برای پیادهسازی بهروزرسانیهای هوایی (OTA) ، بوتلودر باید بتواند به دیسک RAM بازیابی در هنگام بوت دسترسی داشته باشد. اگر دستگاه از یک تصویر بازیابی AOSP اصلاح نشده استفاده کند، بوت لودر 32 بایت اول پارتیشن misc را می خواند. اگر دادههای موجود با boot-recovery مطابقت داشته باشند، بوت لودر به تصویر recovery میشود. این روش هر کار بازیابی معلق (مثلاً اعمال OTA یا حذف داده ها) را قادر می سازد تا تکمیل شود.
برای جزئیات بیشتر در مورد محتوای یک بلوک در فلش که برای ارتباطات توسط بازیابی و بوت لودر استفاده می شود، به bootable/recovery/bootloader_message/bootloader_message.h مراجعه کنید.
دستگاه هایی با به روز رسانی A/B
برای پشتیبانی از بهروزرسانیهای OTA در دستگاههایی که از بهروزرسانیهای A/B استفاده میکنند، مطمئن شوید که بوتلودر دستگاه دارای معیارهای زیر است.
معیارهای عمومی
تمام پارتیشنهایی که از طریق OTA بهروزرسانی میشوند باید در زمانی که سیستم اصلی بوت میشود (و در بازیابی بهروزرسانی نمیشوند) قابل بهروزرسانی باشند.
برای بوت کردن پارتیشن
system، بوت لودر مقدار زیر را در خط فرمان هسته ارسال می کند:ro root=/dev/[node] rootwait init=/init.فراخوانی
markBootSuccessfulاز HAL بر عهده چارچوب Android است. بوت لودر هرگز نباید پارتیشنی را به عنوان بوت شده با موفقیت علامت گذاری کند.
پشتیبانی از کنترل بوت HAL
بوت لودر باید از boot_control HAL همانطور که در hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h تعریف شده است، پشتیبانی کند. بهروزرسانیکننده کنترل راهاندازی HAL را پرس و جو میکند، شکاف راهاندازی را که استفاده نمیشود بهروزرسانی میکند، شکاف فعال را با استفاده از HAL تغییر میدهد و در سیستم عامل بهروزرسانیشده راهاندازی مجدد میشود. برای جزئیات، به پیاده سازی کنترل بوت HAL مراجعه کنید.
پشتیبانی از اسلات
بوت لودر باید از عملکردهای مربوط به پارتیشن ها و اسلات ها پشتیبانی کند، از جمله:
نام پارتیشن ها باید دارای پسوندی باشد که مشخص کند کدام پارتیشن ها به یک اسلات خاص در بوت لودر تعلق دارند. برای هر یک از این پارتیشن ها، یک متغیر متناظر
has-slot: partition base nameبا مقدارyes. اسلات ها بر اساس حروف الفبا به صورت a، b، c و غیره نامگذاری می شوند که مربوط به پارتیشن هایی با پسوند_a،_b،_c، و غیره است. بوت لودر باید با استفاده از ویژگی خط فرمانandroidboot.slot_suffixبه سیستم عامل اطلاع دهد که کدام اسلات بوت شده است. این ویژگی از طریق bootconfig برای دستگاه هایی که با Android 12 یا بالاتر راه اندازی می شوند تنظیم می شود.مقدار
slot-retry-countبه یک مقدار مثبت (معمولاً3) بازنشانی میشود، یا توسط کنترل راهانداز HAL از طریق پاسخ تماسsetActiveBootSlotیا از طریق دستورfastboot set_active. هنگام اصلاح پارتیشنی که بخشی از یک اسلات است، بوت لودر «با موفقیت راهاندازی شده» را پاک میکند و تعداد تلاش مجدد را برای اسلات بازنشانی میکند.
بوت لودر باید تعیین کند که کدام اسلات بارگذاری شود. شکل نمونه ای از فرآیند تصمیم گیری را نشان می دهد.
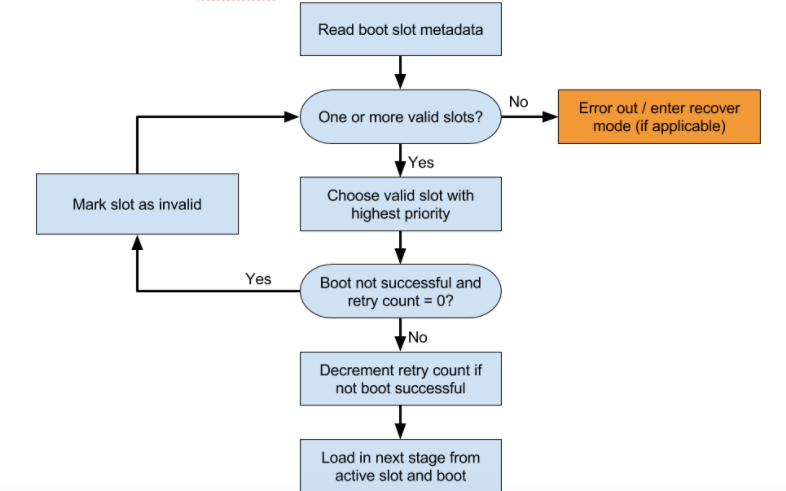
تعیین کنید که کدام شکاف را امتحان کنید. سعی نکنید شکافی را که با علامت
slot-unbootableمشخص شده است، بارگیری نکنید. این اسلات باید با مقادیر بازگردانده شده توسط fastboot مطابقت داشته باشد و به آن اسلات فعلی می گویند.اگر شکاف فعلی بهعنوان
slot-successfulعلامتگذاری نشده است و دارایslot-retry-count = 0است، شکاف فعلی را بهعنوانslot-unbootableعلامتگذاری کنید. سپس یک اسلات متفاوت را انتخاب کنید کهunbootableنیست و بهعنوانslot-successfulعلامتگذاری شده است. این اسلات اکنون اسلات انتخاب شده است. اگر هیچ اسلات فعلی در دسترس نیست، برای بازیابی راهاندازی کنید یا یک پیام خطای معنیدار برای کاربر نمایش دهید.boot.imgمناسب را انتخاب کنید و مسیر تصحیح پارتیشن سیستم را در خط فرمان هسته قرار دهید.پارامتر خط فرمان هسته
slot_suffixرا پر کنید.چکمه. اگر
slot-successfulعلامتگذاری نشد،slot-retry-countکاهش دهید.
ابزار fastboot تعیین می کند که هنگام اجرای هر دستور فلش، کدام پارتیشن فلش شود. برای مثال، اجرای دستور fastboot flash system system.img ابتدا متغیر current-slot را پرس و جو می کند و سپس نتیجه را به سیستم الحاق می کند تا نام پارتیشنی را که باید فلش شود ( system_a ، system_b و غیره) تولید کند.
هنگام تنظیم شکاف فعلی با استفاده از دستور fastboot set_active یا فرمان بوت کنترل HAL setActiveBootSlot ، بوت لودر باید شکاف فعلی را بهروزرسانی کند، slot-unbootable و slot-successful را پاک کند، و تعداد تلاش مجدد را بازنشانی کند (این تنها راه برای پاک کردن slot-unbootable است).
دستگاههای بدون بهروزرسانی A/B
برای پشتیبانی از بهروزرسانیهای OTA در دستگاههایی که از بهروزرسانیهای A/B استفاده نمیکنند (به دستگاههای غیرقابل بهروزرسانی A/B مراجعه کنید)، مطمئن شوید که بوتلودر دستگاه دارای معیارهای زیر است.
پارتیشن
recoveryباید حاوی تصویری باشد که قادر به خواندن تصویر سیستم از برخی پارتیشن های پشتیبانی شده (cache،userdata) و نوشتن آن در پارتیشنsystemباشد.بوت لودر باید از بوت شدن مستقیم به حالت بازیابی پشتیبانی کند.
اگر بهروزرسانیهای تصویر رادیویی پشتیبانی میشوند، پارتیشن
recoveryنیز باید بتواند رادیو را فلش کند. این را می توان به یکی از دو روش انجام داد:بوت لودر رادیو را فلش می کند. در این حالت، باید امکان راه اندازی مجدد از پارتیشن بازیابی به بوت لودر برای تکمیل به روز رسانی وجود داشته باشد.
تصویر بازیابی رادیو را چشمک می زند. این قابلیت می تواند به عنوان یک کتابخانه باینری یا ابزار ارائه شود.

