Partition DTs] (#partition)).
برای جزئیات کامپایل با DTC و تأیید نتایج DTO در میزبان، به Compile and Verify مراجعه کنید.
پارتیشن های DT
برای قرار دادن .dtb و .dtbo ، یک مکان قابل دسترسی و قابل اعتماد در زمان اجرا بوت لودر در حافظه فلش تعیین کنید.
مکان های نمونه برای DT اصلی:
- بخشی از پارتیشن بوت، اضافه شده به هسته (
image.gz) - حباب های DT (
.dtb) را در پارتیشن اختصاصی (dtb) جدا کنید
مکانهای نمونه برای DT روکش:
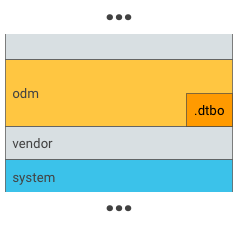
شکل 1. .dtbo را در یک پارتیشن odm قرار دهید (این کار را فقط در صورتی انجام دهید که بوت لودر شما توانایی بارگذاری داده ها از سیستم فایل یک پارتیشن odm را داشته باشد).
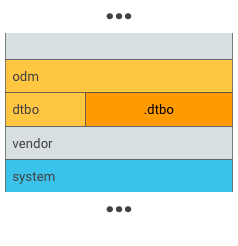
شکل 2. .dtbo را در یک پارتیشن منحصر به فرد، مانند پارتیشن dtbo قرار دهید.
توجه: اندازه پارتیشن DT روکش به دستگاه و میزان تغییرات مورد نیاز در بالای حباب اصلی DT بستگی دارد. به طور معمول، 8 مگابایت بیش از حد کافی است و در صورت نیاز، فضای بیشتری را در آینده ایجاد می کند.
برای دستگاههایی که از بهروزرسانیهای بدون درز (A/B) پشتیبانی میکنند، پارتیشنهای DT اصلی و DT روکش A/B:
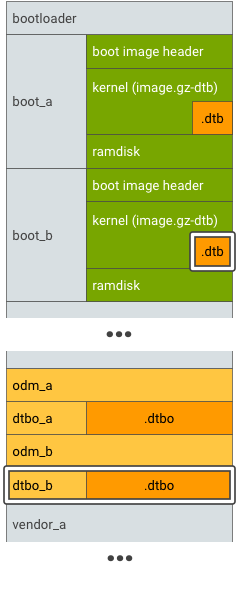
شکل 3. پارتیشن DTBO A/B، مثال 1.
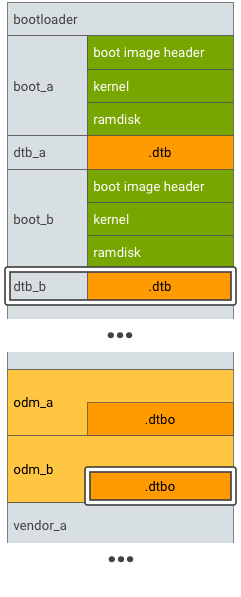
شکل 4. پارتیشن DTBO A/B، مثال 2.
در بوت لودر اجرا شود
برای اجرا:
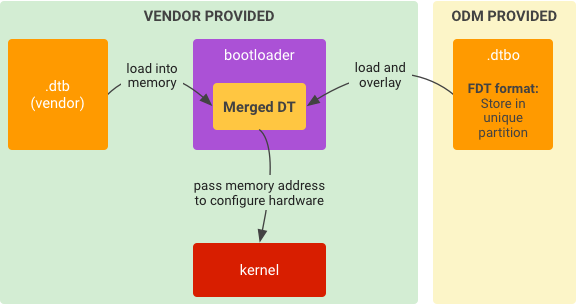
شکل 5. اجرای معمول زمان اجرا برای DTO در بوت لودر.
-
.dtbاز حافظه در حافظه بارگیری کنید. -
.dtboاز حافظه در حافظه بارگیری کنید. - همپوشانی
.dtbبا.dtboتا یک DT ادغام شده باشد. - با توجه به آدرس حافظه DT ادغام شده، هسته را شروع کنید.
سازگاری را حفظ کنید
DTB اصلی (از فروشنده SoC) به عنوان یک سطح API برای DTBO ها در نظر گرفته می شود. پس از جدا کردن DT به یک بخش مشترک SoC و یک بخش خاص دستگاه، باید این دو قسمت را در آینده با یکدیگر سازگار نگه دارید، از جمله:
- تعریف DT در DT اصلی. به عنوان مثال، گره ها، ویژگی ها، برچسب ها. هرگونه تغییر تعریف در DT اصلی می تواند باعث ایجاد تغییرات در DT همپوشانی شود. به عنوان مثال، برای تصحیح نام گره در DT اصلی، یک برچسب "نام مستعار" تعریف کنید که به نام گره اصلی نگاشت شود (برای جلوگیری از تغییر روکش DT).
- محل فروشگاه روکش DT. به عنوان مثال، نام پارتیشن، فرمت فروشگاه.
امنیت را تضمین کند
بوت لودر باید مطمئن شود که DTB یا DTBO ایمن، اصلاح نشده و خراب است. می توانید از هر راه حلی برای ایمن سازی DTB یا DTBO استفاده کنید، به عنوان مثال، امضای تصویر بوت در VBoot 1.0 یا پاورقی AVB HASH (VBoot 2.0).
- اگر DTB یا DTBO در یک پارتیشن منحصر به فرد است، می توانید آن پارتیشن را به زنجیره اعتماد AVB اضافه کنید. زنجیره اعتماد از یک ریشه اعتماد محافظت شده توسط سخت افزار شروع می شود و به بوت لودر می رود که یکپارچگی و صحت پارتیشن DTB یا DTBO را تأیید می کند.
- اگر DTB یا DTBO در یک پارتیشن موجود باشد (مانند پارتیشن
odm)، آن پارتیشن باید در زنجیره اعتماد AVB باشد. (پارتیشن DTBO می تواند یک کلید عمومی را با پارتیشنodmبه اشتراک بگذارد).
برای جزئیات، به بوت تایید شده مراجعه کنید.

