دستگاههای اندرویدی شامل چندین پارتیشن یا بخشهای خاصی از فضای ذخیرهسازی هستند که برای قسمتهای خاصی از نرمافزار دستگاه استفاده میشوند. هر پارتیشن شامل یک تصویر پارتیشن (یک فایل IMG) یا عکس فوری از تمام نرم افزارهای پارتیشن است. شکل 1 طرح پارتیشن های هسته روی یک دستگاه را نشان می دهد:
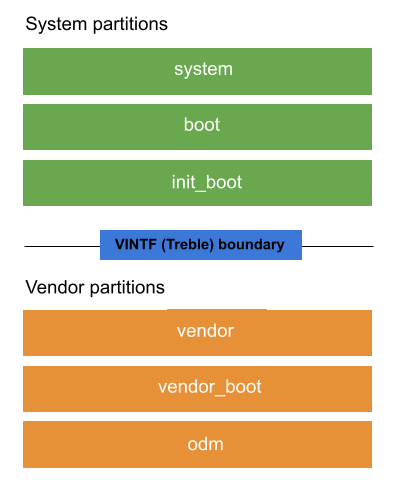
شکل 1. چیدمان پارتیشن های هسته.
پارتیشن ها به سه دسته تقسیم می شوند:
پارتیشن های سیستم پارتیشن هایی هستند که هنگام به روز رسانی سیستم عامل و سایر ویژگی ها به روز می شوند.
system،bootوinit_bootپارتیشن های اصلی سیستم هستند.پارتیشن های فروشنده حاوی کد مخصوص دستگاه و سخت افزار هستند که ممکن است پس از انتشار اولیه هرگز به روز نشوند. پارتیشنهای
vendor،vendor_bootوodmپارتیشنهای فروشنده اصلی هستند.پارتیشنهای غیرقابل بهروزرسانی، پارتیشنهایی هستند که محتوای آنها یا بهروزرسانی نمیشوند یا با دادههای کاربر بهروزرسانی میشوند.
کدهای موجود در سیستم و پارتیشن های فروشنده می توانند با استفاده از یک رابط پایدار به نام رابط فروشنده (VINTF) تعامل داشته باشند.
پارتیشن های سیستم
در زیر لیستی از تمام پارتیشن های سیستم و کاربرد آنها آمده است:
پارتیشن
bootاین پارتیشن حاوی یک تصویر هسته عمومی (GKI) است. این پارتیشن همچنین حاوی ramdisk عمومی در دستگاه های راه اندازی شده در اندروید 12 و پایین تر است. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد ramdisk عمومی، به محتویات تصویر ramdisk عمومی مراجعه کنید.پارتیشن
init_boot(اندروید 13 و بالاتر). این پارتیشن شامل یک ramdisk عمومی است. در اندروید 11 و 12، ramdisk عمومی در پارتیشنbootاست.پارتیشن
systemاین پارتیشن حاوی تصویر سیستم مورد استفاده برای محصولات OEM است.پارتیشن
system_ext. این پارتیشن شامل منابع سیستم و ماژول های سیستم اختصاصی است که تصویر سیستم مشترک را در پارتیشنsystemگسترش می دهد.پارتیشن
system_dlkm. این پارتیشن شامل ماژول های GKI می باشد. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد این پارتیشن، به پیاده سازی پارتیشن ماژول GKI مراجعه کنید.پارتیشن
productاین پارتیشن میتواند شامل ماژولهای خاص محصول باشد که با هیچ پارتیشن دیگری همراه نیستند.پارتیشن
pvmfw. این پارتیشن Firmware ماشین مجازی محافظت شده (pvmfw) را ذخیره می کند که اولین کدی است که در VM های محافظت شده اجرا می شود. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، سفتافزار ماشین مجازی محافظتشده را ببینید.پارتیشن
generic_bootloader. این پارتیشن شامل بوت لودر عمومی است.
پارتیشن های فروشنده
در زیر لیستی از تمام پارتیشن های فروشنده و کاربرد آنها آمده است:
پارتیشن
vendor_boot. این پارتیشن حاوی کد بوت مخصوص فروشنده است. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به پارتیشنهای بوت فروشنده مراجعه کنید.پارتیشن
recoveryاین پارتیشن تصویر بازیابی را ذخیره می کند که در طی فرآیند به روز رسانی over-the-air (OTA) بوت می شود. دستگاههایی که از بهروزرسانیهای یکپارچه پشتیبانی میکنند میتوانند تصاویر بازیابی را بهعنوان یک ramdisk موجود در تصویرbootیاinit_bootذخیره کنند. برای اطلاعات بیشتر درباره بهروزرسانیهای بدون درز، بهروزرسانیهای A/B (بدون درز) را ببینید.پارتیشن
miscاین پارتیشن توسط پارتیشن بازیابی استفاده می شود و 4 کیلوبایت یا بزرگتر است.پارتیشن
vbmeta. این پارتیشن حاوی اطلاعات Verified Boot برای همه پارتیشن ها است. این اطلاعات تایید می کند که تصاویر نصب شده در هر پارتیشن قابل اعتماد هستند. برای اطلاعات بیشتر در مورد بوت تایید شده، به بوت تایید شده مراجعه کنید.پارتیشن
vendorاین پارتیشن حاوی هر باینری است که خاص فروشنده است و به اندازه کافی عمومی نیست تا در AOSP توزیع شود.پارتیشن
vendor_dlkm. این پارتیشن شامل ماژول های هسته فروشنده است. با ذخیره ماژول های هسته فروشنده در این پارتیشن به جای پارتیشنvendor، می توانید ماژول های هسته را بدون به روز رسانی پارتیشنvendorبه روز کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به پارتیشنهای Vendor و ODM DKLM مراجعه کنید.پارتیشن
odmاین پارتیشن شامل سفارشیسازیهای سازنده طراحی اصلی (ODM) برای بستههای پشتیبانی هیئت مدیره فروشنده (BSP) سیستم روی تراشه (SoC) است. چنین سفارشیسازیهایی ODMها را قادر میسازد تا اجزای SoC را جایگزین یا سفارشی کنند و ماژولهای هسته را برای اجزای برد، دیمونها و ویژگیهای خاص ODM بر روی لایههای انتزاعی سختافزاری (HAL) پیادهسازی کنند. این پارتیشن اختیاری است. معمولاً از این پارتیشن برای سفارشیسازی استفاده میشود تا دستگاهها بتوانند از یک تصویر فروشنده برای چندین SKU سختافزاری استفاده کنند. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به پارتیشنهای ODM مراجعه کنید.پارتیشن
odm_dlkm. این پارتیشن به ذخیره سازی ماژول های هسته ODM اختصاص یافته است. با ذخیره ماژول های هسته ODM در این پارتیشن، به جای پارتیشنodm، می توانید ماژول های هسته ODM را بدون به روز رسانی پارتیشنodmبه روز کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، به پارتیشنهای Vendor و ODM DKLM مراجعه کنید.پارتیشن
radioاین پارتیشن حاوی تصویر رادیویی است و فقط برای دستگاه هایی که دارای رادیو با نرم افزار مخصوص رادیو در یک پارتیشن اختصاصی هستند مورد نیاز است.
پارتیشن های غیرقابل به روز رسانی
در زیر لیستی از تمام پارتیشن های غیرقابل به روز رسانی و کاربرد آنها آمده است:
پارتیشن
cacheاین پارتیشن حاوی دادههای موقتی است و اگر دستگاه شما از بهروزرسانیهای یکپارچه استفاده میکند اختیاری است. این پارتیشن نیازی به نوشتن از بوت لودر ندارد، اما باید پاک شود. اندازه پارتیشن به نوع دستگاه و در دسترس بودن فضا درuserdataبستگی دارد. معمولاً 50 تا 100 مگابایت کافی است.پارتیشن
userdataاین پارتیشن شامل برنامه ها و داده های نصب شده توسط کاربر، از جمله داده های سفارشی سازی است.پارتیشن
metadataاگر دستگاه شما از رمزگذاری فراداده استفاده می کند، این پارتیشن حاوی کلید رمزگذاری ابرداده است. اندازه این پارتیشن 16 مگابایت یا بزرگتر است، رمزگذاری نشده است و اطلاعات آن عکس فوری نیست. این پارتیشن با بازنشانی کارخانه ای دستگاه پاک می شود.
قوانین و توصیه های به روز رسانی پارتیشن
توصیه می کنیم تمام پارتیشن های سیستم را به طور کلی و همه پارتیشن های فروشنده را به عنوان یک کل دیگر به روز کنید. با به روز رسانی مجموعه پارتیشن ها به عنوان یک کل، می توانید آزمایش کنید تا بررسی کنید که رابط بین تصاویر در هر پارتیشن ثابت بماند.
صرف نظر از اینکه چگونه پارتیشن های خود را به روز می کنید، پارتیشن های زیر باید به دلیل وابستگی های مرتبط و عدم وجود API های پایدار به روز شوند:
- پارتیشن های
bootوsystem_dlkm - پارتیشنهای
init_boot،system،system_extوproduct
پارتیشن های پویا
دستگاههای دارای Android 11 و بالاتر میتوانند از پارتیشنهای پویا پشتیبانی کنند، این پارتیشنها یک سیستم پارتیشنبندی فضای کاربران برای Android هستند که به شما امکان میدهند پارتیشنها را در طول بهروزرسانیهای هوایی (OTA) ایجاد، تغییر اندازه یا تخریب کنید. برای اطلاعات بیشتر، پارتیشنهای پویا را ببینید.
انواع محصول سونگ
سیستم ساخت Soong از انواع تصویر برای تقسیم وابستگی های ساخت استفاده می کند. ماژولهای بومی ( /build/soong/cc ) میتوانند ماژولهای فرآیند سیستم را به نوع اصلی و ماژولهای فرآیند فروشنده را به نوع فروشنده تغییر دهند. یک ماژول در یک نوع تصویر نمی تواند به ماژول های دیگر در یک نوع تصویر متفاوت پیوند داده شود.
در Android 12 یا بالاتر، یک ماژول سیستم با vendor_available: true یک نوع فروشنده را علاوه بر نوع اصلی ایجاد میکند. برای ایجاد یک نوع محصول، product_available: true باید تعریف شود. برخی از کتابخانه های VNDK بدون product_available: true برای ماژول های محصول در دسترس نیستند.

