デバイスツリー オーバーレイ(DTO)を実装する作業には、デバイスツリー(DT)の分割、ビルド、パーティショニング、実行が含まれます。また、実装を実行した後、2 つの DT 間の互換性を維持するとともに、各 DT パーティションのセキュリティを確保するための戦略を決定する必要があります。
DT を分割する
まず、DT を次の 2 つに分割します。
- メイン DT: SoC のみの部分と、SoC ベンダーが提供するデフォルトの設定。
- オーバーレイ DT: ODM / OEM が提供するデバイス固有の構成。
DT を分割した後、メイン DT とオーバーレイ DT をマージしたときにデバイスの完全な DT になるように、メイン DT とオーバーレイ DT 間の互換性を確保する必要があります。DTO の形式とルールの詳細については、DTO の構文をご覧ください。複数の DT の詳細については、複数の DT の使用 をご覧ください。
メイン DT とオーバーレイ DT をビルドする
メイン DT をビルドする手順は次のとおりです。
- メイン DT
.dtsを.dtbファイルにコンパイルします。 - ブートローダーが実行時にアクセスできるパーティションに
.dtbファイルを書き込みます(詳細は [パーティション DT](#partition) に記載しています)。
オーバーレイ DT をビルドする手順は次のとおりです。
- オーバーレイ DT
.dtsを.dtboファイルにコンパイルします。このファイル形式は、フラット化された DT としてフォーマットされた.dtbファイルと同じですが、ファイル拡張子が異なるためメイン DT と区別できます。 - ブートローダーが実行時にアクセスできるパーティションに
.dtboファイルを書き込みます(詳細は [パーティション DT](#partition) に記載しています)。
DTC を使用したコンパイルと、ホストでの DTO の結果の検証については、コンパイルと検証をご覧ください。
パーティション DT
.dtb と .dtbo を挿入するための、ブートローダーが実行時にアクセスできるフラッシュ メモリ内の信頼できる場所を決定します。
メイン DT の場所の例:
- カーネル(
image.gz)に追加された、ブート パーティションの一部 - 専用パーティション(
dtb)内の個別の DT blob(.dtb)
オーバーレイ DT の場所の例:
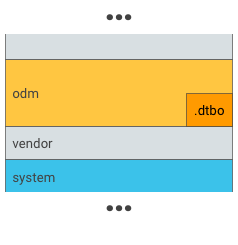
図 1. odm パーティションに .dtbo を挿入します(これは、ブートローダーが odm パーティションのファイル システムからデータを読み込むことができる場合にのみ行います)。
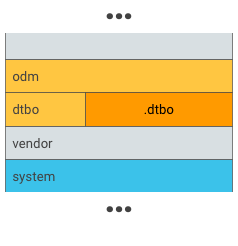
図 2. dtbo パーティションなどの固有のパーティションに .dtbo を挿入します。
注: オーバーレイ DT パーティションのサイズは、デバイスと、メイン DT blob 上で必要な変更の量によって決まります。通常は 8 MB あれば十分です。将来的に、必要に応じてサイズを大きくすることもできます。
シームレス(A/B)アップデートをサポートするデバイスの場合、メイン DT とオーバーレイ DT のパーティション A/B を次のように作成します。
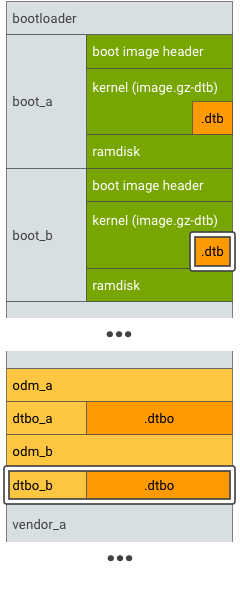
図 3. DTBO パーティション A/B、例 1
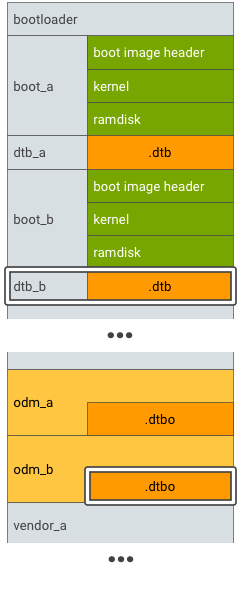
図 4. DTBO パーティション A/B、例 2
ブートローダーで実行する
以下の手順で実行します。
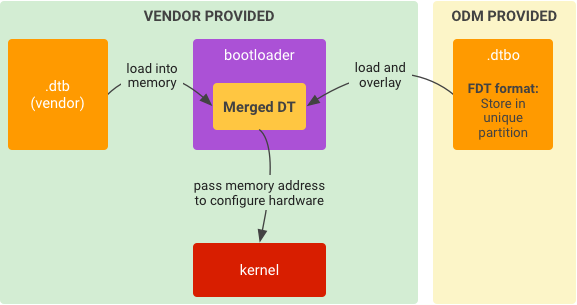
図 5. ブートローダーでの DTO の一般的なランタイム実装。
.dtbをストレージからメモリに読み込みます。.dtboをストレージからメモリに読み込みます。.dtbを.dtboでオーバーレイして、DT を統合します。- 統合した DT のメモリアドレスを指定して、カーネルを起動します。
互換性を維持する
メイン DTB(SoC ベンダーが提供)は、DTBO の API サーフェスとして扱われます。DT を SoC 共通部分とデバイス固有部分に分割した後、将来的にこの 2 つの部分の互換性(たとえば、以下に関する互換性)を維持する必要があります。
- メイン DT での DT 定義。たとえば、ノード、プロパティ、ラベルなど。メイン DT の定義を変更すると、オーバーレイ DT でも変更が必要になる場合があります。たとえば、メイン DT のノード名を修正する場合、元のノード名にマッピングする「エイリアス」ラベルを定義することにより、オーバーレイ DT の変更を回避できます。
- オーバーレイ DT の保存場所。たとえば、パーティション名、保存形式など。
セキュリティを確保する
ブートローダーは、DTB または DTBO が安全で、変更されておらず、破損していないことを確認する必要があります。DTB または DTBO を保護するには、VBoot 1.0 のブートイメージ署名や AVB HASH フッター(VBoot 2.0)などの任意のソリューションを使用できます。
- DTB または DTBO が固有のパーティションにある場合、そのパーティションを AVB のトラスト チェーンに追加できます。トラスト チェーンはハードウェアで保護されたルート オブ トラストからスタートしてブートローダーまで進み、DTB または DTBO パーティションの整合性と真正性を検証します。
- DTB または DTBO が既存のパーティション(
odmパーティションなど)にある場合、そのパーティションは AVB のトラスト チェーン内に存在する必要があります(DTBO パーティションはodmパーティションと公開鍵を共有できます)。
詳細については、確認付きブートを参照してください。
