تحتوي أجهزة Android على عدة أقسام أو أجزاء محدّدة من مساحة التخزين المستخدَمة لاحتواء أجزاء محدّدة من برامج الجهاز. يحتوي كل قسم على صورة قسم (ملف IMG) أو لقطة لجميع البرامج الخاصة بالقسم. يوضّح الشكل 1 تخطيط الأقسام الأساسية على الجهاز:
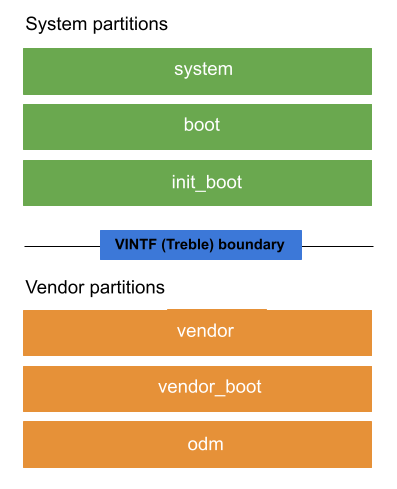
الشكل 1. تخطيط الأقسام الأساسية
يتم تصنيف الأقسام إلى ثلاث فئات:
أقسام النظام هي أقسام يتم تحديثها عند تحديث نظام التشغيل والميزات الأخرى.
systemوbootوinit_bootهي أقسام أساسية في النظام.تحتوي أقسام المورّد على رمز خاص بالجهاز والأجهزة قد لا يتم تعديله مطلقًا بعد الإصدار الأوّلي.
vendorوvendor_bootوodmهي أقسام أساسية خاصة بالمورّد.الأقسام غير القابلة للتحديث هي أقسام لا يتم تحديث محتواها أو يتم تحديثها ببيانات المستخدم.
يمكن أن يتفاعل الرمز في أقسام النظام والمورّد باستخدام واجهة ثابتة تُعرف باسم واجهة المورّد (VINTF).
أقسام النظام
في ما يلي قائمة بجميع أقسام النظام واستخداماتها:
القسم
bootيحتوي هذا القسم على ”صورة نواة عامة” (GKI). يحتوي هذا القسم أيضًا على ملف "مساحة التخزين المؤقت للذاكرة العشوائية" (ramdisk) العام في الأجهزة التي تم إطلاقها في الإصدار 12 من نظام التشغيل Android والإصدارات الأقدم. لمزيد من المعلومات حول ملف ramdisk العام، يُرجى الاطّلاع على محتويات صورة ramdisk العامة.قسم
init_boot(الإصدار 13 من نظام التشغيل Android والإصدارات الأحدث): يحتوي هذا القسم على ملف عام لـ"مساحة التخزين المؤقت للذاكرة العشوائية" (ramdisk). في نظامَي التشغيل Android 11 و12، يكون ملف ramdisk العام في القسمboot.القسم
systemيحتوي هذا القسم على صورة النظام المستخدَمة لمنتجات المصنّع الأصلي للجهاز.القسم
system_extيحتوي هذا القسم على موارد النظام ووحدات النظام الخاصة التي توسّع صورة النظام المشتركة في قسمsystem.القسم
system_dlkmيحتوي هذا القسم على وحدات صورة النواة العامة" (GKI). لمزيد من المعلومات حول هذا القسم، راجِع تنفيذ قسم وحدة GKI.القسم
productيمكن أن يحتوي هذا القسم على وحدات خاصة بالمنتج غير مجمّعة مع أي أقسام أخرى.القسم
pvmfwيخزّن هذا القسم البرامج الثابتة للأجهزة الافتراضية المحمية (pvmfw) الذي يمثّل الرمز الأول الذي يتم تنفيذه في الأجهزة الافتراضية المحمية. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على برامج ثابتة للأجهزة الافتراضية المحمية.القسم
generic_bootloaderيحتوي هذا القسم على برنامج الإقلاع العام.
أقسام المورّدين
في ما يلي قائمة بجميع أقسام المورّدين واستخداماتها:
القسم
vendor_bootيحتوي هذا القسم على رمز تشغيل خاص بالمورّد. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على مقالة أقسام التشغيل الخاصة بالمورّد.القسم
recoveryيخزّن هذا القسم صورة الاسترداد التي يتم تشغيلها أثناء عملية التحديث عبر شبكة غير سلكية (OTA). يمكن للأجهزة التي تتيح التحديثات السلسة تخزين صور الاسترداد كملف ramdisk مضمّن فيbootأو صورةinit_boot. لمزيد من المعلومات حول التحديثات بدون التوقّف عن استخدام الهاتف، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تحديثات النظام (سلسة) من النوع أ/ب.القسم
miscيتم استخدام هذا القسم من خلال قسم الاسترداد، ويبلغ حجمه 4 كيلوبايت أو أكثر.القسم
vbmetaيحتوي هذا القسم على معلومات حول ميزة "التحقّق من صحة التمهيد" لجميع الأقسام. تتحقّق هذه المعلومات من أنّ الصور المثبَّتة في كل قسم موثوق بها. لمزيد من المعلومات حول ميزة "التشغيل المُتحقّق منه"، يُرجى الاطّلاع على مقالة التشغيل المُتحقّق منه.القسم
vendorيحتوي هذا القسم على أي ملف ثنائي خاص بالمورّد ولا يمكن توزيعه على مشروع Android المفتوح المصدر (AOSP) لأنه ليس عامًا بما يكفي.القسم
vendor_dlkmيحتوي هذا القسم على وحدات نواة خاصة بالمورّد. من خلال تخزين وحدات نواة المورّد في هذا القسم بدلاً من قسمvendor، يمكنك تعديل وحدات النواة بدون تعديل قسمvendor. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على أقسام DLKM الخاصة بالمورّد والمصنّع الأصلي للجهاز.القسم
odmيحتوي هذا القسم على تعديلات المصنّع الأصلي للتصميم (ODM) على حِزم دعم اللوحات (BSP) الخاصة بمورّد المنظومة على الرقاقة (SoC). تتيح عمليات التخصيص هذه لمصنّعي الأجهزة الأصلية استبدال أو تخصيص مكونات "منظومة على رقاقة" (SoC)، وتنفيذ وحدات النواة للمكونات الخاصة باللوحة، والبرامج الخفية، والميزات الخاصة بمصنّع الأجهزة الأصلية على طبقات تجريد الأجهزة (HAL). هذا القسم اختياري. يُستخدم هذا القسم عادةً لاحتواء التخصيصات حتى تتمكّن الأجهزة من استخدام صورة مورّد واحدة لعدة وحدات حفظ مخزون للأجهزة. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على أقسام المصنّع الأصلي للجهاز.القسم
odm_dlkmهذا القسم مخصّص لتخزين وحدات نواة المصنّعين الأصليين للأجهزة (ODM). من خلال تخزين وحدات نواة ODM في هذا القسم بدلاً من قسمodm، يمكنك تعديل وحدات نواة ODM بدون تعديل قسمodm. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على أقسام DLKM الخاصة بالمورّد والمصنّع الأصلي للجهاز.القسم
radioيحتوي هذا القسم على صورة الراديو ولا يكون مطلوبًا إلا للأجهزة التي تتضمّن راديو مع برنامج خاص بالراديو في قسم مخصّص.
الأقسام غير القابلة للتعديل
في ما يلي قائمة بجميع الأقسام غير القابلة للتعديل واستخداماتها:
القسم
cacheيحتوي هذا القسم على بيانات مؤقتة وهو اختياري إذا كان جهازك يستخدم التحديثات السلسة. لا يجب أن يكون هذا القسم قابلاً للكتابة من برنامج الإقلاع، ولكن يجب أن يكون قابلاً للمحو. يعتمد حجم القسم على نوع الجهاز ومقدار المساحة المتوفّرة علىuserdata، وعادةً ما تكون مساحة تتراوح بين 50 و100 ميغابايت كافية.القسم
userdataيحتوي هذا القسم على التطبيقات والبيانات التي ثبّتها المستخدم، بما في ذلك بيانات التخصيص.القسم
metadataإذا كان جهازك يستخدم تشفير البيانات الوصفية، يحتوي هذا القسم على مفتاح تشفير البيانات الوصفية. يجب أن يكون حجم هذا القسم 16 ميغابايت أو أكثر، وألا يكون مشفّرًا، وألا يتم أخذ لقطة من بياناته. ويتم محو هذا القسم عند إعادة ضبط الجهاز على الإعدادات الأصلية.
قواعد واقتراحات تعديل الأقسام
ننصحك بتحديث جميع أقسام النظام كوحدة واحدة وجميع أقسام المورّد كوحدة أخرى. من خلال تعديل مجموعة الأقسام ككل، يمكنك إجراء اختبار للتحقّق من أنّ الواجهات بين الصور في كل قسم تظل ثابتة.
بغض النظر عن طريقة تعديل الأقسام، يجب تعديل الأقسام التالية بسبب التبعيات المرتبطة بإحكام وعدم توفّر واجهات برمجة تطبيقات ثابتة:
- القسمان
bootوsystem_dlkm - الأقسام
init_bootوsystemوsystem_extوproduct
الأقسام الديناميكية
يمكن للأجهزة التي تعمل بنظام التشغيل Android 11 والإصدارات الأحدث أن تتوافق مع الأقسام الديناميكية، وهي نظام تقسيم لمساحة المستخدم في Android يتيح لك إنشاء الأقسام أو تغيير حجمها أو إزالتها أثناء إجراء التحديثات عبر الهواء (OTA). لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على الأقسام الديناميكية.
خيارات منتج Soong
يستخدم نظام الإنشاء Soong صيغ الصور لتقسيم تبعيات الإنشاء. يمكن للوحدات الأصلية (/build/soong/cc) تغيير وحدات عمليات النظام إلى نوع أساسي، ووحدات عمليات المورّد إلى نوع المورّد، ولا يمكن لوحدة في أحد أنواع الصور الربط بوحدات أخرى في نوع صورة مختلف.
في نظام التشغيل Android 12 أو الإصدارات الأحدث، ينشئ أحد وحدات النظام التي تتضمّن vendor_available: true صيغة خاصة بالمورّد بالإضافة إلى الصيغة الأساسية. لإنشاء خيار منتج، يجب تحديد السمة product_available: true. بعض مكتبات VNDK التي لا تتضمّن product_available: true غير متاحة لوحدات المنتج.
