Il Vendor Native Development Kit (VNDK) richiede diverse modifiche a una codebase per separare le preoccupazioni tra fornitore e sistema. Utilizza la seguente guida per abilitare VNDK in una codebase fornitore/OEM.
Crea librerie di sistema
Il sistema di compilazione contiene diversi tipi di oggetti, tra cui librerie (condivise, statiche o di intestazione) e file binari.
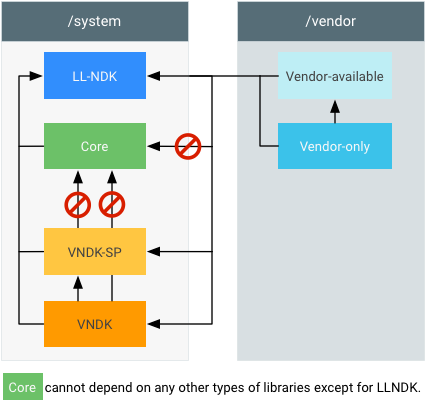
Figura 1. Crea librerie di sistema.
- Le librerie
corevengono utilizzate dall'immagine di sistema, sull'immagine di sistema. Queste librerie non possono essere utilizzate dalle librerievendor,vendor_available,vndkovndk-sp.cc_library { name: "libThatIsCore", ... }
- Le librerie
vendor-only(oproprietary) vengono utilizzate dall'immagine fornitore, sull'immagine fornitore.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVendorOnly", proprietary: true, # or: vendor: true, # (for things in AOSP) ... }
- Le librerie
vendor_availablevengono utilizzate dall'immagine del fornitore, sull'immagine del fornitore (potrebbero contenere duplicati dicore).cc_library { name: "libThatIsVendorAvailable", vendor_available: true, ... }
- Le librerie
vndkvengono utilizzate dall'immagine fornitore, sull'immagine di sistema.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVndk", vendor_available: true, vndk: { enabled: true, } ... }
- Le librerie
vndk-spvengono utilizzate dall'immagine del fornitore e anche dall'immagine di sistema indirettamente.cc_library { name: "libThatIsVndkSp", vendor_available: true, vndk: { enabled: true, support_system_process: true, } ... }
- Le librerie
llndkvengono utilizzate sia dalle immagini di sistema sia da quelle del fornitore.cc_library { name: "libThatIsLlndk", llndk: { symbol_file: "libthatisllndk.map.txt" } ... }
Quando una libreria è contrassegnata come vendor_available:true, viene creata
due volte:
- Una volta per la piattaforma (e quindi installato su
/system/lib) - Una volta per il fornitore (e quindi installato in
/vendor/libo VNDK APEX)
Le versioni fornitore delle librerie sono create con -D__ANDROID_VNDK__.
I componenti di sistema privati che potrebbero cambiare in modo significativo nelle versioni future di
Android sono disattivati con questo flag. Inoltre, librerie diverse esportano un insieme diverso di intestazioni (ad esempio liblog). Le opzioni specifiche per una variante del fornitore di una destinazione possono essere specificate in un file Android.bp in:
target: { vendor: { … } }Attivare VNDK per un codebase
Per attivare VNDK per un codebase:
- Determina l'idoneità calcolando le dimensioni richieste delle partizioni
vendor.imgesystem.img. - Attiva
BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current. Puoi aggiungere aBoardConfig.mko creare componenti direttamente (ad esempio,m -j BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current MY-LIB).
Dopo aver abilitato BOARD_VNDK_VERSION=current, il sistema di compilazione
applica i seguenti requisiti di dipendenza e intestazione.
Gestisci dipendenze
Un oggetto vendor che dipende da un componente core
che non esiste in vndk o come oggetto vendor
deve essere risolto utilizzando una delle seguenti opzioni:
- La dipendenza può essere rimossa.
- Se il componente
coreè di proprietà divendor, può essere contrassegnato comevendor_availableovendor. - Una modifica che rende l'oggetto principale parte di
vndkpotrebbe essere caricata su Google.
Inoltre, se un componente core ha dipendenze da un componente vendor, quest'ultimo deve essere trasformato in un componente core o la dipendenza deve essere rimossa in un altro modo (ad esempio, rimuovendo la dipendenza o spostandola in un componente vendor).vendor
Gestire le intestazioni
Le dipendenze delle intestazioni globali devono essere rimosse per consentire al sistema di build di sapere
se creare le intestazioni con o senza -D__ANDROID_VNDK__.
Ad esempio, le intestazioni libutils come utils/StrongPointer.h possono
essere ancora accessibili utilizzando la libreria di intestazioni
libutils_headers.
Alcune intestazioni (ad esempio unistd.h) non possono più essere incluse in modo transitivo,
ma possono essere incluse localmente.
Infine, la parte pubblica di private/android_filesystem_config.h
è stata spostata in cutils/android_filesystem_config.h. Per gestire
queste intestazioni, procedi in uno dei seguenti modi:
- Rimuovi la dipendenza da
private/android_filesystem_config.hsostituendo tutte le macroAID_*con chiamategetgrnam/getpwnam, se possibile. Ad esempio:(uid_t)AID_WIFIdiventagetpwnam("wifi")->pw_uid.(gid_t)AID_SDCARD_Rdiventagetgrnam("sdcard_r")->gr_gid.
private/android_filesystem_config.h. - Per gli AIS hardcoded, includi
cutils/android_filesystem_config.h.
