جریان های خروجی
زیرسیستم دوربین فقط بر روی خط لوله مبتنی بر ANativeWindow برای همه وضوحها و فرمتهای خروجی کار میکند. چندین جریان را می توان در یک زمان پیکربندی کرد تا یک فریم را به اهداف زیادی مانند GPU، رمزگذار ویدیو، RenderScript یا بافرهای قابل مشاهده برنامه (RAW Bayer، بافرهای YUV پردازش شده، یا بافرهای رمزگذاری شده با JPEG) ارسال کند.
به عنوان یک بهینهسازی، این جریانهای خروجی باید زودتر از موعد پیکربندی شوند و ممکن است تعداد محدودی همزمان وجود داشته باشد. این امکان پیشتخصیص بافرهای حافظه و پیکربندی سختافزار دوربین را فراهم میکند، به طوری که وقتی درخواستها با خطوط لوله خروجی متعدد یا متفاوت ارائه میشوند، تاخیر یا تاخیری در انجام درخواست وجود نداشته باشد.
برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد ترکیبهای خروجی جریان تضمین شده که به سطح سختافزار پشتیبانیشده بستگی دارد، به createCaptureSession() مراجعه کنید.
برداشت
برش آرایه پیکسل کامل (برای زوم دیجیتال و سایر موارد استفاده که در آن FOV کوچکتر مطلوب است) از طریق تنظیم ANDROID_SCALER_CROP_REGION اطلاع رسانی می شود. این یک تنظیم برای هر درخواست است و میتواند بر اساس هر درخواست تغییر کند، که برای پیادهسازی بزرگنمایی دیجیتال روان بسیار مهم است.
منطقه به عنوان یک مستطیل (x، y، عرض، ارتفاع) تعریف می شود که (x، y) گوشه سمت چپ بالای مستطیل را توصیف می کند. مستطیل بر روی سیستم مختصات آرایه پیکسل فعال حسگر تعریف شده است که (0,0) پیکسل بالای سمت چپ آرایه پیکسل فعال است. بنابراین، عرض و ارتفاع نمیتواند بزرگتر از ابعاد گزارششده در قسمت اطلاعات ثابت ANDROID_SENSOR_ACTIVE_PIXEL_ARRAY باشد. حداقل عرض و ارتفاع مجاز توسط HAL از طریق فیلد اطلاعات ثابت ANDROID_SCALER_MAX_DIGITAL_ZOOM گزارش می شود که حداکثر ضریب بزرگنمایی پشتیبانی شده را توصیف می کند. بنابراین، حداقل عرض و ارتفاع منطقه محصول عبارتند از:
{width, height} =
{ floor(ANDROID_SENSOR_ACTIVE_PIXEL_ARRAY[0] /
ANDROID_SCALER_MAX_DIGITAL_ZOOM),
floor(ANDROID_SENSOR_ACTIVE_PIXEL_ARRAY[1] /
ANDROID_SCALER_MAX_DIGITAL_ZOOM) }
اگر منطقه محصول نیاز به برآورده کردن الزامات خاص داشته باشد (برای مثال، باید از مختصات زوج شروع شود، و عرض/ارتفاع آن باید یکنواخت باشد)، HAL باید گرد کردن لازم را انجام دهد و منطقه برش نهایی مورد استفاده در فراداده نتیجه خروجی را بنویسد. به طور مشابه، اگر HAL تثبیتکننده ویدیو را پیادهسازی کند، باید ناحیه برش نتیجه را برای توصیف منطقهای که واقعاً در خروجی پس از اعمال تثبیتکننده ویدیو گنجانده شده است، تنظیم کند. به طور کلی، برنامه ای که از دوربین استفاده می کند باید بتواند بر اساس ناحیه برش، ابعاد حسگر تصویر و فاصله کانونی لنز، میدان دیدی را که دریافت می کند، تعیین کند.
از آنجایی که منطقه برش برای همه جریانها اعمال میشود، که ممکن است نسبتهای ابعادی متفاوتی نسبت به منطقه برش داشته باشند، منطقه حسگر دقیق استفادهشده برای هر جریان ممکن است کوچکتر از منطقه برداشت باشد. به طور خاص، هر جریان باید پیکسلهای مربعی و نسبت ابعاد آن را با برش بیشتر منطقه برش تعریفشده حفظ کند. اگر نسبت ابعاد جریان بیشتر از ناحیه برش باشد، جریان باید بیشتر به صورت عمودی برش داده شود و اگر نسبت ابعاد جریان باریکتر از منطقه برش باشد، جریان باید بیشتر به صورت افقی برش داده شود.
در همه موارد، محصول جریان باید در مرکز منطقه کامل محصول باشد، و هر جریان فقط به صورت افقی یا عمودی نسبت به منطقه کامل محصول برش داده می شود، نه هر دو.
برای مثال، اگر دو جریان تعریف شده باشد، یک جریان 640x480 (وجهه 4:3) و یک جریان 1280x720 (وجهه 16:9)، در زیر مناطق خروجی مورد انتظار برای هر جریان را برای چند منطقه برش نمونه، روی یک آرایه سنسور 3 مگاپیکسلی (2000 x 1500 پیکسل) فرضی نشان میدهد.
منطقه برش: (500، 375، 1000، 750) (نسبت تصویر 4:3)
برش جریان 640x480: (500، 375، 1000، 750) (برابر با منطقه محصول)
برش جریان 1280x720: (500، 469، 1000، 562)
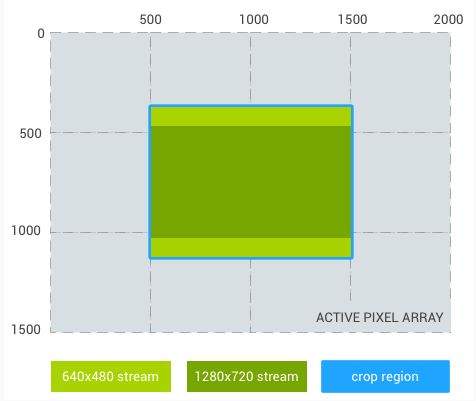
شکل 1. نسبت تصویر 4:3
منطقه برش: (500، 375، 1333، 750) (نسبت تصویر 16:9)
برش جریان 640x480: (666، 375، 1000، 750)
برش جریان 1280x720: (500، 375، 1333، 750) (برابر با منطقه محصول)
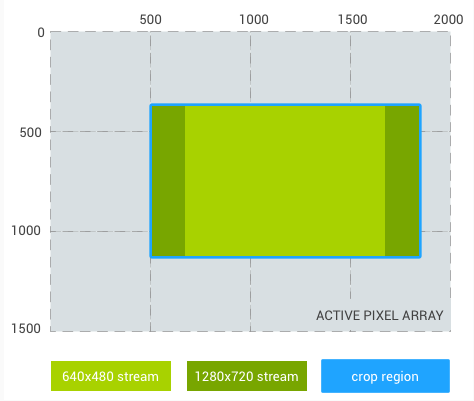
شکل 2. نسبت تصویر 16:9
منطقه برش: (500، 375، 750، 750) (نسبت تصویر 1:1)
برش جریانی 640x480: (500، 469، 750، 562)
برش جریان 1280x720: (500، 543، 750، 414)
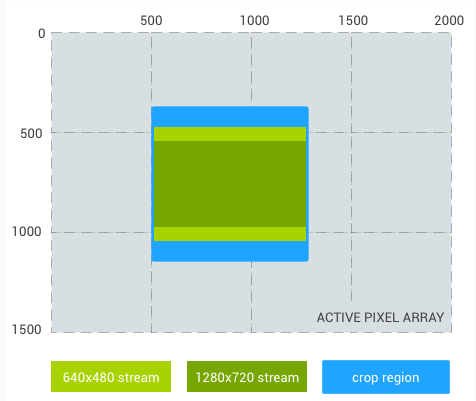
شکل 3. نسبت تصویر 1:1
و یک مثال آخر، یک جریان با نسبت ابعاد مربعی 1024x1024 به جای جریان 480p:
منطقه برش: (500، 375، 1000، 750) (نسبت تصویر 4:3)
برش جریانی 1024x1024: (625، 375، 750، 750)
برش جریان 1280x720: (500، 469، 1000، 562)
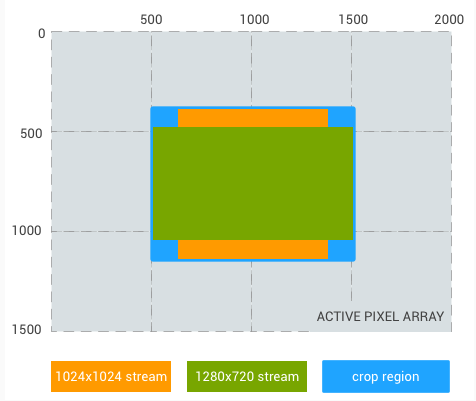
شکل 4. نسبت تصویر 4:3، مربع
پردازش مجدد
پشتیبانی اضافی برای فایل های تصویر خام با پشتیبانی از پردازش مجدد داده های RAW Bayer ارائه می شود. این پشتیبانی به خط لوله دوربین اجازه میدهد تا یک بافر و ابرداده RAW قبلاً گرفته شده را پردازش کند (کل فریمی که قبلاً ضبط شده است) تا خروجی YUV یا JPEG رندر شده جدیدی تولید کند.
بزرگنمایی ضربه بزنید؛
برای دستگاههای دارای Android 11 یا بالاتر، یک برنامه میتواند از زوم دوربین (دیجیتال و اپتیکال) از طریق تنظیم ANDROID_CONTROL_ZOOM_RATIO استفاده کند.
نسبت بزرگنمایی به عنوان یک ضریب ممیز شناور تعریف می شود. بهجای استفاده از ANDROID_SCALER_CROP_REGION برای برش و بزرگنمایی، یک برنامه میتواند از ANDROID_CONTROL_ZOOM_RATIO برای کنترل سطح بزرگنمایی استفاده کند و از ANDROID_SCALER_CROP_REGION برای برش افقی و عمودی برای دستیابی به نسبتهایی متفاوت از حسگر دوربین اصلی استفاده کند.
یک سیستم چند دوربینی ممکن است حاوی بیش از یک لنز با فواصل کانونی متفاوت باشد و کاربر می تواند با جابجایی بین لنزها از زوم اپتیکال استفاده کند. استفاده از ANDROID_CONTROL_ZOOM_RATIO در سناریوهای زیر مزایایی دارد:
- بزرگنمایی از یک لنز واید به یک لنز تله فوتو: نسبت ممیز شناور در مقایسه با مقادیر صحیح
ANDROID_SCALER_CROP_REGIONدقت بهتری را ارائه می دهد. - بزرگنمایی از یک لنز عریض به یک لنز فوق عریض:
ANDROID_CONTROL_ZOOM_RATIOاز بزرگنمایی (<1.0f) پشتیبانی می کند در حالی کهANDROID_SCALER_CROP_REGIONاین کار را نمی کند.
نسبت بزرگنمایی: 2.0; 1/4 میدان دید اصلی
منطقه برش: (0، 0، 2000، 1500) (نسبت تصویر 4:3)
برش جریان 640x480: (0، 0، 2000، 1500) (برابر با منطقه برش)
برش جریان 1280x720: (0، 187، 2000، 1125)
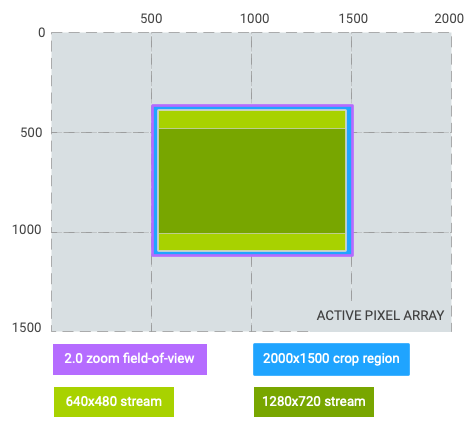
شکل 5. زوم 2.0، نسبت تصویر 4:3
نسبت بزرگنمایی: 2.0; 1/4 میدان دید اصلی
منطقه برش: (0، 187، 2000، 1125) (نسبت تصویر 16:9)
برش جریانی 640x480: (250، 187، 1500، 1125) (با جعبه ستونی)
برش جریان 1280x720: (0، 187، 2000، 1125) (برابر با منطقه برش)
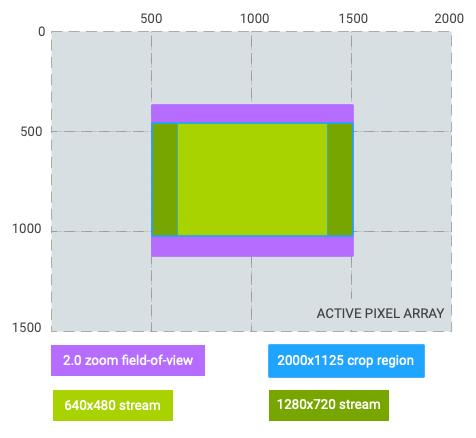
شکل 6. زوم 2.0، نسبت تصویر 16:9
نسبت بزرگنمایی: 0.5; 4 برابر میدان دید اصلی (تغییر از لنز واید به لنز فوق عریض)
منطقه برش: (250، 0، 1500، 1500) (نسبت تصویر 1:1)
برش جریانی 640x480: (250، 187، 1500، 1125) (با جعبه نامه)
برش جریانی 1280x720: (250، 328، 1500، 844) (با جعبه نامه)
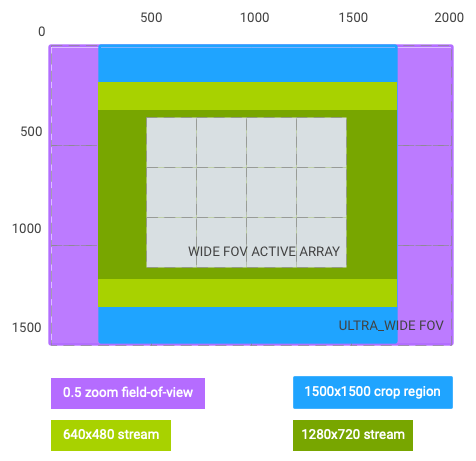
شکل 7. زوم 0.5، نسبت تصویر 1:1
همانطور که از نمودارهای بالا مشاهده می شود، سیستم مختصات ناحیه برش به میدان دید موثر پس از زوم تغییر می کند و با مستطیل با ابعاد زیر نشان داده می شود: ( 0 ، 0 ، activeArrayWith ، activeArrayHeight ). همین امر در مورد مناطق و چهره های AE/AWB/AF نیز صدق می کند. این تغییر سیستم مختصات برای ضبط RAW و ابردادههای مرتبط با آن مانند intrinsicCalibration و lensShadingMap اعمال نمیشود.
با استفاده از همان مثال فرضی بالا، و با فرض اینکه جریان خروجی #1 (640x480) جریان منظره یاب است، زوم 2.0 برابری را می توان به یکی از دو روش به دست آورد:
-
zoomRatio = 2.0،scaler.cropRegion = (0, 0, 2000, 1500) -
zoomRatio = 1.0(پیشفرض)،scaler.cropRegion = (500, 375, 1000, 750)
برای اینکه برنامهای که android.control.aeRegions به عنوان یک چهارم سمت چپ بالای میدان دید نمایاب تنظیم کند، android.control.aeRegions را روی (0, 0, 1000, 750) با android.control.zoomRatio روی 2.0 تنظیم کنید. از طرف دیگر، این برنامه میتواند android.control.aeRegions به منطقه معادل (500, 375, 1000, 750) برای android.control.zoomRatio 1.0 تنظیم کند.

