تستند نواة Android إلى نواة Linux Long Term Supported (LTS). في Google، يتم دمج نواة LTS مع تصحيحات خاصة بنظام Android لتشكيل نواة Android المشتركة (ACK).
يتم إنشاء حِزم ACK من مستودع kernel/common. هذا المستودع هو مجموعة شاملة من نواة Linux الأصلية، ويتضمّن تصحيحات إضافية خاصة بنظام Android.
تُعرف حزم ACK بالإصدار 5.10 والإصدارات الأحدث أيضًا باسم نِوى *صور النواة العامة (GKI). تتيح نِوى GKI فصل رمز نواة النظام الأساسي العامة غير المرتبطة بالأجهزة ووحدات GKI عن وحدات المورّد الخاصة بالأجهزة.
يتم تفعيل التفاعل بين نواة GKI ووحدات البائع من خلال واجهة وحدة النواة (KMI) التي تتألف من قوائم الرموز التي تحدّد الوظائف والبيانات العامة التي تتطلّبها وحدات البائع. يوضّح الشكل 1 بنية نواة GKI ووحدة المورّد:
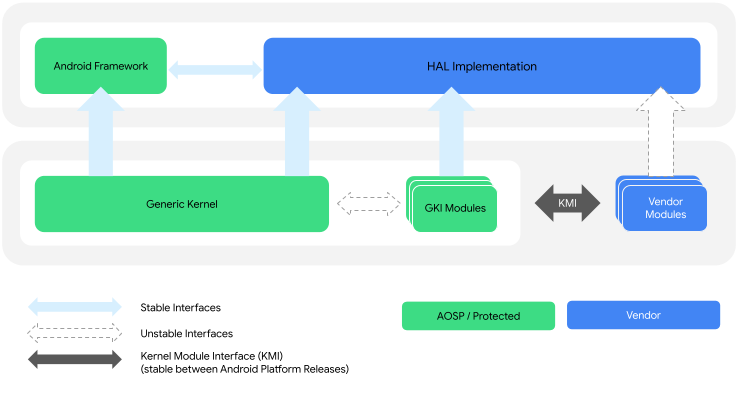
الشكل 1. بنية نواة GKI ووحدة المورّد
مسرد مصطلحات النواة
في ما يلي المصطلحات المستخدَمة في مستندات النواة.
أنواع النواة
- نواة Android المشتركة (ACK)
- نواة مشتقة من نواة LTS وتتضمّن تصحيحات مهمة لمنتدى Android. لم يتم دمج هذه التصحيحات في نواة Linux الرئيسية أو نواة GKI طويلة الأمد.
يُشار أيضًا إلى النواة التي تتضمّن الإصدار 5.10 والإصدارات الأحدث باسم نواة صورة النواة العامة (GKI).
- نواة "مشروع Android المفتوح المصدر" (AOSP)
- اطّلِع على نواة Android المشتركة.
لا يمكن نقل ميزات Android 12 إلى الإصدارات السابقة من النواة 4.19، وستكون مجموعة الميزات مشابهة لتلك المتوفّرة على جهاز تم إطلاقه بالإصدار 4.19 من نظام التشغيل Android 11 وتمت ترقيته إلى Android 12.
- نواة "صورة النواة العامة" (GKI)
أي إصدار 5.10 والإصدارات الأحدث من نواة ACK(aarch64 فقط) تتضمّن نواة GKI هذين الجزأين:
نواة عامة: هي جزء من نواة GKI يكون مشتركًا بين جميع الأجهزة.
وحدات GKI: وحدات نواة أنشأتها Google ويمكن تحميلها بشكل ديناميكي على الأجهزة عند الاقتضاء. يتم إنشاء هذه الوحدات النمطية كعناصر من نواة GKI ويتم توفيرها مع GKI كأرشيف
system_dlkm_staging_archive.tar.gz. توقّع Google وحدات GKI باستخدام زوج المفاتيح الخاص بوقت إنشاء النواة، ولا تكون هذه الوحدات متوافقة إلا مع نواة GKI التي تم إنشاؤها بها.
- نواة Kernel Module Interface (KMI)
راجِع نواة GKI.
- نواة الدعم الطويل الأمد (LTS)
نواة Linux متوافقة لمدة تتراوح بين سنتَين و6 سنوات يتم إصدار نواة LTS مرة واحدة في السنة، وهي الأساس لكل نواة Android المشتركة من Google.
أنواع الفروع
- فرع نواة ACK KMI
- الفرع الذي يتم إنشاء نواة GKI له. تتوافق أسماء الفروع مع إصدارات النواة، مثل
android15-6.6. - Android-mainline
- فرع التطوير الأساسي لميزات Android عند الإعلان عن نواة LTS جديدة في المصدر الرئيسي، يتم إنشاء فرع من نواة GKI الجديدة المطابقة من android-mainline.
الإصدار الرئيسي من Linux : هو فرع التطوير الأساسي لنواة Linux الأصلية، بما في ذلك نواة LTS.
مصطلحات أخرى
- صورة التشغيل المتحقَّق منه
- يتم تسليم النواة في شكل ثنائي (
boot.img) وتثبيتها على الجهاز. تُعدّ هذه الصورة معتمَدة لأنّها تتضمّن شهادات مضمّنة، وبالتالي يمكن لـ Google التحقّق من أنّ الجهاز يتضمّن نواة معتمَدة من Google. - وحدة نواة قابلة للتحميل بشكل ديناميكي (DLKM)
- وحدة يمكن تحميلها بشكل ديناميكي أثناء تشغيل الجهاز، وذلك حسب احتياجات الجهاز. وحدات GKI ووحدات المورّد هي نوعان من وحدات DLKM. يتم إصدار وحدات DLKM بتنسيق
.ko، ويمكن أن تكون برامج تشغيل أو يمكنها توفير وظائف أخرى لنواة النظام. - مشروع GKI
- أحد مشاريع Google التي تهدف إلى معالجة تجزئة النواة من خلال فصل وظائف النواة الأساسية الشائعة عن وظائف SoC الخاصة بالمورّد ووظائف دعم اللوحة في وحدات قابلة للتحميل.
صورة النواة العامة (GKI) : هي صورة تمهيد معتمَدة من Google تحتوي على نواة GKI تم إنشاؤها من شجرة مصدر ACK ومناسبة لتثبيتها في قسم التمهيد لجهاز يعمل بنظام التشغيل Android.
- واجهة وحدة النواة (KMI)
- واجهة بين نواة GKI ووحدات المورّدين تتيح تعديل وحدات المورّدين بشكل مستقل عن نواة GKI تتألف هذه الواجهة من دوال النواة والبيانات العامة التي تم تحديدها على أنّها تبعيات المورّد/مصنّع المعدات الأصلية باستخدام قوائم الرموز لكل شريك.
- وحدة المورّدين
- وحدة نمطية خاصة بالأجهزة طوّرها أحد الشركاء وتحتوي على وظائف خاصة بالمنظومة على الرقاقة (SoC) والجهاز. وحدة البائع هي نوع من وحدات النواة التي يمكن تحميلها بشكل ديناميكي.
الخطوات التالية
إذا كنت حديث العهد بتطوير نواة Android، ابدأ بقراءة ما يلي:
- نواة الإصدارات الثابتة الطويلة الأمد - معلومات أساسية عن نواة الإصدارات الثابتة الطويلة الأمد التي يتم دمجها في حِزم ACK.
- نواة Android الشائعة - معلومات أساسية عن نواة Android الشائعة
إذا كنت حديث العهد بتطوير نواة GKI، ابدأ بقراءة تطوير GKI.
