การจัดสรรคีย์จากระยะไกล (RKP) เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ AOSP มาตั้งแต่ Android 12 Android 14 เปิดตัว โมดูลที่อัปเดตได้สำหรับการจัดสรรระยะไกล ซึ่งช่วยเพิ่มความยืดหยุ่นของฟีเจอร์โดย การปรับปรุงความแข็งแกร่งของ API บริการและลดเวลาในการ เปิดตัวการปรับปรุงต่างๆ
แรงจูงใจ
ลดความซับซ้อนของบริการ RKP โดยรวมทุกอย่างไว้ใน APEX
ก่อน Android 14 นั้น RKP จะแยกออกเป็นแอป
RemoteProvisionerและ Keystore 2.0 RemoteProvisionerแอปมีหน้าที่ติดต่อแบ็กเอนด์ RKP และ Keystore 2.0 มีหน้าที่
ทั้งจัดเก็บคีย์และสื่อสารกับ HAL ซึ่งไม่ใช่สถาปัตยกรรมที่ดีเนื่องจากคีย์ RKP แตกต่างจากคีย์ Keystore อย่างมากในแง่ของข้อมูลเมตาที่แนบมา นอกจากนี้ ยังต้องมีการแก้ไขโค้ดเฟรมเวิร์ก Keystore ที่ไม่สะดวกเพื่อแจ้งเตือน RemoteProvisioner เกี่ยวกับ
การขาดแคลนทรัพยากรที่อาจเกิดขึ้น
RKP ในฐานะโมดูล Mainline ได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อปรับปรุงจุดเหล่านี้ด้วยการ รวมทุกอย่างไว้ใน APEX อย่างเรียบร้อย
ขอบเขตของโมดูล
APEX หลักของ RKP, com.android.rkpd มีแอปพลิเคชัน Daemon การจัดสรรคีย์จากระยะไกล (RKPD) และคอมโพเนนต์เซิร์ฟเวอร์ของระบบการจัดสรรจากระยะไกล
(สร้างด้วย Java)
สถาปัตยกรรมสแต็ก
รูปที่ 1 แสดงสถาปัตยกรรมของสแต็ก RKP
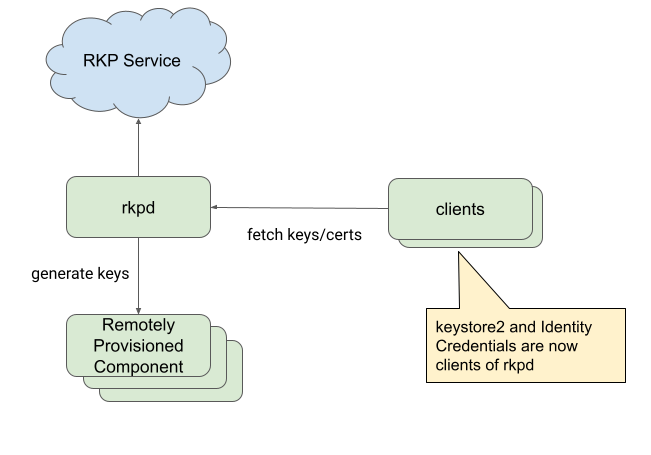
รูปที่ 1 สถาปัตยกรรมของสแต็ก RKP
สถาปัตยกรรมภายใน
รูปที่ 2 แสดงสถาปัตยกรรมภายในของ RKP
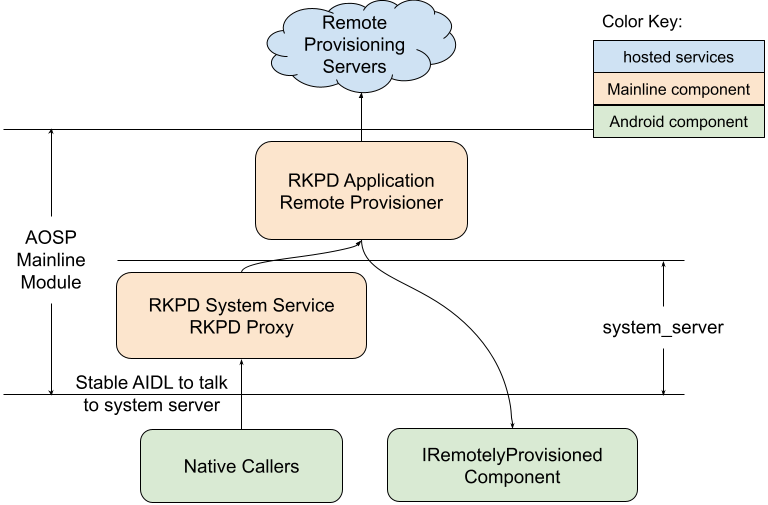
รูปที่ 2 สถาปัตยกรรมภายในของ RKP
ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสถาปัตยกรรมภายในของ RKP
RKPD Mainline APEX -
com.android.rkpd- แอป RKPD (Java)
packages/modules/RemoteKeyProvisioning/app
- ส่วนเซิร์ฟเวอร์ระบบ RKPD (Java)
packages/modules/RemoteKeyProvisioning/system-server
- แอป RKPD (Java)
อินเทอร์เฟซ/การใช้งาน HAL (Rust/C++)
IRemotelyProvisionedComponenthardware/interfaces/security/keymint
รูปแบบแพ็กเกจ
แอปพลิเคชันและฟังก์ชันอื่นๆ ของโมดูลจะรวมอยู่ในไฟล์ APEX
com.android.rkpd
การขึ้นต่อกัน
โมดูล RKP ยังคงต้องอาศัยการใช้งาน IRemotelyProvisionedComponent เพื่อให้คีย์การรับรอง
และคำขอใบรับรอง
กลยุทธ์การทดสอบ
แอปพลิเคชัน APEX เวอร์ชัน AOSP มีการทดสอบหน่วยที่ OEM สามารถเรียกใช้ได้
