การประเมินฮาร์ดแวร์เกี่ยวข้องกับการกำหนดเอฟเฟกต์การสัมผัส 3 รายการ โดยมีป้ายกำกับเป็นเอฟเฟกต์ 1, 2 และ 3 สำหรับการประเมินนี้โดยเฉพาะ
เอฟเฟกต์ 1: ค่าคงที่แบบสัมผัสสั้นๆ ที่กำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้า
ค่าคงที่
VibrationEffect.EFFECT_CLICK
คือผลกระทบพื้นฐานหรือตัวหารร่วมในการแมป HAL กับ API
ที่ระบุไว้ในแมปค่าคงที่ระหว่าง HAL กับ API
โดยจะแมปกับเอฟเฟกต์ที่ใช้บ่อยที่สุดอย่าง HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_PRESS
การประเมินเอฟเฟกต์นี้จะช่วยพิจารณาความพร้อมของอุปกรณ์เป้าหมายสำหรับการสั่นที่ชัดเจน
เอฟเฟกต์ 2: เอฟเฟกต์การสั่นที่กำหนดเองแบบสั้น
ค่าคงที่
VibrationEffect.createOneShot(20,255)
ใช้สำหรับเอฟเฟกต์การสัมผัสที่กำหนดเอง สำหรับแรงกระตุ้นแบบกำหนดเองแบบสั้นๆ แบบครั้งเดียว
20 มิลลิวินาทีคือเกณฑ์สูงสุดที่แนะนำในการกำหนดระยะเวลา เราไม่แนะนำให้ใช้แรงกระตุ้นเดียวที่ยาวกว่า 20 มิลลิวินาที เนื่องจากจะรับรู้ได้ว่าเป็นการสั่นแบบหึ่งๆ
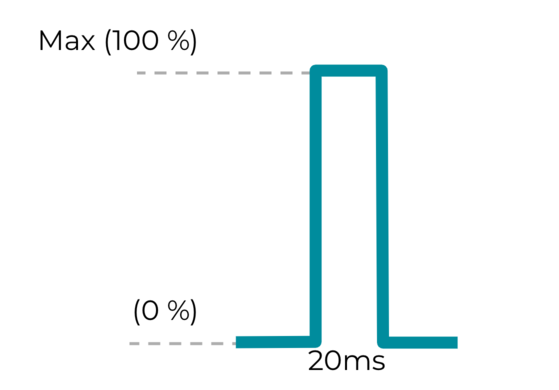
รูปที่ 19 เอฟเฟกต์การสั่นแบบกำหนดเองสั้นๆ
เอฟเฟกต์ 3: เอฟเฟกต์การสั่นแบบกำหนดเองยาวที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงแอมพลิจูด
ค่าคงที่ VibrationEffect.createWaveform(timings[], amplitudes[], int
repeat)
ใช้สำหรับเอฟเฟกต์ที่กำหนดเองแบบยาวที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงแอมพลิจูด ความสามารถในการ
สร้างแอมพลิจูดที่แตกต่างกันสำหรับเอฟเฟกต์การสั่นที่กำหนดเองเป็นตัวบ่งชี้อย่างหนึ่งในการ
ประเมินความสามารถของอุปกรณ์สำหรับการสั่นที่สมบูรณ์ timings []และamplitudes []ที่แนะนำคือ{500, 500}และ{128, 255}
ตามลำดับ ซึ่งแสดงแนวโน้มที่เพิ่มขึ้นของแอมพลิจูดจาก 50% เป็น 100%
โดยมีอัตราการสุ่มตัวอย่าง 500 มิลลิวินาที
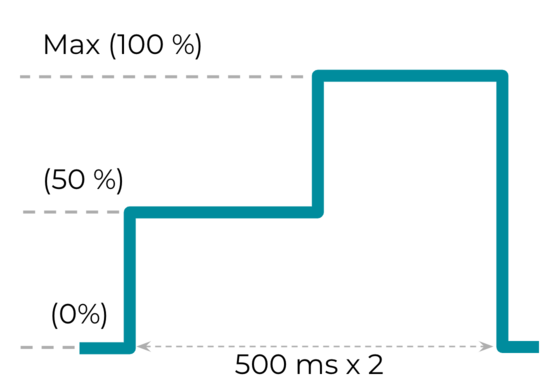
รูปที่ 20 เอฟเฟกต์การสั่นแบบกำหนดเองที่ยาวพร้อมการเปลี่ยนแปลงแอมพลิจูด
หากต้องการตรวจสอบความสามารถของฮาร์ดแวร์ในการควบคุมแอมพลิจูดสำหรับเอฟเฟกต์ 3 ให้ใช้วิธี
Vibrator.hasAmplitudeControl()
ผลลัพธ์ต้องเป็น true เพื่อดำเนินการ
VibrationEffect.createWaveform
โดยมีแอมพลิจูดที่แตกต่างกันตามที่ตั้งใจไว้
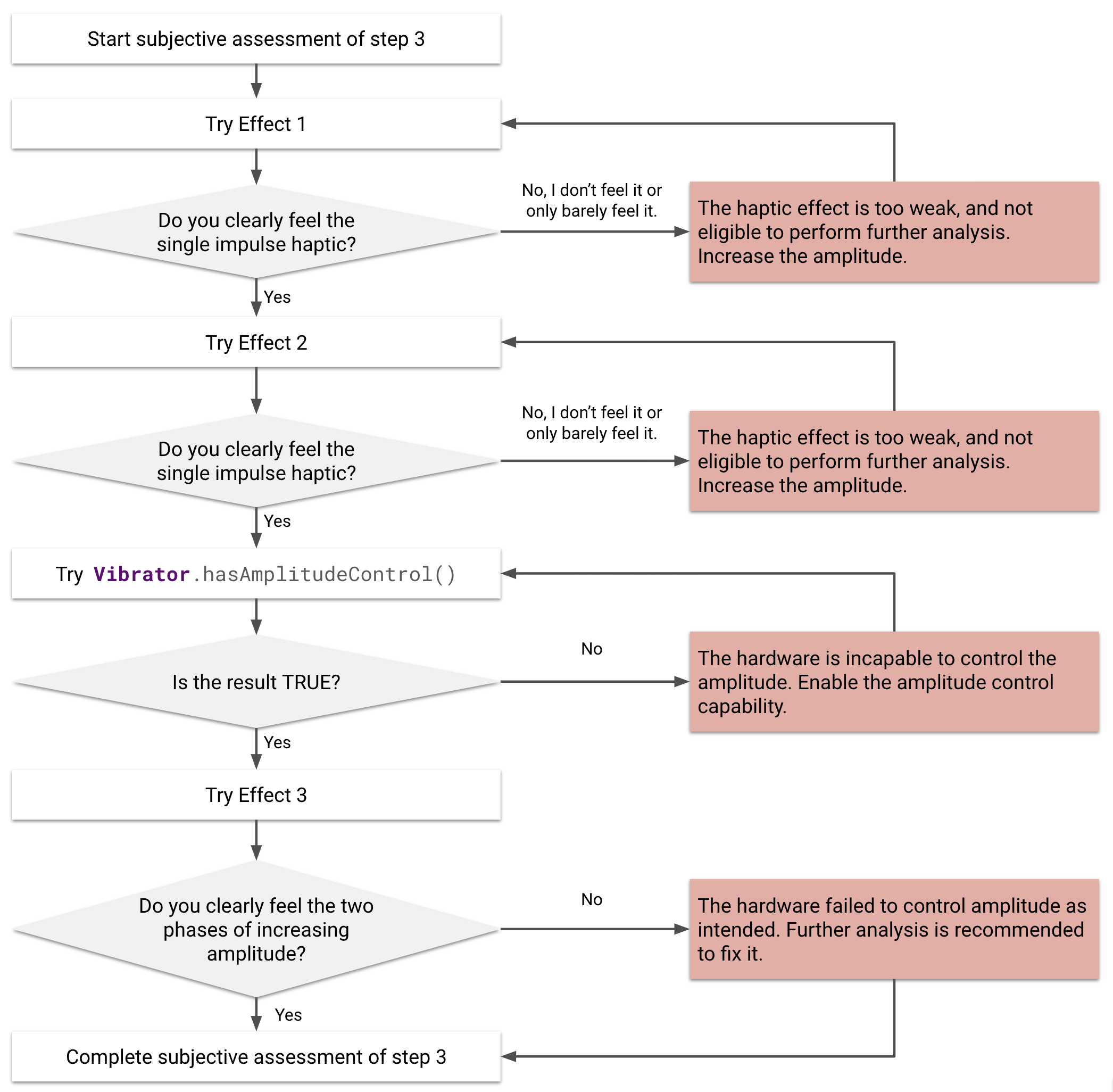
รูปที่ 21 การประเมินผลกระทบแบบสัมผัส 1, 2 และ 3 โดยผู้เข้าร่วม
ทำการประเมินตามความคิดเห็นส่วนตัว
หากต้องการตรวจสอบความสอดคล้องอย่างรวดเร็ว ให้ทำการประเมินเชิงอัตวิสัยก่อน เป้าหมายของการประเมินเชิงอัตวิสัยคือการสังเกตแอมพลิจูดของเอฟเฟกต์การสัมผัสเพื่อพิจารณาว่าอุปกรณ์สามารถสร้างการสัมผัสที่มีแอมพลิจูดที่มนุษย์รับรู้ได้หรือไม่
คำถามที่เฉพาะเจาะจงซึ่งมีโครงสร้างตามแนวคิดนี้มีลักษณะดังนี้ อุปกรณ์สร้างเอฟเฟกต์การสั่นที่ผู้ใช้รับรู้ได้ตามที่คาดไว้ได้ไหม การตอบคำถามนี้จะช่วยให้คุณหลีกเลี่ยงการสั่นที่ล้มเหลว ซึ่งรวมถึงการสั่นที่เบามากจนผู้ใช้ไม่รู้สึก หรือการสั่นที่ไม่ตั้งใจซึ่งรูปคลื่นไม่สร้าง รูปแบบตามที่ต้องการ
ทำการประเมินขั้นสูง
ขอแนะนำอย่างยิ่งให้ทำการประเมินคุณภาพขั้นสูง การประเมินคุณภาพขั้นสูงจะระบุลักษณะของแอตทริบิวต์ที่วัดค่าได้ของเอฟเฟกต์การสัมผัสเพื่อใช้การสัมผัสคุณภาพ เมื่อเสร็จแล้ว ผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ควรจะสามารถ วินิจฉัยสถานะการสั่นปัจจุบันได้ ซึ่งหมายความว่าผู้ผลิตสามารถตั้งเป้าหมายเพื่อปรับปรุง คุณภาพโดยรวมได้ ดูการประเมิน ฮาร์ดแวร์
