आम तौर पर, डिवाइस बनाने वाली कंपनियों को हर डिवाइस के लिए बनाई गई निजी ऐसेट का मालिक माना जाता है. इसलिए, उनकी इंजीनियरिंग टीम अक्सर हर डिवाइस के हिसाब से काम करती है. वे इकोसिस्टम में शामिल अन्य डिवाइसों के बीच एक जैसा अनुभव देने पर ज़्यादा ध्यान नहीं देती हैं.
इसके उलट, डेवलपर ऐसे ऐप्लिकेशन बनाने की कोशिश करते हैं जो Android के पूरे इकोसिस्टम में मौजूद सभी फ़ोन पर काम करें. भले ही, हर डिवाइस की तकनीकी खासियतें अलग-अलग हों. इस तरह के अलग-अलग तरीकों की वजह से, फ़्रैगमेंटेशन की समस्या हो सकती है. उदाहरण के लिए, कुछ फ़ोन के हार्डवेयर की क्षमताएं, ऐप्लिकेशन डेवलपर की तय की गई उम्मीदों से मेल नहीं खाती हैं. इसलिए, अगर हैप्टिक एपीआई कुछ Android फ़ोन पर काम करते हैं, लेकिन अन्य पर नहीं, तो इसका मतलब है कि अलग-अलग डिवाइसों पर एक जैसा अनुभव नहीं मिल रहा है. इसलिए, हार्डवेयर कॉन्फ़िगरेशन यह पक्का करने में अहम भूमिका निभाता है कि मैन्युफ़ैक्चरर, हर डिवाइस पर Android हैप्टिक्स एपीआई लागू कर सकें.
इस पेज पर, Android हैप्टिक्स एपीआई का बेहतर तरीके से इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, हार्डवेयर के मानकों का पालन करने से जुड़ी चेकलिस्ट दी गई है.
नीचे दिए गए डायग्राम में, डिवाइस बनाने वाली कंपनियों और डेवलपर के बीच सामान्य जानकारी शेयर करने की प्रोसेस दिखाई गई है. एक साथ काम करने वाले इकोसिस्टम को बनाने के लिए, यह एक ज़रूरी चरण है:
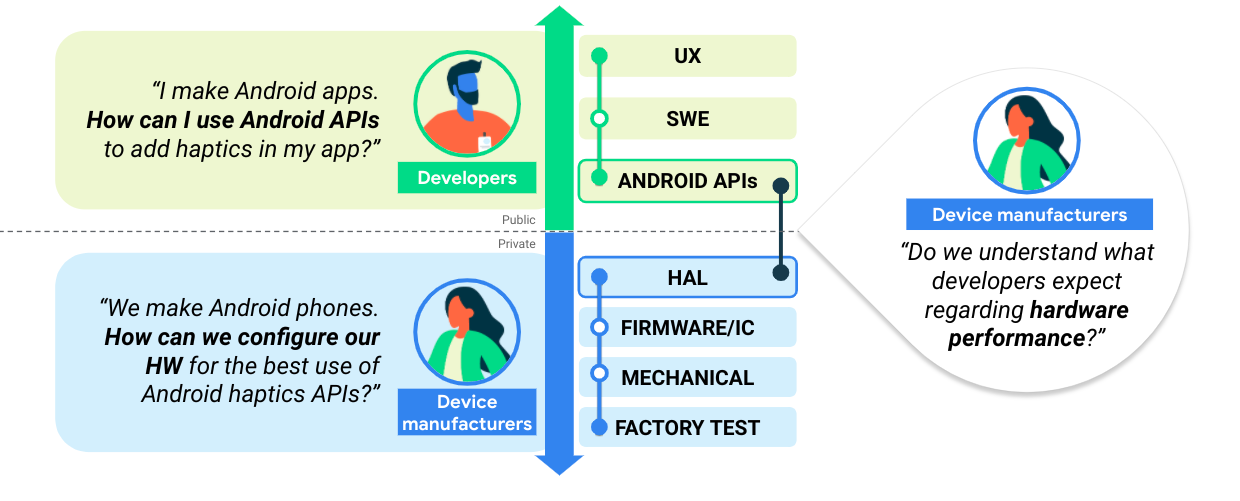
पहली इमेज. डिवाइस बनाने वाली कंपनियों और डेवलपर के बीच जानकारी शेयर करना
हैप्टिक्स की सुविधा लागू करने से जुड़ी चेकलिस्ट
-
- हैप्टिक लागू करने के लिए कॉन्स्टेंट की सूची.
-
- एचएएल कंपोज़िशन प्रिमिटिव को लागू करने के लिए दिशा-निर्देश.
HAL और एपीआई के बीच कॉन्स्टेंट मैप करना
- सार्वजनिक एपीआई के कॉन्स्टेंट (फ़्रेमवर्क में इन्हें प्लेसहोल्डर कहा जाता है) और HAL कॉन्स्टेंट के बीच मैपिंग के सुझाव. ये सुझाव, प्लेसहोल्डर लागू करते हैं.
- इस प्रोसेस के बारे में ज़्यादा जानने के लिए, सुझाए गए मैपिंग के लिए डिज़ाइन के सिद्धांत देखें.
पीसवॉइस लीनियर एनवलप (पीडब्ल्यूएलई) इफ़ेक्ट लागू करना
- ऐंप्लीट्यूड और फ़्रीक्वेंसी एनवलप लागू करने के लिए दिशा-निर्देश.
-
- टारगेट हैप्टिक इफ़ेक्ट से जुड़े निर्देश. अपने हार्डवेयर की तुरंत जांच करने के लिए, इन निर्देशों का पालन करें.
