แพ็กเกจอินเทอร์เฟซ HIDL จะอยู่ในไดเรกทอรี hardware/interfaces หรือ vendor/ ยกเว้นบางกรณี ระดับhardware/interfacesบนสุดจะแมปกับเนมสเปซของแพ็กเกจandroid.hardwareโดยตรง โดยเวอร์ชันจะเป็นไดเรกทอรีย่อยภายใต้เนมสเปซของแพ็กเกจ (ไม่ใช่อินเทอร์เฟซ)
คอมไพเลอร์ hidl-gen จะคอมไพล์ไฟล์ .hal เป็นชุดไฟล์ .h และ .cpp ระบบจะสร้างไลบรารีที่ใช้ร่วมกันซึ่งการนําใช้งานไคลเอ็นต์/เซิร์ฟเวอร์จะลิงก์กับไฟล์เหล่านี้
ไฟล์ Android.bp ที่สร้างคลังที่ใช้ร่วมกันนี้จะสร้างขึ้นโดยสคริปต์ hardware/interfaces/update-makefiles.sh โดยอัตโนมัติ ทุกครั้งที่คุณเพิ่มแพ็กเกจใหม่ลงใน hardware/interfaces หรือเพิ่ม/นําไฟล์ .hal ไปยัง/ออกจากแพ็กเกจที่มีอยู่ คุณต้องเรียกใช้สคริปต์อีกครั้งเพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าไลบรารีที่แชร์ซึ่งสร้างขึ้นเป็นเวอร์ชันล่าสุด
เช่น ไฟล์ตัวอย่าง IFoo.hal ควรอยู่ใน hardware/interfaces/samples/1.0 ไฟล์ตัวอย่าง IFoo.hal สร้างอินเทอร์เฟซ IFoo ในแพ็กเกจ samples
package android.hardware.samples@1.0; interface IFoo { struct Foo { int64_t someValue; handle myHandle; }; someMethod() generates (vec<uint32_t>); anotherMethod(Foo foo) generates (int32_t ret); };
ไฟล์ที่สร้างขึ้น
ไฟล์ที่สร้างขึ้นโดยอัตโนมัติในแพ็กเกจ HIDL จะลิงก์ไปยังไลบรารีที่แชร์ไฟล์เดียวซึ่งมีชื่อเดียวกับแพ็กเกจ (เช่น android.hardware.samples@1.0) นอกจากนี้ ไลบรารีที่แชร์ยังส่งออกส่วนหัวเดียว IFoo.h ซึ่งไคลเอ็นต์และเซิร์ฟเวอร์สามารถรวมไว้ได้ เมื่อใช้คอมไพเลอร์ hidl-gen กับไฟล์อินเทอร์เฟซ IFoo.hal เป็นอินพุต โหมด Binderized จะมีไฟล์ที่สร้างขึ้นโดยอัตโนมัติดังต่อไปนี้
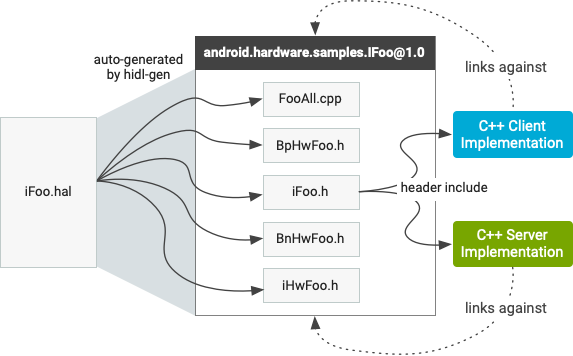
รูปที่ 1 ไฟล์ที่คอมไพเลอร์สร้างขึ้น
IFoo.h. อธิบายอินเทอร์เฟซIFooล้วนๆ ในคลาส C++ ซึ่งมีเมธอดและประเภทที่กําหนดไว้ในอินเทอร์เฟซIFooในไฟล์IFoo.halซึ่งแปลเป็นประเภท C++ ตามความจําเป็น ไม่มีรายละเอียดที่เกี่ยวข้องกับกลไก RPC (เช่นHwBinder) ที่ใช้เพื่อติดตั้งใช้งานอินเทอร์เฟซนี้ โดยชั้นเรียนจะอยู่ในเนมสเปซเดียวกับแพ็กเกจและเวอร์ชัน เช่น::android::hardware::samples::IFoo::V1_0ทั้งไคลเอ็นต์และเซิร์ฟเวอร์จะรวมส่วนหัวนี้ไว้ด้วย โดยไคลเอ็นต์จะรวมไว้เพื่อเรียกใช้เมธอด และเซิร์ฟเวอร์จะรวมไว้เพื่อใช้เมธอดเหล่านั้นIHwFoo.h. ไฟล์ส่วนหัวที่มีประกาศสำหรับฟังก์ชันที่จัดรูปแบบข้อมูลประเภทต่างๆ ที่ใช้ในอินเทอร์เฟซ นักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ไม่ควรรวมส่วนหัวนี้โดยตรง (ไม่มีคลาสใดๆ)BpHwFoo.h. คลาสที่รับค่ามาจากIFooและอธิบายการใช้งานอินเทอร์เฟซHwBinderพร็อกซี (ฝั่งไคลเอ็นต์) นักพัฒนาแอปไม่ควรอ้างอิงคลาสนี้โดยตรงBnHwFoo.h. คลาสที่มีข้อมูลอ้างอิงถึงการใช้งานIFooและอธิบายการใช้งานHwBinderสแต็บ (ฝั่งเซิร์ฟเวอร์) ของอินเทอร์เฟซ นักพัฒนาแอปไม่ควรอ้างอิงคลาสนี้โดยตรงFooAll.cpp. คลาสที่มีการใช้งานทั้งพร็อกซีHwBinderและสตับHwBinderเมื่อไคลเอ็นต์เรียกเมธอดอินเทอร์เฟซ พร็อพซีจะจัดระเบียบอาร์กิวเมนต์จากไคลเอ็นต์โดยอัตโนมัติและส่งธุรกรรมไปยังไดรเวอร์เคอร์เนล Binder ซึ่งจะส่งธุรกรรมไปยังสแต็บที่อีกฝั่งหนึ่ง (ซึ่งจะเรียกใช้การใช้งานเซิร์ฟเวอร์จริง)
ไฟล์มีโครงสร้างคล้ายกับไฟล์ที่สร้างขึ้นโดย aidl-cpp (ดูรายละเอียดที่ "โหมดการส่งผ่าน" ในภาพรวม HIDL) ไฟล์เดียวที่สร้างขึ้นโดยอัตโนมัติซึ่งไม่ขึ้นอยู่กับกลไก RPC ที่ HIDL ใช้คือIFoo.h ส่วนไฟล์อื่นๆ ทั้งหมดจะเชื่อมโยงกับกลไก HwBinder RPC ที่ HIDL ใช้ ดังนั้น การใช้งานไคลเอ็นต์และเซิร์ฟเวอร์จึงไม่ควรอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งอื่นใดโดยตรงนอกจาก IFoo หากต้องการดำเนินการดังกล่าว ให้ใส่เฉพาะ IFoo.h และลิงก์กับคลังที่ใช้ร่วมกันที่สร้างขึ้น
ลิงก์ไปยังคลังภาพที่แชร์
ไคลเอ็นต์หรือเซิร์ฟเวอร์ที่ใช้อินเทอร์เฟซในแพ็กเกจต้องมีไลบรารีที่แชร์ของแพ็กเกจนั้นในตำแหน่งที่ใดที่หนึ่ง (1) ตำแหน่งต่อไปนี้
- ใน Android.mk
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES += android.hardware.samples@1.0
- ใน Android.bp
shared_libs: [ /* ... */ "android.hardware.samples@1.0", ],
ไลบรารีเพิ่มเติมที่คุณอาจต้องใส่มีดังนี้
libhidlbase |
มีประเภทข้อมูล HIDL มาตรฐาน ตั้งแต่ Android 10 เป็นต้นไป แป้นพิมพ์นี้จะมีสัญลักษณ์ทั้งหมดที่เคยอยู่ใน libhidltransport และ libhwbinder ด้วย
|
|---|---|
libhidltransport |
จัดการการรับส่งการเรียก HIDL ผ่านกลไก RPC/IPC ต่างๆ Android 10 เลิกใช้งานไลบรารีนี้ |
libhwbinder |
สัญลักษณ์เฉพาะของ Binder Android 10 เลิกใช้งานไลบรารีนี้ |
libfmq |
Fast Message Queue IPC |
เนมสเปซ
ฟังก์ชันและประเภท HIDL เช่น Return<T> และ
Void() จะประกาศในเนมสเปซ ::android::hardware
เนมสเปซ C++ ของแพ็กเกจจะกำหนดโดยชื่อและเวอร์ชันของแพ็กเกจ
ตัวอย่างเช่น แพ็กเกจ mypackage เวอร์ชัน 1.2 ในส่วน hardware/interfaces มีคุณสมบัติดังต่อไปนี้
- เนมสเปซ C++ คือ
::android::hardware::mypackage::V1_2 - ชื่อที่สมบูรณ์ในตัวเอง ของ
IMyInterfaceในแพ็กเกจนั้นคือ::android::hardware::mypackage::V1_2::IMyInterface(IMyInterfaceคือตัวระบุ ไม่ใช่ส่วนหนึ่งของเนมสเปซ) - ประเภทที่กําหนดไว้ในไฟล์
types.halของแพ็กเกจจะระบุเป็นดังนี้::android::hardware::mypackage::V1_2::MyPackageType
