Effective in 2026, to align with our trunk stable development model and ensure platform stability for the ecosystem, we will publish source code to AOSP in Q2 and Q4. For building and contributing to AOSP, we recommend utilizing android-latest-release instead of aosp-main. The android-latest-release manifest branch will always reference the most recent release pushed to AOSP. For more information, see Changes to AOSP.
Host controller architecture
Stay organized with collections
Save and categorize content based on your preferences.
The architecture of VTS test framework integrates with its cloud-based test
serving service. A VTS host controller runs on a host machine and controls a
test harness (for example, Tradefed) instance as shown below:
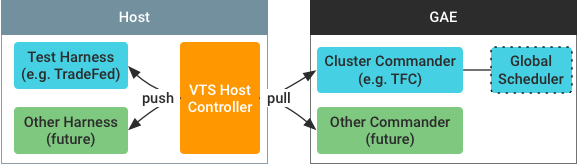
Figure 1. VTS host controller architecture.
The controller pulls commands from a cluster commander running as a Google App
Engine (GAE) instance, then relays commands and responses between its cluster
commander and the test harness instance.
This architecture includes the following advantages:
- Because it's decoupled from any test harness instance,
it can control different types of test harnesses and is more robust. The
alternative design (embedding the host control logic in a test harness) does
not block errors from propagating.
- Because it uses a pull-based command-and-control (C&C)
model, it can work with different types of cloud-side cluster
commanders as well as hosts that exist behind a firewall (for ingress
connections). The alternative design (push-based C&C model) might not allow
a cloud commander to access host controller instances that exist on host
computers in a private network.
Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-02 UTC.
[[["Easy to understand","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["Solved my problem","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["Other","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["Missing the information I need","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["Too complicated / too many steps","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["Out of date","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["Samples / code issue","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["Other","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["Last updated 2025-12-02 UTC."],[],[]]

