باستثناء بعض الحالات، يمكن العثور على حِزم واجهة HIDL في directory
hardware/interfaces أو vendor/. تتمّ ترجمة المستوى الأعلى
hardware/interfaces مباشرةً إلى مساحة اسم الحزمة
android.hardware، ويكون الإصدار دليلاً فرعيًا
ضمن مساحة اسم الحزمة (وليس الواجهة).
يُجمِّع مُجمِّع hidl-gen ملفات .hal في
مجموعة من ملفات .h و.cpp. من هذه الملفات التي تم إنشاؤها تلقائيًا، يتم إنشاء مكتبة مشتركة ترتبط بها عمليات تنفيذ العميل/الخادم.
يتم إنشاء ملف Android.bp الذي ينشئ هذه المكتبة المشتركة
تلقائيًا بواسطة نص hardware/interfaces/update-makefiles.sh. في كل مرة تضيف فيها حزمة جديدة إلى hardware/interfaces، أو تتم فيها
إضافة ملفات .hal أو إزالتها من حزمة حالية أو إليها، عليك إعادة تنفيذ
النص البرمجي للتأكّد من أنّ المكتبة المشتركة التي تم إنشاؤها محدّثة.
على سبيل المثال، يجب أن يكون ملف IFoo.hal نموذجًا في
hardware/interfaces/samples/1.0. ينشئ ملف النموذج
IFoo.hal واجهة IFoo في حزمة
samples:
package android.hardware.samples@1.0; interface IFoo { struct Foo { int64_t someValue; handle myHandle; }; someMethod() generates (vec<uint32_t>); anotherMethod(Foo foo) generates (int32_t ret); };
الملفات التي تم إنشاؤها
يتم ربط الملفات التي يتم إنشاؤها تلقائيًا في حزمة HIDL بمكتبة مشتركة واحدة
بالاسم نفسه للحزمة (على سبيل المثال،
android.hardware.samples@1.0). تُصدِّر المكتبة المشتركة أيضًا عنوانًا واحدًا، وهو IFoo.h، ويمكن أن يتضمّنه العملاء
والخوادم. باستخدام المُجمِّع hidl-gen مع ملف IFoo.hal
واجهة كإدخال، يتضمّن الوضع المرتبط ملفَّي
التلقائيَين التاليَين:
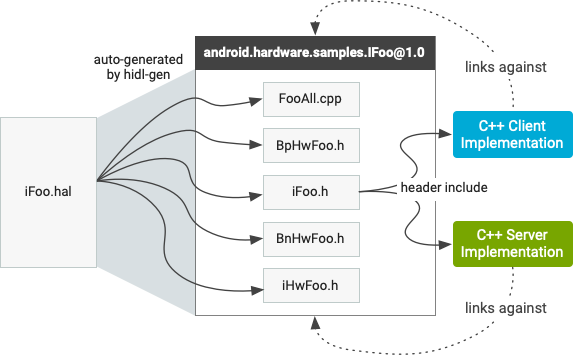
الشكل 1: الملفات التي أنشأها المُجمِّع
IFoo.h: يصف واجهةIFooالخالصة في فئة C++، ويحتوي على الطرق والأنواع المحدّدة في واجهةIFooفي ملفIFoo.hal، والتي تم ترجمتها إلى أنواع C++ عند الضرورة. لا تحتوي على تفاصيل متعلّقة بآلية RPC (مثلHwBinder) المستخدَمة لتنفيذ هذه الواجهة يتم إنشاء مساحة اسم للصف باستخدام الحزمة والإصدار، على سبيل المثال،::android::hardware::samples::IFoo::V1_0. يتضمن كلّ من العملاء والخوادم هذا الرأس: العملاء لاستدعاء الطرق عليه والخوادم لتنفيذ هذه الطرق.IHwFoo.h. ملف الرأس الذي يحتوي على بيانات الدوالّ التي تسلسل أنواع البيانات المستخدَمة في الواجهة يجب ألا يدرج المطوّرون العنوان مباشرةً (لا يحتوي على أي فئات).BpHwFoo.h: فئة تُكتسَب منIFooوتصف تنفيذHwBinderالوكيل (من جهة العميل) للواجهة ويجب ألا يشير المطوّرون إلى هذه الفئة بشكل مباشر.BnHwFoo.h: فئة تحتوي على إشارة إلى تنفيذIFooوتصف تنفيذHwBinder(من جهة الخادم) للواجهة ويجب ألا يشير المطوّرون إلى هذه الفئة مباشرةً.FooAll.cpp: فئة تحتوي على عمليات التنفيذ لكل من الوكيلHwBinderوHwBinderالرمز المرجعي عندما يستدعي أحد العملاء طريقة واجهة، يُجمِّع الوكيل تلقائيًا الوسيطات من العميل ويرسل المعاملة إلى برنامج تشغيل نواة الربط الذي يرسل المعاملة إلى العنصر المرجعي على الجانب الآخر (الذي يستدعي بعد ذلك تنفيذ الخادم الفعلي).
تكون بنية الملفات مشابهة لبنية الملفات التي تم إنشاؤها باستخدام IDE IDE
aidl-cpp (للاطّلاع على التفاصيل، يُرجى الاطّلاع على "وضع السماح بالمرور" في
نظرة عامة على HIDL). إنّ الملف الوحيد الذي يتم إنشاؤه تلقائيًا والذي لا يعتمد على آلية RPC المستخدَمة في HIDL هوIFoo.h، وجميع الملفات الأخرى مرتبطة بآلية HwBinder RPC المستخدَمة في HIDL. لذلك، يجب ألا تشيرعمليات تنفيذ العميل والخادم مطلقًا مباشرةً إلى أي شيء آخر غير IFoo. لتحقيق
هذا، أدرِج IFoo.h فقط واربطه بالمكتبة المشترَكة التي تم إنشاؤها.
رابط يؤدي إلى المكتبات المشتركة
يجب أن يتضمّن العميل أو الخادم الذي يستخدم أي واجهة في حزمة مكتبة المشترَكة لهذه الحزمة في مكان واحد (1) من المواقع التالية:
- في Android.mk:
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES += android.hardware.samples@1.0
- في Android.bp:
shared_libs: [ /* ... */ "android.hardware.samples@1.0", ],
المكتبات الإضافية التي قد تحتاج إلى تضمينها:
libhidlbase |
يتضمّن أنواع بيانات HIDL العادية. بدءًا من الإصدار
10 من Android، يتضمّن هذا الجدول أيضًا جميع الرموز التي كانت مضمّنة سابقًا في رمزَي
libhidltransport و
libhwbinder.
|
|---|---|
libhidltransport |
تعالج نقل طلبات HIDL عبر آليات مختلفة لبروتوكول RPC/IPC. سيتم إيقاف هذه المكتبة نهائيًا في Android 10. |
libhwbinder |
الرموز الخاصة بدفتر الربط يتوقف نظام التشغيل Android 10 عن استخدام هذه المكتبة نهائيًا. |
libfmq |
واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لميزة "قائمة الرسائل السريعة" |
مساحات الأسماء
يتم تعريف دوال HIDL وأنواعها، مثل Return<T> و
Void()، في مساحة الاسم ::android::hardware.
يتم تحديد مساحة الاسم C++ لأي حزمة حسب اسم الحزمة وإصدارها.
على سبيل المثال، الحزمة mypackage التي تستخدم الإصدار 1.2 ضمن
hardware/interfaces تتضمّن الخصائص التالية:
- مساحة الاسم C++ هي
::android::hardware::mypackage::V1_2 - الاسم المؤهَّل بالكامل لـ
IMyInterfaceفي تلك الحزمة هو:::android::hardware::mypackage::V1_2::IMyInterface. (IMyInterfaceهو معرّف، وليس جزءًا من مساحة الاسم). - الأنواع المحدّدة في ملف
types.halللحزمة يتم تحديدها على النحو التالي:::android::hardware::mypackage::V1_2::MyPackageType
