
Android provides a default Bluetooth stack that supports both Classic Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). Using Bluetooth, Android devices can create personal area networks to send and receive data with nearby Bluetooth devices.
In Android 4.3 and higher, the Android Bluetooth stack provides the ability to implement BLE. To fully use the BLE APIs, follow the Android Bluetooth HCI Requirements. Android devices with a qualified chipset can implement either Classic Bluetooth or both Classic Bluetooth and BLE. BLE isn't backward compatible with older Bluetooth chipsets.
In Android 8.0, the Bluetooth stack is fully qualified for Bluetooth 5. To use available Bluetooth 5 features, the device needs to have a Bluetooth 5 qualified chipset.
Android architecture
A Bluetooth app communicates with the Bluetooth process through Binder. The Bluetooth process uses Java Native Interface (JNI) to communicate with the Bluetooth stack and provides developers with access to various Bluetooth profiles. This diagram shows the general structure of the Bluetooth stack:
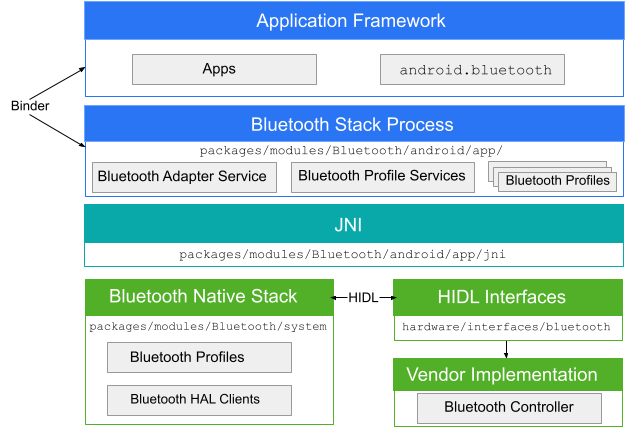
Figure 1. Android Bluetooth architecture.
- app framework
- At the app framework level is app code, which uses the
android.bluetoothAPIs to interact with the Bluetooth hardware. Internally, this code calls the Bluetooth process through the Binder IPC mechanism. - Bluetooth app
- The Bluetooth app, located in
packages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app, is packaged as an Android app and implements the Bluetooth profiles at the Android framework layer. This app calls into the Bluetooth stack through JNI. - JNI
- The JNI code associated with
android.bluetoothis located inpackages/modules/Bluetooth/android/app/jni. The JNI code calls into the Bluetooth stack when certain Bluetooth operations occur, such as when devices are discovered. - Bluetooth stack
- The default Bluetooth stack is provided in AOSP and is located in
packages/modules/Bluetooth/system. The stack implements the generic Bluetooth HAL and customizes it with extensions and configuration changes. - vendor implementation
- Vendor devices interact with the Bluetooth stack using the HAL interface definition language (HIDL).
HIDL
HIDL defines the interface between the
Bluetooth stack and the vendor implementation. To generate the Bluetooth
HIDL files, pass the Bluetooth interface files into the HIDL generation
tool. The interface files are located in
hardware/interfaces/bluetooth.
Bluetooth stack development
The Android Bluetooth stack is a fully qualified Bluetooth stack. The qualification listing is on the Bluetooth SIG website (requires sign-in) under QDID 169365.
The core Bluetooth stack resides in
packages/modules/Bluetooth.
Development happens in AOSP, and contributions are welcome.
