Ocena sprzętu jest przeprowadzana za pomocą tego oprogramowania:
- Audacity (zainstalowany na komputerze)
- MATLAB (zainstalowany na komputerze)
- Aplikacja do testowania haptyki (zainstalowana na testowanym urządzeniu)
Więcej informacji o wymaganiach systemowych znajdziesz w artykułach Audacity na Windowsa, Audacity na Maca i MATLAB.
Konfigurowanie Audacity
Audacity musi być skonfigurowany tak, aby odbierać sygnał z karty dźwiękowej Sound Blaster z określoną częstotliwością próbkowania danych. Po podłączeniu Sound Blastera do portu USB komputera otwórz Audacity i postępuj zgodnie z tymi instrukcjami.
Wybierz Line (USB Sound Blaster HD) jako źródło mikrofonu wejściowego, podłączając fizycznie wyjście CCLD do portu wejściowego Line In karty Sound Blaster.
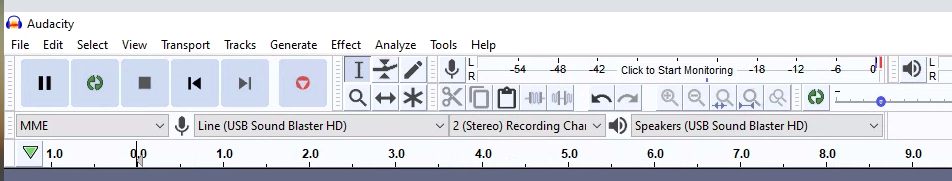
Rysunek 1. Wybieranie wejścia mikrofonu
Ustaw częstotliwość próbkowania na 48 kHz, wybierając 48000 w menu Częstotliwość projektu.

Rysunek 2. Ustawianie częstotliwości próbkowania
Pobierz MATLAB
Pobierz plik MATLAB.
Rozpakuj plik i znajdź
Effect1NEffect2_V1p0_2020PM.m(w przypadku efektu 1 i efektu 2) orazEffect3_V1p0_2020PM.m(w przypadku efektu 3).
Konfigurowanie aplikacji testowej na telefonie
W tej sekcji opisujemy, jak skonfigurować aplikację testową na telefonie.
Przygotowanie aplikacji testowej
- Skopiuj kod źródłowy z bloków kodu Java i Kotlin poniżej. Wybierz opcję, która najbardziej Ci odpowiada.
- Napisz własny kod, korzystając z parametrów interfejsu graficznego przedstawionych na rysunku 3. W razie potrzeby dostosuj szczegóły kodu źródłowego układu do swojego telefonu.
Upewnij się, że interfejs graficzny zawiera 3 przyciski, które można kliknąć, oraz wskaźnik wizualny określający obszar, w którym ma się znajdować akcelerometr.
- Obszar, w którym ma się znajdować akcelerometr, odpowiada obszarowi ekranu urządzenia, który jest zwykle dotykany ręką.
- Podczas tego pomiaru możesz przesuwać akcelerometr w turkusowym obszarze, aby znaleźć obszar ekranu, który rejestruje najsilniejszy sygnał.
Zainstaluj kod na urządzeniu z Androidem.
Jeśli domyślny tryb nawigacji to przyciski, zalecamy ustawienie trybu gestów.
- Ustawiając tryb gestów, możesz umieścić akcelerometr jak najniżej na telefonie, nie przeszkadzając w działaniu interfejsów nawigacji systemowej telefonu.
kod źródłowy Java,
package com.example.hapticeffectassessment;
import static android.os.VibrationEffect.EFFECT_CLICK;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.VibrationEffect;
import android.os.Vibrator;
import android.widget.Button;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final long oneShotTiming = 20;
private static final int oneShotAmplitude = 255;
private static final long[] waveformTimings = {500, 500};
private static final int[] waveformAmplitudes = {128, 255};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Vibrator vibrator = getSystemService(Vibrator.class);
// Click R.id.button1 button to generate Effect 1
findViewById(R.id.button1).setOnClickListener(
view -> vibrator.vibrate(VibrationEffect.createPredefined(EFFECT_CLICK)));
// Click R.id.button2 button to generate Effect 2
findViewById(R.id.button2).setOnClickListener(
view -> vibrator.vibrate(VibrationEffect.createOneShot(oneShotTiming, oneShotAmplitude)));
// Click R.id.button3 button to generate Effect 3
findViewById(R.id.button3).setOnClickListener(view -> {
vibrator.vibrate(VibrationEffect.createWaveform(waveformTimings, waveformAmplitudes, -1));
// See quick results of Effect 3
Button button = (Button) view;
if (vibrator.hasAmplitudeControl()) {
button.setText("Effect 3: PASS");
button.setBackgroundColor(Color.GREEN);
button.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
} else {
button.setText("Effect 3: FAIL");
button.setBackgroundColor(Color.RED);
button.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
}
});
}
}
Kod źródłowy w języku Kotlin
package com.example.hapticeffectassessment
import android.graphics.Color
import android.os.Bundle
import android.os.VibrationEffect
import android.os.VibrationEffect.EFFECT_CLICK
import android.os.Vibrator
import android.widget.Button
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
class MainActivityKt : AppCompatActivity() {
private val oneShotTiming: Long = 20
private val oneShotAmplitude = 255
private val waveformTimings = longArrayOf(500, 500)
private val waveformAmplitudes = intArrayOf(128, 255)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val vibrator = getSystemService(Vibrator::class.java)
// Click button1 to generate Effect 1
button1.setOnClickListener {
vibrator.vibrate(VibrationEffect.createPredefined(EFFECT_CLICK))
}
// Click button2 to generate Effect 2
button2.setOnClickListener {
vibrator.vibrate(VibrationEffect.createOneShot(oneShotTiming, oneShotAmplitude))
}
// Click button3 to generate Effect 3
button3.setOnClickListener {
vibrator.vibrate(
VibrationEffect.createWaveform(waveformTimings, waveformAmplitudes, -1))
// See quick results of Effect 3
if (vibrator.hasAmplitudeControl()) {
button3.text = "Effect 3: PASS"
button3.setBackgroundColor(Color.GREEN)
button3.setTextColor(Color.BLACK)
} else {
button3.text = "Effect 3: FAIL"
button3.setBackgroundColor(Color.RED)
button3.setTextColor(Color.WHITE)
}
}
}
}
Kod źródłowy układu (activity_main.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="350dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_marginStart="32dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="32dp"
android:text="Effect 1"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="350dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_marginStart="32dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="32dp"
android:text="Effect 2"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="350dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_marginStart="32dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="32dp"
android:text="Effect 3"
android:textSize="18sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button2" />
<View
android:id="@+id/divider"
android:layout_width="363dp"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:layout_marginStart="32dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="32dp"
android:background="?android:attr/listDivider"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.5"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button3" />
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:layout_width="363dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.5"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/divider">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:adjustViewBounds="true"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.5"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:srcCompat="@drawable/bluebar" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
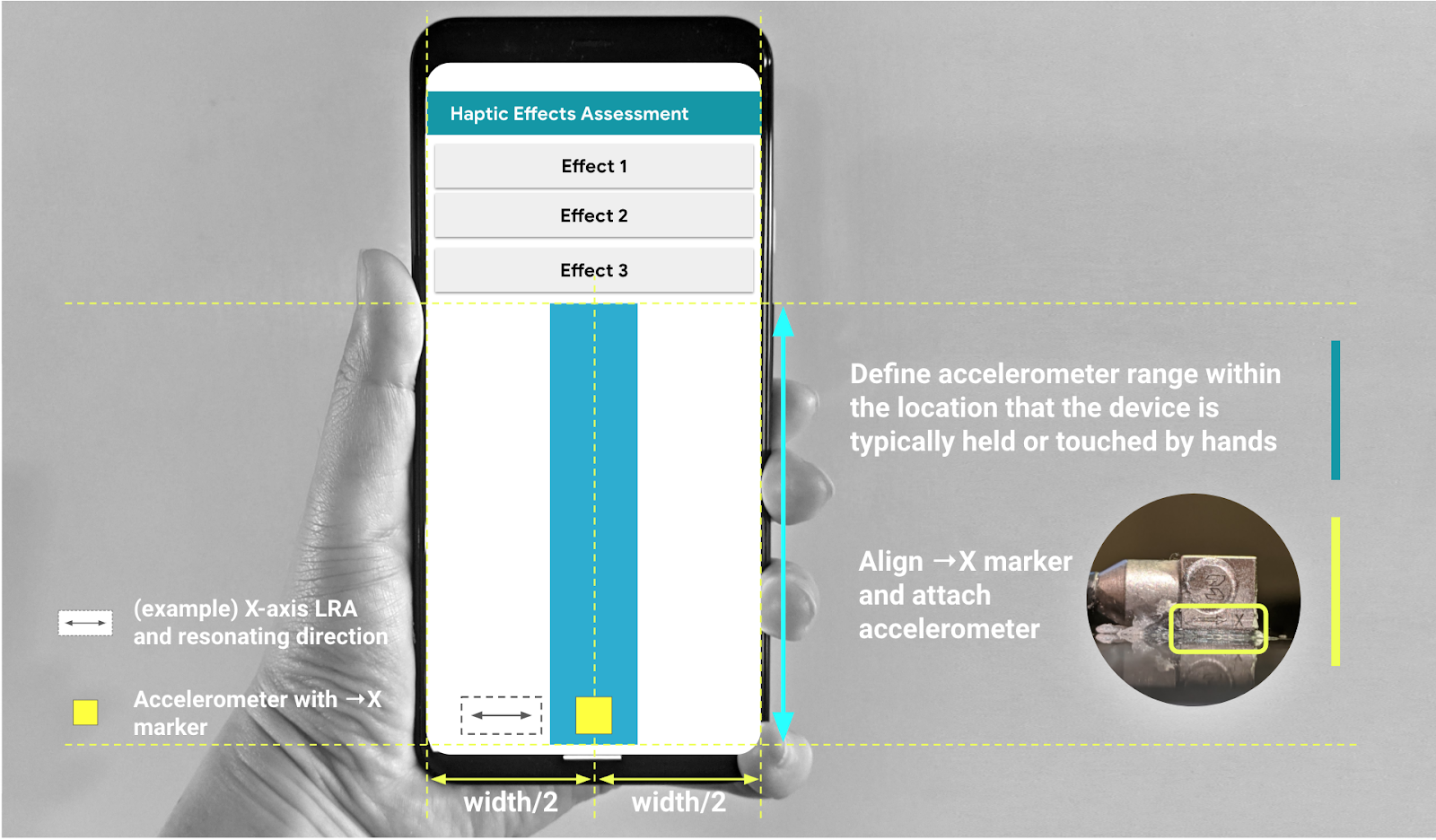
Rysunek 3. Przymocuj akcelerometr w miejscu zalecanym w GUI.
