Android 9 شامل پشتیبانی برای به دست آوردن نام سرویس یک نمونه HAL معین بر اساس دستگاهی است که تستهای مجموعه تست فروشنده (VTS) روی آن اجرا میشود. اجرای آزمایشهای VTS HAL که از نام سرویس آگاه هستند، توسعهدهندگان را قادر میسازد تا برنامههای افزودنی فروشنده، HALهای متعدد و نمونههای HAL متعدد را در هر دو اجرای آزمایشی VTS سمت مقصد و میزبان، خودکار کنند.
درباره نام خدمات
هر نمونه از سرویس HAL در حال اجرا خود را با نام سرویس ثبت می کند.
در نسخههای قبلی اندروید، توسعهدهندگانی که آزمایشهای VTS HAL را اجرا میکردند، باید نام سرویس صحیح را برای سرویس گیرنده آزمایشی در getService() تنظیم میکردند یا نام را خالی میگذاشتند و به نام سرویس پیشفرض برگردانیدند. معایب این روش عبارتند از:
- برای تنظیم نام صحیح سرویس، به دانش توسعه دهنده آزمون تکیه کنید.
- به طور پیش فرض محدود به آزمایش در برابر یک نمونه سرویس واحد است.
- نگهداری دستی نامهای سرویس (یعنی چون نامها سختکد هستند، در صورت تغییر نام سرویس، باید بهصورت دستی بهروزرسانی شوند.
در اندروید 9، توسعه دهندگان می توانند به طور خودکار نام سرویس را برای یک نمونه HAL بر اساس دستگاه تحت آزمایش دریافت کنند. از مزایای این روش می توان به پشتیبانی از آزمایش اشاره کرد:
- پسوند HAL فروشنده . به عنوان مثال، هنگامی که یک فروشنده یک پیاده سازی از camera.provider HAL دارد که بر روی دستگاه های فروشنده با نام سرویس سفارشی اجرا می شود، VTS می تواند نمونه فروشنده را شناسایی کرده و آزمایش را در برابر آن اجرا کند.
- چند نمونه HAL . به عنوان مثال، زمانی که
graphics.composerHAL دو نمونه دارد (یکی با نام سرویس "default" و دیگری با نام سرویس "vr")، VTS می تواند هر دو نمونه را شناسایی کرده و آزمایش را بر روی هر یک از آنها اجرا کند. - تست Multi-HAL . برای آزمایش چندین HAL با چندین نمونه استفاده میشود، بهعنوان مثال، هنگام اجرای آزمایش VTS که بررسی میکند چگونه KeyMint (قبلاً Keymaster) و HALهای Gatekeeper با هم کار میکنند، VTS میتواند تمام ترکیبهای نمونههای سرویس را برای آن HALها آزمایش کند.
تست های سمت هدف
برای فعال کردن آگاهی از نام سرویس برای آزمایش سمت هدف، Android 9 شامل یک محیط آزمایشی قابل تنظیم ( VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase ) است که رابطهایی را برای موارد زیر ارائه میکند:
- HAL(های) هدف را در آزمون ثبت کنید.
- تمام HAL(های) ثبت شده را فهرست کنید.
- نام(های) سرویس را برای HAL(های) ثبت شده ارائه شده توسط چارچوب VTS دریافت کنید.
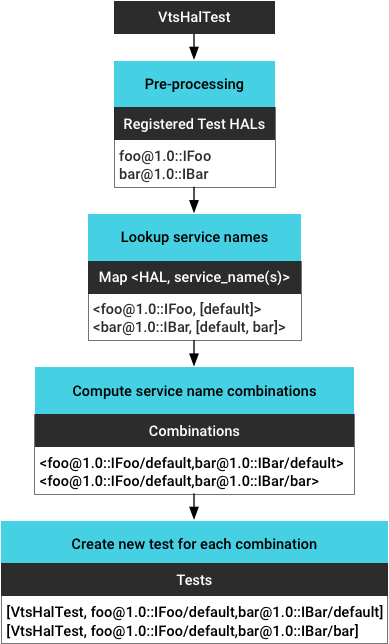
علاوه بر این، چارچوب VTS پشتیبانی از زمان اجرا را برای:
- پیش پردازش باینری تست برای دریافت همه HAL(های) تست ثبت شده.
- شناسایی تمام نمونههای سرویس در حال اجرا و دریافت نام سرویس برای هر نمونه (بازیابی شده بر اساس
vendor/manifest.xml). - محاسبه تمام ترکیبات نمونه (برای پشتیبانی از آزمایش HAL چندگانه).
- ایجاد یک تست جدید برای هر نمونه سرویس (ترکیب).
مثال:
تستهای سمت هدف آگاه از نام سرویس را تنظیم کنید
برای راهاندازی محیط آزمایشی خود برای آزمایش نام سرویس هدف:
- یک
testEnvironmentبر اساسVtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBaseتعریف کنید و HAL های آزمایشی را ثبت کنید:#include <VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase.h> class testEnvironment : public::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestEnvBase { virtual void registerTestServices() override { registerTestService<IFoo>(); } };
- از
getServiceName()ارائه شده توسط محیط تست برای عبور نام سرویس استفاده کنید:::testing::VtsHalHidlTargetTestBase::getService<IFoo>(testEnv->getServiceName<IFoo>("default")); // "default" is the default service name you want to use.
- محیط تست را در
main()وinitTestثبت کنید:int main(int argc, char** argv) { testEnv = new testEnvironment(); ::testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(testEnv); ::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv); testEnv->init(argc, argv); return RUN_ALL_TESTS(); }
برای مثالهای بیشتر، به VtsHalCameraProviderV2_4TargetTest.cpp مراجعه کنید.
تست های میزبان VTS
تست های سمت میزبان VTS اسکریپت های آزمایشی را در سمت میزبان به جای تست های باینری روی دستگاه مورد نظر اجرا می کنند. برای فعال کردن آگاهی از نام سرویس برای این آزمایشها، میتوانید از الگوهای سمت میزبان برای اجرای یک اسکریپت آزمایشی چندین بار در برابر پارامترهای مختلف استفاده کنید (شبیه به آزمایش پارامتری gtest).

- اسکریپت تست hal سرویس(های) هدف HAL را در تست مشخص می کند.
-
hal_hidl_host_test(زیر کلاسparam_test) HAL(های) تست ثبت شده را از اسکریپت تست می گیرد، نام(های) سرویس مربوطه را برای HAL آزمایشی شناسایی می کند، سپس ترکیبات نام سرویس (برای تست چند HAL) را به عنوان پارامترهای تست تولید می کند. همچنین یک متدgetHalServiceName()را ارائه میکند که نام سرویس مربوطه را با توجه به پارامتر ارسال شده به مورد آزمایشی فعلی برمیگرداند. - الگوی param_test از منطق پشتیبانی می کند تا لیستی از پارامترها را بپذیرد و تمام موارد تست داده شده را در برابر هر پارامتر اجرا کند. یعنی برای هر مورد آزمایشی N مورد آزمایشی پارامتری جدید (N = اندازه پارامترها) ایجاد می کند که هر کدام یک پارامتر معین دارند.
تستهای سمت میزبان آگاه از نام سرویس را تنظیم کنید
برای راهاندازی محیط آزمایشی خود برای آزمایش نام سرویس میزبان:
- سرویس HAL هدف را در اسکریپت تست مشخص کنید:
TEST_HAL_SERVICES = { "android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo" }
getHalServiceName()را فراخوانی کنید و نام را برای init hal ارسال کنید:self.dut.hal.InitHidlHal( target_type='foo', target_basepaths=self.dut.libPaths, target_version=1.0, target_package='android.hardware.foo', target_component_name='IFoo', hw_binder_service_name =self.getHalServiceName("android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo"), bits=int(self.abi_bitness))
برای مثالهای بیشتر، به VtsHalMediaOmxStoreV1_0HostTest.py مراجعه کنید.
HAL های آزمایشی را ثبت کنید
در نسخه های قبلی Android، VTS با استفاده از گزینه <precondition-lshal> پیکربندی شده در AndroidTest.xml ، HAL آزمایشی را شناسایی کرد. حفظ این رویکرد دشوار بود (زیرا به توسعه دهندگان متکی بود تا آزمایش را به درستی پیکربندی کنند و پیکربندی را متناسب با آن به روز کنند) و نادرست بود (زیرا فقط اطلاعات بسته و نسخه را شامل می شد و نه اطلاعات رابط).
در اندروید 9، VTS با استفاده از آگاهی از نام سرویس، HAL آزمایشی را شناسایی میکند. HAL های تست ثبت شده نیز برای موارد زیر مفید هستند:
- بررسی های پیش شرط قبل از اجرای آزمایش HAL، VTS میتواند تأیید کند که HAL آزمایشی در دستگاه مورد نظر در دسترس است و در صورت عدم وجود آن، از آزمایشها صرفنظر کند (به بررسی آزمایشپذیری VTS مراجعه کنید).
- اندازه گیری پوشش . VTS از اندازهگیری پوشش کد متقابل فرآیند از طریق دانش در مورد سرویسهای آزمایشی HAL که میخواهد اندازهگیری کند، پشتیبانی میکند (یعنی برای شستشوی پوشش فرآیند خدمات hal).

