يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 9 إمكانية الحصول على اسم الخدمة لمثيل HAL معيّن استنادًا إلى الجهاز الذي يتم عليه تنفيذ اختبارات Vendor Test Suite (VTS). يؤدي تشغيل اختبارات VTS HAL التي تتعرّف على أسماء الخدمات إلى تمكين المطوّرين من تنفيذ الاختبارات تلقائيًا على إضافات المورّدين، وواجهات HAL المتعددة، ومثيلات HAL المتعددة في عمليات تشغيل اختبارات VTS على كل من الجهاز المستهدف والمضيف.
لمحة عن أسماء الخدمات
تسجّل كل نسخة من خدمة HAL قيد التشغيل نفسها باسم خدمة.
في الإصدارات السابقة من Android، كان على المطوّرين الذين ينفّذون اختبارات VTS HAL ضبط اسم الخدمة الصحيح لبرنامج الاختبار في getService() أو ترك الاسم فارغًا والرجوع إلى اسم الخدمة التلقائي. تشمل عيوب هذا النهج ما يلي:
- الاعتماد على معرفة مطوّر الاختبار لضبط اسم الخدمة الصحيح
- يقتصر الاختبار تلقائيًا على مثيل خدمة واحد.
- الصيانة اليدوية لأسماء الخدمات (أي لأنّ الأسماء مبرمَجة بشكل ثابت، يجب تعديلها يدويًا في حال تغيّر اسم الخدمة)
في نظام التشغيل Android 9، يمكن للمطوّرين الحصول تلقائيًا على اسم الخدمة لمثيل HAL معيّن استنادًا إلى الجهاز قيد الاختبار. تشمل مزايا هذا النهج إمكانية إجراء الاختبارات:
- إضافات Vendor HAL على سبيل المثال، عندما يكون لدى مورّد عملية تنفيذ لواجهة HAL الخاصة بـ camera.provider تعمل على أجهزة المورّدين مع اسم خدمة مخصّص، يمكن لأداة VTS تحديد مثيل المورّد وتشغيل الاختبار عليه.
- نُسخ متعددة من طبقة تجريد الأجهزة (HAL) على سبيل المثال، عندما يحتوي
graphics.composerHAL على مثيلَين (أحدهما يحمل اسم الخدمة "default" والآخر يحمل اسم الخدمة "vr")، يمكن لأداة VTS تحديد كلا المثيلَين وتشغيل الاختبار على كل منهما. - اختبار HAL المتعدّد يتم استخدامها عند اختبار عدة طبقات HAL مع عدة مثيلات، مثلاً عند تشغيل اختبار VTS الذي يتحقّق من كيفية عمل طبقتَي KeyMint (المعروفة سابقًا باسم Keymaster) وGatekeeper HAL معًا، يمكن أن يختبر VTS جميع مجموعات مثيلات الخدمة لهاتين الطبقتين.
اختبارات من جهة الاستهداف
لتفعيل ميزة التعرّف على اسم الخدمة لأغراض الاختبار على الجهاز المستهدف، يتضمّن الإصدار 9 من نظام التشغيل Android بيئة اختبار قابلة للتخصيص (VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase) توفّر واجهات من أجل:
- تسجيل استهداف HAL في الاختبار
- أدرِج جميع طبقات تجريد الأجهزة(HAL) المسجّلة.
- الحصول على أسماء الخدمات الخاصة بطبقات HAL المسجّلة التي يوفّرها إطار عمل VTS
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يوفّر إطار عمل VTS إمكانية التشغيل في وقت التنفيذ لما يلي:
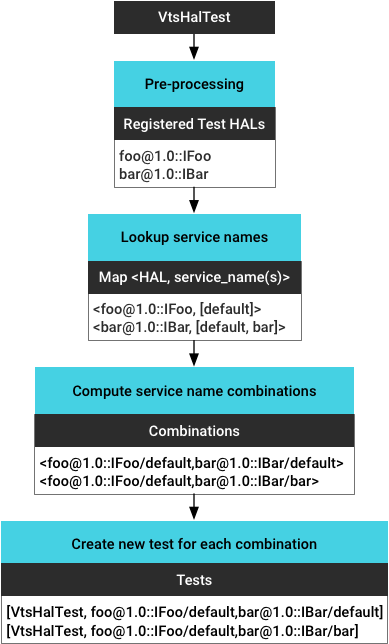
- المعالجة المُسبَقة لملف الاختبار الثنائي للحصول على جميع حِزم HAL المسجَّلة للاختبار
- تحديد جميع مثيلات الخدمة قيد التشغيل والحصول على اسم الخدمة لكل مثيل (يتم استرداده استنادًا إلى
vendor/manifest.xml) - احتساب جميع مجموعات المثيلات (لإتاحة اختبارات متعددة لطبقة تجريد الأجهزة).
- إنشاء اختبار جديد لكل مثيل خدمة (مجموعة).
مثال:
إعداد اختبارات من جهة الاستهداف تتضمّن اسم الخدمة
لإعداد بيئة الاختبار من أجل إجراء اختبارات تتضمّن معرفة اسم الخدمة من جهة الهدف، اتّبِع الخطوات التالية:
- حدِّد
testEnvironmentاستنادًا إلىVtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBaseوسجِّل حِزم HAL الاختبارية:#include <VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase.h> class testEnvironment : public::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase { virtual void registerTestServices() override { registerTestService<IFoo>(); } };
- استخدِم
getServiceName()المقدَّم من بيئة الاختبار لتمرير اسم الخدمة:::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestBase::getService<IFoo>(testEnv->getServiceName<IFoo>("default")); // "default" is the default service name you want to use.
- سجِّل بيئة الاختبار في
main()وinitTestباتّباع الخطوات التالية:int main(int argc, char** argv) { testEnv = new testEnvironment(); ::testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(testEnv); ::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); testEnv->init(argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); }
للاطّلاع على أمثلة إضافية، يُرجى الرجوع إلى VtsHalCameraProviderV2_4TargetTest.cpp.
اختبارات VTS من جهة المضيف
تُشغّل اختبارات VTS من جهة المضيف نصوص الاختبار من جهة المضيف بدلاً من تشغيل ملفات الاختبار الثنائية على الجهاز المستهدف. لتفعيل ميزة التعرّف على اسم الخدمة لهذه الاختبارات، يمكنك استخدام قوالب من جهة المضيف لتشغيل نص الاختبار البرمجي نفسه عدة مرات مع مَعلمات مختلفة (على غرار اختبار gtest المحدّد المَعلمات).

- يحدّد النص البرمجي hal test خدمات HAL المستهدَفة في الاختبار.
- يأخذ
hal_hidl_host_test(فئة فرعية منparam_test) وحدات HAL المسجّلة للاختبار من نص الاختبار، ويحدّد أسماء الخدمات المقابلة لوحدة HAL للاختبار، ثم ينشئ مجموعات من أسماء الخدمات (للاختبار المتعدد لوحدات HAL) كمعلمات للاختبار. ويوفّر أيضًا طريقةgetHalServiceName()تعرض اسم الخدمة المناسب وفقًا للمَعلمة التي تم تمريرها إلى حالة الاختبار الحالية. - يتوافق نموذج param_test مع منطق قبول قائمة من المَعلمات وتنفيذ جميع حالات الاختبار المحدّدة لكل مَعلمة. أي أنّه لكل حالة اختبار، يتم إنشاء N حالة اختبار جديدة تتضمّن مَعلمات (N = حجم المَعلمات)، كلّ منها تتضمّن مَعلمة معيّنة.
إعداد اختبارات من جهة المضيف تتضمّن اسم الخدمة
لإعداد بيئة الاختبار من أجل إجراء اختبارات على مستوى المضيف تتضمّن اسم الخدمة، اتّبِع الخطوات التالية:
- حدِّد خدمة HAL المستهدَفة في نص الاختبار البرمجي:
TEST_HAL_SERVICES = { "android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo" }
- الاتصال بـ
getHalServiceName()وتمرير الاسم إلى init hal:self.dut.hal.InitHidlHal( target_type='foo', target_basepaths=self.dut.libPaths, target_version=1.0, target_package='android.hardware.foo', target_component_name='IFoo', hw_binder_service_name =self.getHalServiceName("android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo"), bits=int(self.abi_bitness))
للاطّلاع على أمثلة إضافية، يُرجى الرجوع إلى VtsHalMediaOmxStoreV1_0HostTest.py.
تسجيل حِزم HAL التجريبية
في الإصدارات السابقة من Android، كان VTS يحدّد HAL الخاص بالاختبار باستخدام الخيار <precondition-lshal> الذي تم ضبطه في AndroidTest.xml. كان من الصعب الحفاظ على هذا النهج (لأنّه كان يعتمد على المطوّرين في ضبط الاختبار بشكلٍ سليم وتعديل الإعدادات وفقًا لذلك) وغير دقيق (لأنّه كان يحتوي فقط على معلومات الحزمة والإصدار وليس معلومات الواجهة).
في Android 9، يحدّد VTS واجهة HAL للاختبار باستخدام ميزة التعرّف على اسم الخدمة. تفيد أيضًا حزم HAL المسجّلة للاختبار في ما يلي:
- عمليات التحقّق من الشروط المسبقة: قبل تشغيل اختبار HAL، يمكن لأداة VTS التأكّد من توفُّر HAL المراد اختباره على الجهاز المستهدف وتخطّي الاختبارات إذا لم يكن متوفّرًا (راجِع فحص إمكانية اختبار VTS).
- قياس التغطية: تتيح "مجموعة أدوات اختبارات VTS" قياس مدى تغطية الرموز البرمجية على مستوى العمليات المختلفة من خلال معرفة خدمات HAL للاختبار التي تريد قياسها (أي إزالة التغطية لعملية خدمة HAL).
