Android 執行階段 (ART) 包含即時 (JIT) 編譯器,可進行程式碼剖析,持續提升 Android 應用程式的執行效能。JIT 編譯器可輔助 ART 目前的預先 (AOT) 編譯器,提升執行階段效能、節省儲存空間,並加快應用程式和系統更新速度。此外,這項技術還能避免系統在自動更新應用程式或無線更新 (OTA) 期間重新編譯應用程式時變慢,進而提升 AOT 編譯器效能。
雖然 JIT 和 AOT 使用相同的編譯器和類似的最佳化組合,但產生的程式碼可能不盡相同。JIT 會使用執行階段型別資訊,可進行更完善的內嵌作業,並支援堆疊上取代 (OSR) 編譯,這些都會產生略有不同的程式碼。
JIT 架構
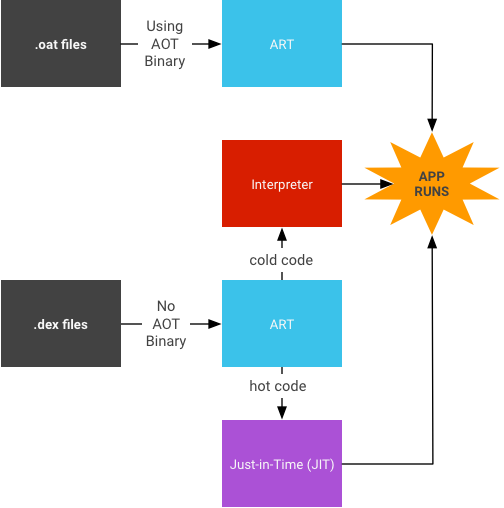
JIT 編譯
JIT 編譯包含下列活動:
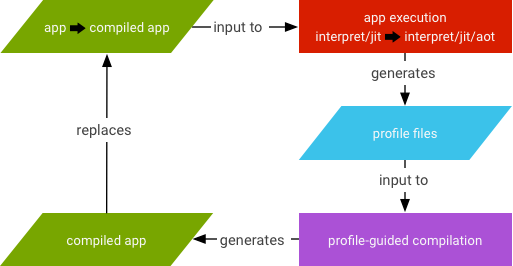
- 使用者執行應用程式,這時 ART 會觸發載入
.dex檔案。- 如果
.oat檔案 (.dex檔案的 AOT 二進位檔) 可用,ART 會直接使用。雖然系統會定期產生.oat檔案,但這些檔案不一定包含已編譯的程式碼 (AOT 二進位檔)。 - 如果
.oat檔案不含已編譯的程式碼,ART 會透過 JIT 和解譯器執行.dex檔案。
- 如果
- 如果應用程式並非根據
speed編譯篩選條件 (表示「盡可能編譯應用程式」) 編譯,系統就會啟用 JIT。 - 系統會將 JIT 設定檔資料傾印至系統目錄中的檔案,只有應用程式可以存取該檔案。
- AOT 編譯 (
dex2oat) 精靈會剖析該檔案,以驅動編譯作業。
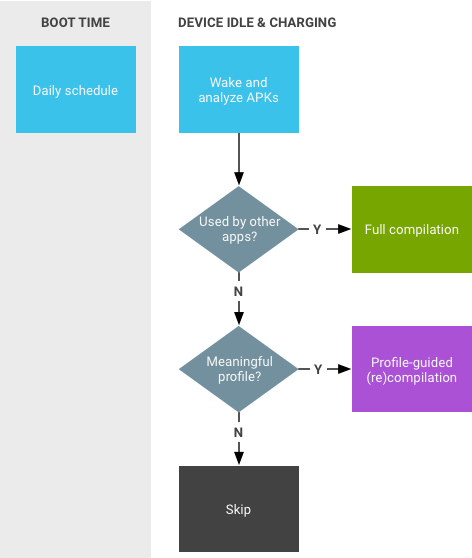
圖 3. JIT 精靈活動。
Google Play 服務就是一個例子,其他應用程式的行為與共用程式庫類似。
JIT 工作流程
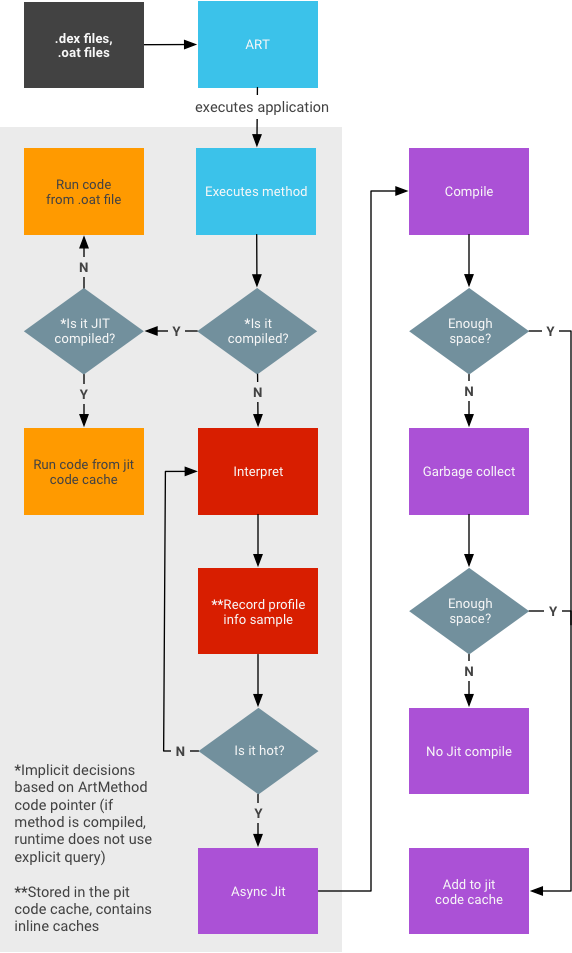
- 剖析資訊會儲存在程式碼快取中,並在記憶體壓力下進行垃圾收集。
- 我們無法保證應用程式在背景執行時擷取的快照會包含完整資料 (即所有 JIT 編譯的內容)。
- 系統不會嘗試確保所有內容都已錄製 (因為這可能會影響執行階段效能)。
- 方法可處於三種不同狀態:
- 解譯 (DEX 程式碼)
- JIT 編譯
- 已編譯 AOT
- 執行 JIT 時不影響前景應用程式效能的記憶體需求,取決於相關應用程式。大型應用程式比小型應用程式需要更多記憶體。一般來說,大型應用程式的穩定大小約為 4 MB。
啟用 JIT 記錄
如要開啟 JIT 記錄功能,請執行下列指令:
adb rootadb shell stopadb shell setprop dalvik.vm.extra-opts -verbose:jitadb shell start
停用 JIT
如要停用 JIT,請執行下列指令:
adb rootadb shell stopadb shell setprop dalvik.vm.usejit falseadb shell start
強制編譯
如要強制編譯,請執行下列指令:
adb shell cmd package compile
強制編譯特定套件的常見用途:
- 以設定檔為依據:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed-profile -f my-package
- 完整:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed -f my-package
強制編譯所有套件的常見用途:
- 以設定檔為依據:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed-profile -f -a
- 完整:
adb shell cmd package compile -m speed -f -a
清除設定檔資料
Android 13 以下版本
如要清除本機設定檔資料並移除已編譯的程式碼,請執行下列指令:
adb shell pm compile --reset
Android 14 以上版本
如要只清除本機設定檔資料,請按照下列步驟操作:
adb shell pm art clear-app-profiles
注意:與 Android 13 以下版本的指令不同,這個指令不會清除隨應用程式安裝的外部設定檔資料 (`.dm`)。
如要清除本機設定檔資料,並移除從本機設定檔資料產生的已編譯程式碼 (即重設為安裝狀態),請執行下列指令:
adb shell pm compile --reset
注意:這個指令不會移除從外部設定檔資料 (`.dm`) 產生的已編譯程式碼,這些程式碼會隨應用程式一併安裝。
如要清除所有已編譯的程式碼,請執行下列指令:
adb shell cmd package compile -m verify -f
注意:這項指令會保留本機設定檔資料。
