يتضمّن تقييم الأجهزة تحديد ثلاثة تأثيرات لمسية، تحمل التصنيفات "التأثير 1" و"التأثير 2" و"التأثير 3" لهذا التقييم المحدّد.
التأثير 1: ثوابت لمسية قصيرة محدّدة مسبقًا
الثابت
VibrationEffect.EFFECT_CLICK
هو التأثير الأساسي أو القاسم المشترك في عملية الربط بين HAL وAPI
الموضّحة في ربط الثوابت بين HAL وAPI
. يتم ربطها بالتأثير الأكثر استخدامًا، HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_PRESS
. يساعد تقييم هذا التأثير في تحديد مدى استعداد الجهاز المستهدف لتلقّي اللمسات الواضحة.
التأثير 2: تأثير لمسي مخصّص قصير
الثابت
VibrationEffect.createOneShot(20,255)
مخصّص للمؤثرات الحسية المخصّصة. بالنسبة إلى النبضات المخصّصة القصيرة والفردية،
ننصح بأن يكون الحدّ الأقصى لمدة النبضة 20 مللي ثانية. لا يُنصح باستخدام نبضة واحدة تزيد مدتها على 20 مللي ثانية لأنّها تُعتبر اهتزازًا مزعجًا.
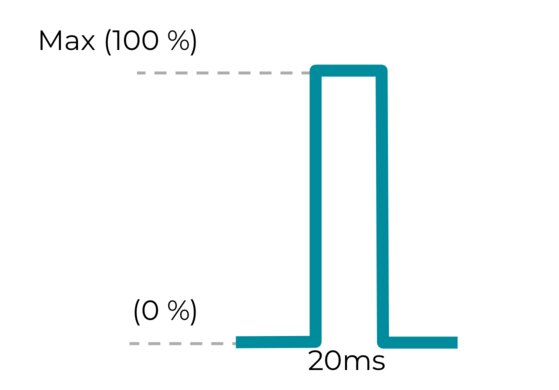
الشكل 19. تأثير لمسي مخصّص قصير
التأثير 3: تأثير لمس مخصّص طويل مع اختلاف في السعة
الثابت VibrationEffect.createWaveform(timings[], amplitudes[], int
repeat)
مخصّص للتأثيرات المخصّصة الطويلة التي تتضمّن اختلافًا في السعة. تُعد القدرة على إنتاج سعات مختلفة للتأثيرات اللمسية المخصّصة أحد المؤشرات التي يتم الاستناد إليها لتقييم إمكانات الجهاز في ما يتعلق بالتأثيرات اللمسية
الغنية. timings [] وamplitudes [] هما {500, 500} و{128, 255} على التوالي، ما يشير إلى اتجاه متزايد في السعة من% 50 إلى %100، مع معدّل أخذ عينات يبلغ 500 مللي ثانية.
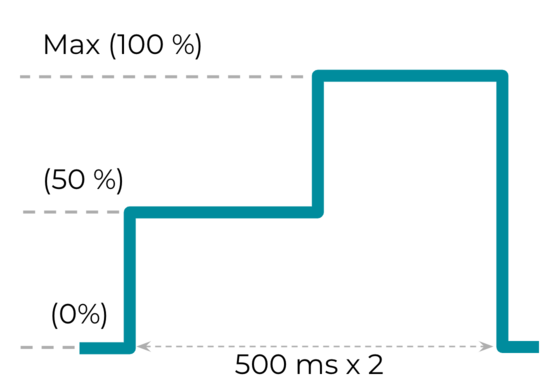
الشكل 20. تأثير لمسي مخصّص طويل مع اختلاف في السعة
للتحقّق من إمكانات الأجهزة المتوافقة مع التحكّم في مستوى الصوت الخاص بالتأثير 3، استخدِم طريقة
Vibrator.hasAmplitudeControl(). يجب أن تكون النتيجة true لتنفيذ
VibrationEffect.createWaveform
بسعة متغيرة على النحو المطلوب.
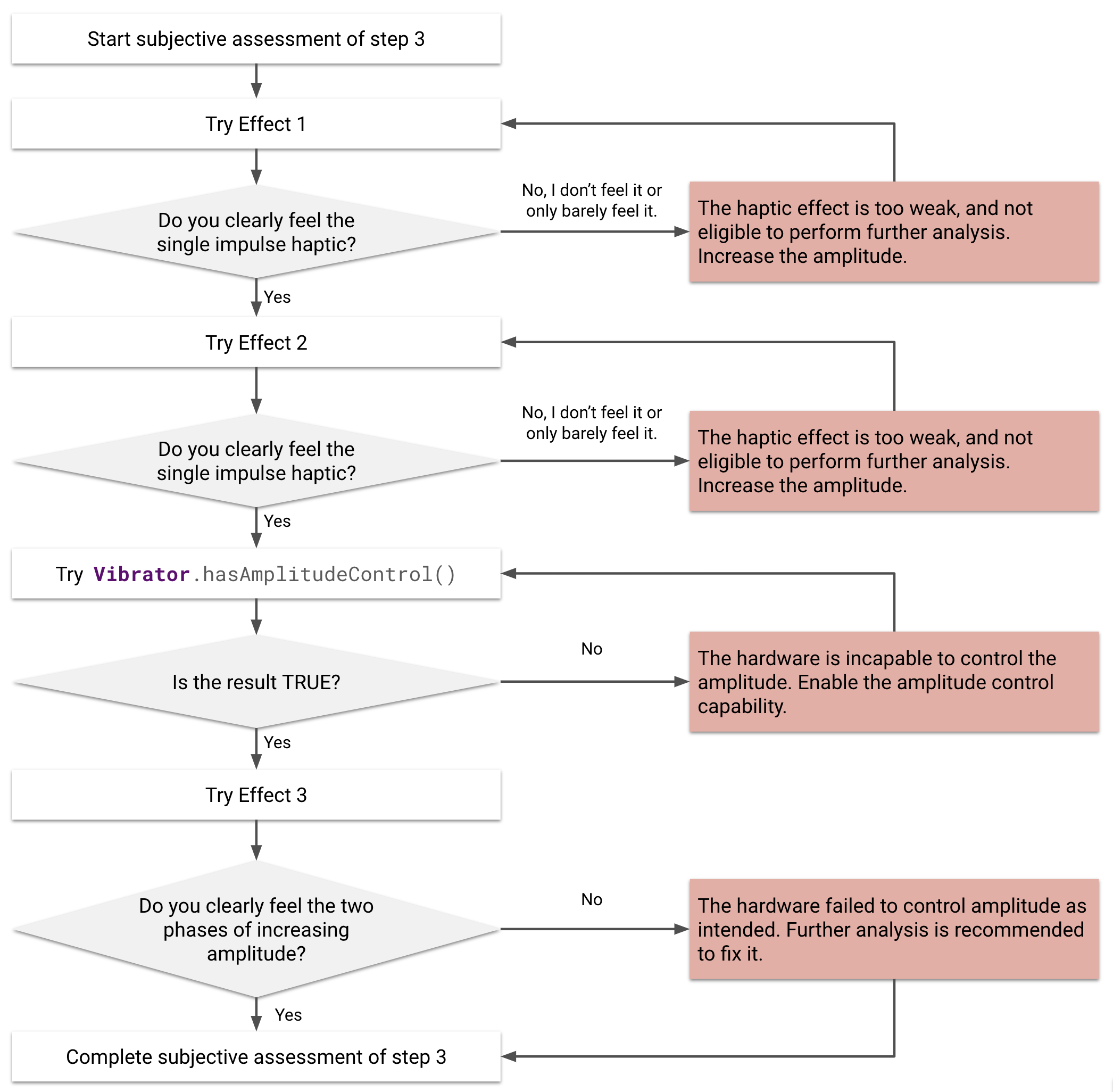
الشكل 21. التقييم الذاتي للتأثير اللمسي 1 و2 و3
إجراء تقييم ذاتي
لإجراء فحص سريع للتناسق، عليك أولاً إجراء تقييم ذاتي. والهدف من التقييم الذاتي هو مراقبة مدى قوة التأثيرات الحسية لتحديد ما إذا كان الجهاز يمكنه إنشاء تأثيرات حسية بقوة يمكن أن يدركها الإنسان.
يبدو السؤال المحدّد الذي تم تصميمه حول هذه الفكرة على النحو التالي: هل يمكن للجهاز أن ينتج تأثيرات لمسية محسوسة للمستخدمين على النحو المتوقّع؟ تساعدك الإجابة عن هذا السؤال في تجنُّب اللمسات غير الناجحة، بما في ذلك اللمسات غير المحسوسة التي لا يشعر بها المستخدمون، أو اللمسات غير المقصودة التي لا تنتج فيها الأشكال الموجية أنماطًا كما هو مطلوب.
إجراء تقييم متقدّم
ننصح بشدة بإجراء تقييمات متقدّمة للجودة. تحدّد تقييمات الجودة المتقدّمة السمات القابلة للقياس الخاصة بالتأثيرات اللمسية من أجل تنفيذ تأثيرات لمسية عالية الجودة. عند الانتهاء، يجب أن تتمكّن الشركات المصنّعة للأجهزة من تشخيص حالة ردود الفعل اللمسية الحالية، ما يعني أنّه يمكنها وضع أهداف لتحسين الجودة الإجمالية. يُرجى الاطّلاع على تقييم الأجهزة.
