โดยทั่วไปแล้ว ผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์จะถือเป็นเจ้าของชิ้นงานส่วนตัว ที่สร้างขึ้นสำหรับอุปกรณ์แต่ละเครื่อง ด้วยเหตุนี้ ความพยายามด้านวิศวกรรมของบริษัทจึงมุ่งเน้นไปที่อุปกรณ์แต่ละเครื่องเป็นส่วนใหญ่ และแทบไม่ได้ให้ความสำคัญกับความสอดคล้องกันของอุปกรณ์อื่นๆ ในระบบนิเวศเลย
ในทางตรงกันข้าม นักพัฒนาแอปพยายามสร้างแอปที่ทำงานบนโทรศัพท์ Android ทุกรุ่นในระบบนิเวศ ไม่ว่าอุปกรณ์แต่ละเครื่องจะมีข้อกำหนดทางเทคนิคอย่างไรก็ตาม ความแตกต่างในแนวทางนี้อาจทำให้เกิดปัญหาการแยกส่วน เช่น ความสามารถของฮาร์ดแวร์ของโทรศัพท์บางรุ่นไม่ตรงกับความคาดหวังที่นักพัฒนาแอปตั้งไว้ ดังนั้นหาก API การสั่นทำงานในโทรศัพท์ Android บางรุ่นแต่ไม่ทำงานในรุ่นอื่นๆ ผลลัพธ์ที่ได้คือระบบนิเวศที่ไม่สอดคล้องกัน ด้วยเหตุนี้ การกำหนดค่าฮาร์ดแวร์จึงมีบทบาทสำคัญในการช่วยให้ผู้ผลิตสามารถใช้ Haptics API ของ Android ในอุปกรณ์ทุกเครื่อง
หน้านี้มีรายการตรวจสอบแบบทีละขั้นตอนเพื่อตั้งค่าการปฏิบัติตามข้อกำหนดของฮาร์ดแวร์สำหรับการใช้ Android Haptics API ให้ดีที่สุด
รูปภาพต่อไปนี้แสดงการสร้างความรู้ร่วมกันระหว่างผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์และนักพัฒนาแอป ซึ่งเป็นขั้นตอนสําคัญในการสร้างระบบนิเวศที่สอดคล้องกัน
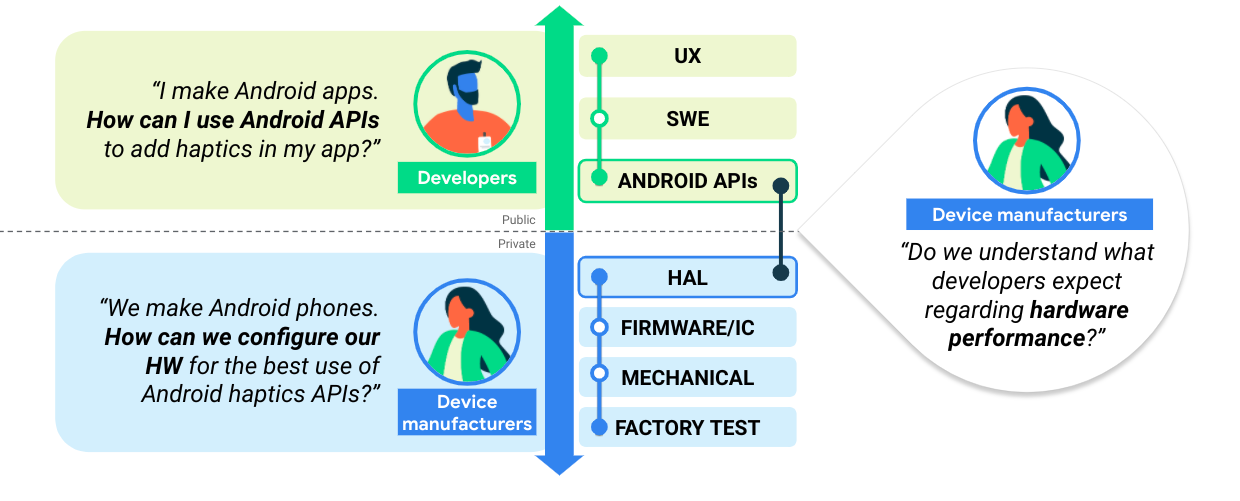
รูปที่ 1 สร้างความรู้ระหว่างผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์และนักพัฒนาแอป
รายการตรวจสอบการใช้งานการโต้ตอบการสัมผัส
-
- รายการค่าคงที่เพื่อใช้การสั่น
-
- คำแนะนำการใช้งานสำหรับองค์ประกอบพื้นฐานของการเขียน HAL
แมปค่าคงที่ระหว่าง HAL กับ API
- คำแนะนำในการแมประหว่างค่าคงที่ของ API สาธารณะ (ตั้งชื่อเป็นตัวยึดตำแหน่งในเฟรมเวิร์ก) กับค่าคงที่ของ HAL ซึ่งใช้ตัวยึดตำแหน่ง
- ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับกระบวนการนี้ได้ที่หลักการออกแบบเพื่อเป็นแนวทางในการแมปที่แนะนำ
ใช้เอฟเฟกต์เอนเวโลปเชิงเส้นแบบเป็นช่วง (PWLE)
- คำแนะนำการใช้งานสำหรับซองจดหมายแอมพลิจูดและความถี่
-
- วิธีการเกี่ยวกับเอฟเฟกต์การสัมผัสเป้าหมาย ใช้วิธีการต่อไปนี้เพื่อ ตรวจสอบฮาร์ดแวร์อย่างรวดเร็ว
