ליבת Android מבוססת על ליבת Linux Long Term Supported (LTS). ב-Google, ליבות LTS משולבות עם תיקונים ספציפיים ל-Android כדי ליצור ליבות משותפות של Android (ACK).
קובצי ה-ACK נוצרים ממאגר kernel/common. המאגר הזה הוא קבוצת-על של ליבת Linux במעלה הזרם, עם תיקונים נוספים שספציפיים ל-Android.
ליבות ACK מגרסה 5.10 ואילך נקראות גם *ליבות של תמונות ליבה גנריות (GKI). ליבות GKI תומכות בהפרדה בין קוד ליבת ה-kernel הגנרית שאינו תלוי בחומרה לבין מודולי GKI, ובין מודולי הספק שספציפיים לחומרה.
האינטראקציה בין ליבת ה-GKI לבין מודולי הספק מתאפשרת באמצעות ממשק מודול הליבה (KMI), שמורכב מרשימות של סמלים שמזהים את הפונקציות והנתונים הגלובליים שנדרשים למודולי הספק. איור 1 מציג את ארכיטקטורת מודול הספק וליבת ה-GKI:
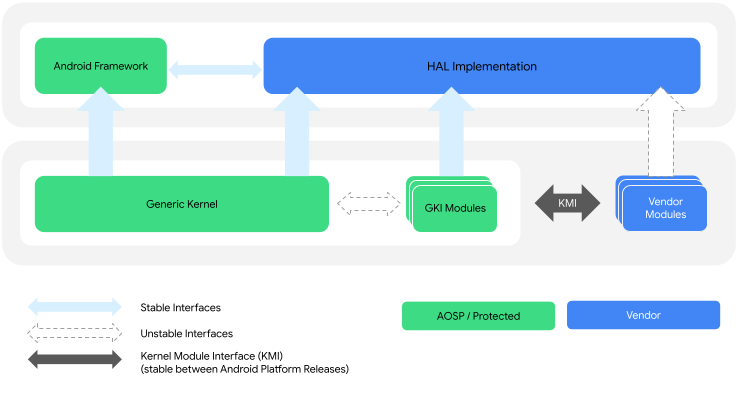
איור 1. ארכיטקטורת מודול הספק וליבת ה-GKI.
מילון מונחים בנושא ליבה
בהמשך מפורטים מונחים שמופיעים במשאבי העזרה בנושא ליבת המערכת.
סוגי ליבה
- Android Common Kernel (ACK)
- ליבת מערכת שהיא downstream של ליבת LTS וכוללת תיקונים שחשובים לקהילת Android. התיקונים האלה לא מוזגו לליבת Linux או לליבות GKI לטווח ארוך.
ליבות בגרסה 5.10 ואילך נקראות גם ליבות Generic Kernel Image (GKI).
- ליבת פרויקט קוד פתוח של Android (AOSP)
- מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא ליבת Android נפוצה.
אי אפשר להעביר תכונות של Android 12 לגרסאות קודמות של ליבות 4.19. קבוצת התכונות תהיה דומה לזו של מכשיר שהושק עם גרסה 4.19 ב-Android 11 ושודרג ל-Android 12.
- ליבת Generic Kernel Image (GKI)
כל ליבת ACK מגרסה 5.10 ואילך(רק aarch64). ליבת ה-GKI מורכבת משני חלקים:
ליבת מערכת הפעלה גנרית – החלק בליבת ה-GKI שמשותף לכל המכשירים.
מודולי GKI – מודולי ליבה שנוצרו על ידי Google ואפשר לטעון אותם באופן דינמי במכשירים שבהם זה רלוונטי. המודולים האלה נוצרים כארטיפקטים של ליבת ה-GKI, והם מועברים לצד ה-GKI כארכיון
system_dlkm_staging_archive.tar.gz. מודולי GKI חתומים על ידי Google באמצעות צמד המפתחות של משך זמן של תהליך build של הליבה, והם תואמים רק לליבת GKI שאיתה הם נבנו.
- ליבת Kernel Module Interface (KMI)
מידע נוסף זמין במאמר בנושא ליבת GKI.
- ליבת מערכת הפעלה עם תמיכה לטווח ארוך (LTS)
ליבת Linux שנתמכת למשך שנתיים עד 6 שנים. ליבות LTS יוצאות פעם בשנה ומהוות את הבסיס לכל הליבות המשותפות של Android של Google.
סוגי הסתעפויות
- ACK KMI kernel branch
- הענף שעבורו נבנים ליבות GKI. שמות הסניפים תואמים לגרסאות הליבה, כמו
android15-6.6. - Android-mainline
- ההסתעפות הראשית של הפיתוח לתכונות של Android. כשמכריזים על ליבת LTS חדשה ב-upstream, יוצרים הסתעפות של ליבת GKI חדשה תואמת מ-android-mainline.
Linux mainline : ההסתעפות הראשית של הפיתוח לליבות Linux במעלה הזרם, כולל ליבות LTS.
תנאים אחרים
- קובץ אימג' לאתחול מאומת
- הליבה מועברת בפורמט בינארי (
boot.img) ומוטמעת במכשיר. התמונה הזו נחשבת מאושרת כי היא מכילה אישורים מוטמעים, ולכן Google יכולה לאמת שהמכשיר נשלח עם ליבת מערכת שאושרה על ידי Google. - מודול ליבה שניתן לטעינה באופן דינמי (DLKM)
- מודול שאפשר לטעון באופן דינמי במהלך אתחול המכשיר, בהתאם לצרכים של המכשיר. GKI ומודולים של ספקים הם שני סוגים של DLKM. מודולי DLKM מופצים בפורמט
.koויכולים להיות מנהלי התקנים או לספק פונקציונליות אחרת של ליבת מערכת ההפעלה. - פרויקט GKI
- פרויקט Google שמטפל בפיצול של ליבת המערכת על ידי הפרדה של פונקציונליות ליבה משותפת מ-SoC ספציפי לספק ותמיכה בלוח למודולים שניתנים לטעינה.
Generic Kernel Image (GKI) (קובץ אימג' כללי של ליבת מערכת): קובץ אימג' לאתחול שאושר על ידי Google ומכיל ליבת GKI שנבנתה מתוך עץ מקור של ACK ומתאים להעברה למחיצת האתחול של מכשיר עם Android.
- ממשק מודול ליבת המערכת (KMI)
- ממשק בין ליבת GKI לבין מודולים של ספקים, שמאפשר לעדכן מודולים של ספקים באופן עצמאי בלי קשר לליבת GKI. הממשק הזה מורכב מפונקציות ליבה ומנתונים גלובליים שזוהו כתלות בספק או ביצרן ציוד מקורי (OEM) באמצעות רשימות סמלים לכל שותף.
- Vendor module
- מודול ספציפי לחומרה שפותח על ידי שותף ומכיל SoC ופונקציונליות ספציפית למכשיר. מודול ספק הוא סוג של מודול ליבה שאפשר לטעון באופן דינמי.
השלבים הבאים
אם אתם חדשים בפיתוח ליבת Android, כדאי להתחיל בקריאת המאמרים הבאים:
- Long Term Stable Kernels - רקע על ליבות LTS במעלה הזרם שמוזנות ל-ACK.
- Android Common Kernels – מידע כללי על ACKs.
אם אתם חדשים בפיתוח ליבת GKI, כדאי להתחיל בקריאת המאמר פיתוח GKI.
