يصف هذا المستند تصميم عنصر واجهة المورّد (VINTF)، الذي يجمع المعلومات ذات الصلة بالجهاز ويُتيح هذه المعلومات من خلال واجهة برمجة تطبيقات قابلة للبحث.
تصميم عنصر VINTF
يجمع عنصر VINTF بعض المعلومات التي يحتاجها مباشرةً من الجهاز. ويتم وصف الجوانب الأخرى، مثل ملفات البيان، بشكل ثابت في ملف XML.
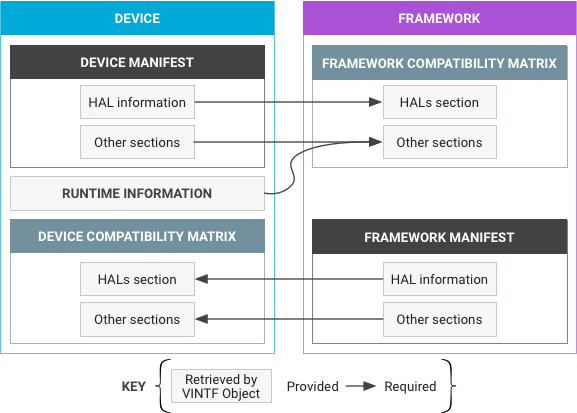
الشكل 1: ملفات البيان ومصفوفات التوافق والمعلومات التي يمكن جمعها في وقت التشغيل
يقدّم تصميم عنصر VINTF ما يلي لمكونات الإطار والجهاز:
| للجهاز | بالنسبة إلى "إطار العمل" |
|---|---|
|
|
يجب أن يكون عنصر VINTF موثوقًا وأن يقدّم المعلومات الكاملة نفسها بغض النظر عن وقت طلب العنصر (راجِع الاحتياطات).
ملفات البيانات والمصفّحات
اعتبارًا من Android 8.0، تبحث واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لوقت التشغيل في المحتوى المتوفّر على الجهاز وترسل هذه
المعلومات إلى خادم التحديث اللاسلكي (OTA)
والجهات المعنيّة الأخرى (مثل CTS
DeviceInfo). ويتم استرداد بعض المعلومات في وقت التشغيل، ويكون بعضها
محددًا بشكل ثابت.
- يصف بيان الجهاز المكوّن الثابت لما يمكن أن يوفّره الجهاز للإطار.
- تصف مصفوفة توافق إطار العمل المتطلبات التي يتوقعها إطار عمل Android من جهاز معيّن. المصفوفة هي عنصر ثابت يتم تحديد تركيبته يدويًا أثناء تطوير الإصدار التالي من إطار عمل Android.
- يصف بيان إطار العمل الخدمات العالية المستوى التي يمكن لإطار العمل تقديمها للجهاز.
- توضِّح مصفوفة توافق الأجهزة الخدمات التي تتطلّب صورة المورّد من إطار العمل. ويتم تحديد تركيبته يدويًا أثناء تطوير الجهاز.
يجب مراجعة هذين الزوجين من البيانات والمصفّحات في وقت التحديث عبر شبكة غير سلكيّة لضمان حصول الجهاز على تحديثات إطار العمل المتوافقة مع إمكانات الجهاز. بشكل عام، يصف البيان ما يتم تقديمه، وتصف مصفوفة التوافق ما هو مطلوب.
يتضمّن هذا القسم التفاصيل التالية حول نماذج البيانات والمصفّحات:
- تحدِّد ملفات البيان بيان الجهاز وبيان إطار العمل ومخطّط ملف البيان.
- مصفوفات التوافق: تحدِّد هذه السمة مخطّط مصفوفة التوافق.
- تفاصيل دورة حياة FCM: كيفية إيقاف واجهات HIDL HAL نهائيًا وإزالتها وكيفية تعديل ملفات FCM لعكس حالة إصدار HAL
- يصف تطوير إدارة الخدمات كيفية تحديد المورّدين للإصدار المستهدَف من "إطار عمل إدارة إشعارات Android" وتعريفه في بيان الجهاز للأجهزة الجديدة أو تنفيذ إصدارات جديدة من HAL وزيادة الإصدار المستهدَف من "إطار عمل إدارة إشعارات Android" عند ترقية صورة المورّد للأجهزة القديمة.
- تحدِّد قواعد المطابقة قواعد المطابقة الناجحة بين مصفوفة التوافق وملف البيان.
