Android 7.0에는 앱에서 실수로 자체 라이브러리 대신 플랫폼 라이브러리를 사용하게 되었을 때 네이티브 라이브러리에서 내부 API 가시성을 제한하고 상황을 해결할 수 있도록 하기 위한 네임스페이스가 도입되었습니다. 애플리케이션 관련 변경사항은 Android 개발자 블로그 게시물, Android 7.0의 비공개 C/C++ 기호 제한을 통한 안정성 개선을 참조하세요.
아키텍처
Android 7.0 이상에서는 시스템 라이브러리가 앱 라이브러리와 구분됩니다.
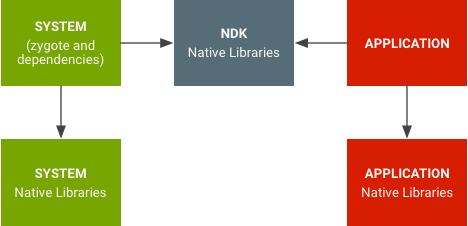
그림 1. 네이티브 라이브러리의 네임스페이스
네이티브 라이브러리의 네임스페이스는 OpenSSL의 경우처럼 앱이 비공개 플랫폼 네이티브 API를 사용하지 못하게 합니다. 또한 libpng에서 볼 수 있는 것처럼 앱이 실수로 자체 라이브러리 대신 플랫폼 라이브러리를 사용하게 되는 상황을 없앱니다. 즉, 앱 라이브러리가 실수로 시스템 라이브러리를 사용하는 경우나 그 반대의 경우가 발생하기 어려워집니다.
부가적인 네이티브 라이브러리 추가
표준 공개 네이티브 라이브러리 외에도 실리콘 공급업체(Android 7.0부터) 및 기기 제조업체(Android 9부터)는 원하는 경우 앱에서 액세스 가능한 추가적인 네이티브 라이브러리를 제공할 수 있으며, 이를 위해 네이티브 라이브러리를 각각의 라이브러리 폴더 아래에 배치하고 이를 .txt 파일에 명시적으로 나열합니다.
라이브러리 폴더는 다음과 같습니다.
- 실리콘 공급업체의 라이브러리를 위한
/vendor/lib(32비트용)과/vendor/lib64(64비트용) - 기기 제조업체의 라이브러리를 위한
/system/lib(32비트용)과/system/lib64(64비트용)
.txt 파일은 다음과 같습니다.
- 실리콘 공급업체의 라이브러리를 위한
/vendor/etc/public.libraries.txt - 기기 제조업체의 라이브러리를 위한
/system/etc/public.libraries-COMPANYNAME.txt. 여기서COMPANYNAME은 제조업체 이름을 나타냅니다(예:awesome.company).COMPANYNAME은[A-Za-z0-9_.-]+, 즉 영숫자 문자, _, .(점), -와 일치해야 합니다. 일부 라이브러리가 외부 솔루션 제공업체의 라이브러리라면 기기에 이러한 .txt 파일이 여러 개 있을 수 있습니다.
기기 제조업체에서 공개한 system 파티션의 네이티브 라이브러리 이름은 lib*COMPANYNAME.so로 지정해야 합니다(예: libFoo.awesome.company.so).
즉, 회사 이름 접미사가 없는 libFoo.so는 공개하면 안 됩니다.
라이브러리 파일 이름의 COMPANYNAME은 라이브러리 이름이 나열되는 txt 파일 이름의 COMPANYNAME과 일치해야 합니다.
AOSP의 일부인 네이티브 라이브러리는 공개해서는 안 됩니다(기본적으로 공개인 표준 공개 네이티브 라이브러리는 예외). 실리콘 공급업체 또는 기기 제조업체에서 추가한 라이브러리만 앱에서 액세스할 수 있습니다.
Android 8.0부터는 공급업체 공개 라이브러리에 다음과 같은 추가적인 제한사항 및 필수 설정이 적용됩니다.
- 앱에서 액세스할 수 있도록 공급업체의 네이티브 라이브러리 라벨을 제대로 지정해야 합니다. 서드 파티 앱을 비롯하여 앱에서 액세스가 필요하면 라이브러리는 다음과 같이 공급업체별
file_contexts파일에서same_process_hal_file로 라벨이 지정되어야 합니다./vendor/lib(64)?/libnative.so u:object_r:same_process_hal_file:s0
여기서libnative.so는 네이티브 라이브러리의 이름입니다. - 라이브러리는 VNDK-SP 및 LLNDK 라이브러리 이외의 시스템 라이브러리에 종속 항목을 통해 직접적으로 또는 간접적으로 종속되면 안 됩니다. VNDK-SP 및 LLNDK 라이브러리 목록은
development/vndk/tools/definition/tool/datasets/eligible-list-<version>-release.csv에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
비공개 네이티브 라이브러리를 사용하지 않도록 앱을 업데이트
이 기능은 SDK 버전 24 이상을 타겟팅하는 애플리케이션에만 이전 버전과의 호환성을 위해 사용 설정됩니다. 표 1. 앱이 비공개 네이티브 라이브러리에 링크된 경우 예상 결과를 참조하세요. 앱에서 액세스 가능한 Android 네이티브 라이브러리(공개 네이티브 라이브러리라고도 알려짐) 목록은 CDD 섹션 3.1.1에 나열되어 있습니다. 24 이상을 타겟팅하고 비공개 라이브러리를 사용하는 앱을 업데이트해야 합니다. 자세한 내용은 플랫폼 라이브러리에 연결되는 NDK 앱을 참조하세요.
네이티브 라이브러리 종속 항목을 지정하도록 앱을 업데이트
SDK 버전 31(Android 12) 이상을 타겟팅하는 애플리케이션은 앱 매니페스트에서 <uses-native-library> 태그를 사용하여 네이티브 공유 라이브러리 종속 항목을 명시적으로 지정해야 합니다. 요청된 라이브러리의 일부라도 기기에 존재하지 않으면 앱이 설치되지 않습니다. 앱이 설치되면 앱에서 요청한 네이티브 공유 라이브러리만 제공됩니다. 즉, 앱 매니페스트에 나타나지 않는 네이티브 공유 라이브러리에는 액세스할 수 없습니다.
